(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. – A Cornell University-led project has added a new chapter to the story of Balto – the most famous sled dog in history – by using ancient DNA extraction and analysis to reconstruct his phenotype and identify his genetic connections to modern dog breeds.
The research reveals Balto’s lineage was genetically healthier and less inbred than modern breeds, with characteristics adapted to the extreme environment of 1920s Alaska.
The team’s paper, “Comparative Genomics of Balto, a Famous Historic Dog, Captures Lost Diversity of 1920s Sled Dogs,” published April 27 in Science.
Heather Huson, associate professor of animal science and the paper’s co-lead author, has a personal connection to dog sledding, having raced competitively for almost 25 years throughout North America. Now she studies how genetics shapes the traits – from physiology and speed to behavior and diet – that produce the ideal working canine, including detection and seeing-eye dogs.
“I was enthralled growing up with sled dogs,” Huson said. “They’re amazing athletes, they’re fast, but they have a lot of endurance. Mentally, they have to be tough. What are the genes that make them an awesome sled dog? Why can they do these amazing things that your average dog can’t do?”
While Balto was clearly a sled dog, his owner, Leonhard Seppala, was one of the founding breeders of the Siberian husky, raising the potential for some interesting overlap.
Huson teamed up with a group of researchers who were able to extract Balto’s ancient DNA – a difficult task, given how degraded and unstable the genetic material becomes over time – and they conducted the DNA sequencing and analysis. The team then compared the results of this “sample size of one” with data, provided by the Zoonomia Project, of 240 mammal species and 682 genomes from dogs and wolves of the 21st century.
The researchers found that Balto clusters most closely with Alaskan sled dogs, with a high genetic diversity and a lower burden of potentially damaging genetic variants. He also had substantial ancestral similarity to Siberian huskies, Alaskan malamutes, Greenland sled dogs and outbred dogs from Asia.
“Siberians were kind of being created at the same time as the modern Alaskan sled dogs. This shows Balto is at the crux of that. He is showing that early foundation that’s actually similar between sled dogs and Siberians,” Huson said.
There is something to be learned from any dog – even unfamous ones – whose genetic diversity has changed over time, Huson said.
“It’s kind of funny, because for evolutionary geneticists, what I’m looking at is a drop in the bucket, the 1930s versus the 2000s, while they are looking at thousands to millions of years,” she said. “Yet, the domestication of most modern breeds has been in the last couple hundred years, so there’s been a huge selection intensity on dogs in that time.”
For additional information, see this Cornell Chronicle story.
Cornell University has dedicated television and audio studios available for media interviews.
-30-
END
Geneticists link phenotype of Balto, famed sled dog, to modern breeds
2023-04-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Highly dexterous robot hand can operate in the dark -- just like us
2023-04-27
New York, NY—April 27, 2023—Think about what you do with your hands when you’re home at night pushing buttons on your TV’s remote control, or at a restaurant using all kinds of cutlery and glassware. These skills are all based on touch, while you’re watching a TV program or choosing something from the menu. Our hands and fingers are incredibly skilled mechanisms, and highly sensitive to boot.
Robotics researchers have long been trying to create “true” dexterity in robot ...
Texas Tech researchers contribute to groundbreaking mammal research
2023-04-27
Why was Balto, a famous sled dog from the 1920s, able to survive the unforgiving conditions of Alaska? It was one of many findings uncovered through the Zoonomia Project, which involved researchers from Texas Tech University.
More than a dozen researchers from the Department of Biological Sciences were among the major collaborators in the Zoonomia Project who will publish their multi-year comparative genomic analysis of mammals and the influence of genetic change on health and disease in the April 28 issue of Science magazine.
The laboratory of David Ray, professor and associate chair of the department, studies transposable elements ...
Snowballing effects of beech leaf disease hurt helpful root fungi
2023-04-27
The American beech, Fagus grandifolia, is a North American staple and the dominant species in many northeastern forests. In 2012, a new disease was first spotted, infecting trees in northeastern Ohio. The worst afflicted had dark banding on their leaves, which emerged crumpled and leathery in the spring. Not until 2018 would experts discover the nematode pest, Litylenchus crenatae mccannii, overwintering in the buds of infected trees.
As it marches across the continent, researchers are still ...
