Researchers explore why some people get motion sick playing VR games while others don’t
2023-05-01
(Press-News.org)
The way our senses adjust while playing high-intensity virtual reality games plays a critical role in understanding why some people experience severe cybersickness and others don’t.
Cybersickness is a form of motion sickness that occurs from exposure to immersive VR and augmented reality applications.
A new study, led by researchers at the University of Waterloo, found that the subjective visual vertical – a measure of how individuals perceive the orientation of vertical lines – shifted considerably after participants played a high-intensity VR game.
“Our findings suggest that the severity of a person’s cybersickness is affected by how our senses adjust to the conflict between reality and virtual reality,” said Michael Barnett-Cowan, a professor in the Department of Kinesiology and Health Sciences. “This knowledge could be invaluable for developers and designers of VR experiences, enabling them to create more comfortable and enjoyable environments for users.”
The researchers collected data from 31 participants. They assessed their perceptions of the vertical before and after playing two VR games, one high-intensity and one low-intensity.
Those who experienced less sickness were more likely to have the largest change in the subjective visual vertical following exposure to VR, particularly at a high intensity. Conversely, those who had the highest levels of cybersickness were less likely to have changed how they perceived vertical lines. There were no significant differences between males and females, nor between participants with low and high gaming experience.
“While the subjective vertical visual task significantly predicted the severity of cybersickness symptoms, there is still much to be explained,” said co-author William Chung, a former Waterloo doctoral student who is now a postdoctoral fellow at the Toronto Rehabilitation Institute.
“By understanding the relationship between sensory reweighting and cybersickness susceptibility, we can potentially develop personalized cybersickness mitigation strategies and VR experiences that take into account individual differences in sensory processing and hopefully lower the occurrence of cybersickness.”
As VR continues to revolutionize gaming, education and social interaction, addressing the pervasive issue of cybersickness – marked by symptoms such as nausea, disorientation, eye strain and fatigue – is critical for ensuring a positive user experience.
The study, Sensory reweighting: a common mechanism for subjective visual vertical and cybersickness susceptibility,” was published in the journal Virtual Reality.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-04-30
In the race to make the world more livable for people and nature, progress on land outpaced successes in the seas, raising red flags that wealthier countries’ advantages may be upsetting a balance, a Michigan State University study shows.
Progress in oceans actually slowed after the United Nations member states adopted the 17 Sustainable Development Goals in 2015. That action aims to facilitate global partnerships among developed and developing countries in sustainable development.
So far, though, a new study in the open-access journal iScience reveals evidence that ...
2023-04-30
About The Study: The intervention examined in this randomized clinical trial resulted in improvements in the receipt of preventive care services versus usual care for children insured by Medicaid by incorporating community health workers in a team-based approach to early childhood