Higher rates of autism and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in American children
2023-04-27
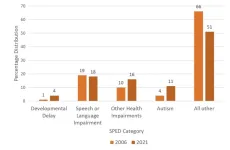
In a recent publication released by PubMed, American scientists led by Dr. Dufault at the Food Ingredient and Health Research Institute, reported alarming increases in the numbers of children requiring special education services. While student enrollment in US schools remained stable from 2006-2021, the percentage of children receiving special education services increased 10.4%. Of the three disability categories under which children with autism may receive services, autism caseload percentages tripled jumping from 4% to 11% while developmental delay caseload ...
Improving geriatric surgical quality is feasible for a wide range of hospitals
2023-04-27
Key takeaways
Feasible for small and large hospitals: Pilot institutions in the study included community hospitals and academic medical centers representing every region of the United States.
Geriatric surgical patients are a growing population: American College of Surgeons standards for geriatric surgery address a growing population that most hospitals serve.
Standards help address barriers to implementation: ACS geriatric surgery standards help hospitals identify and address challenges to providing optimal care, including staffing, manpower, and lack of geriatricians in many hospitals.
CHICAGO: ...
Scripps Research preclinical study finds insomnia drug blocks oxycodone relapse
2023-04-27
LA JOLLA, CA—The insomnia drug suvorexant (Belsomra®) might be an effective treatment for opioid use disorder, according to a preclinical study from Scripps Research.
In the study, published April 27, 2023, in Frontiers in Pharmacology, the Scripps Research scientists found that suvorexant reduced prescription opioid intake and helped protect against relapse in rats modeling opioid use disorder (OUD). If the results translate to humans in clinical trials, the insomnia drug could offer a promising approach for the millions of people who have OUD.
“Our results suggest that repurposing suvorexant could be a good strategy for reducing drug intake and blocking relapse in cases ...
Calling all canines: Help sniff out the dangerous spotted lanternfly
2023-04-27
From New York to North Carolina and as far west as Illinois, the invasive spotted lanternfly is causing chaos in many states where agricultural and forestry industries are essential to the economy. It has been estimated that crops and forest production losses caused by insects and pathogens are close to $40 billion a year.
Spotted laternflies, native to mainland China, prey upon 70-plus host plant species, stealing their nutrients with their piercing snouts, called stylets. They are often characterized as “hitchhikers” for their ability to move ...
AGS honors expert & emerging geriatrics leaders at 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting (#AGS23)
2023-04-27
New York (April 27, 2023) – The American Geriatrics Society (AGS) annually honors researchers, clinicians, educators, and emerging health professionals who have made outstanding contributions to high-quality, person-centered care for older adults. This year’s award recipients include 19 leaders representing the breadth of medical disciplines championing care for us all as we age.
Clinical Student Research Award
Matthew Ryan Cosmai
Clinician of the Year Award
Shelley R. McDonald, DO, PhD
David H. Solomon Memorial Public Service Award
Alan Lazaroff, ...
Plastic particles themselves, not just chemical additives, can alter sex hormones
2023-04-27
Amid rising evidence that additives designed to improve plastics also disrupt sex hormones, a Rutgers laboratory trial shows that plastic itself can do likewise when inhaled at moderate levels.
Previous studies focused on chemicals such as bisphenol-A (BPA) that make plastics stiffer or more flexible. These findings spurred ongoing efforts to find safer plastic additives.
The Rutgers study showed that microscale and nanoscale particles (MNPs) of polyamide, a common plastic better known as nylon, produced endocrine-disrupting ...
ATS 2023 International Conference announces late-breaking clinical trials
2023-04-27
April 27, 2023 – One of the most highly-anticipated events at the ATS 2023 International Conference, which kicks off May 19, is the “Breaking News: Clinical Trial Results in Pulmonary Medicine.” Taking place on Monday, May 22, the series of presentations will focus on the latest regarding COPD and asthma treatment.
Register now to hear these presentations live. A question-and-answer period will follow all presentations:
Seralutinib Treatment in Adult Subjects with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Results from the TORREY Study
Effect of Ensifentrine, a Novel PDE3 and PDE4 Inhibitor, on Lung Function, Symptoms and Exacerbations in Patients with COPD: ...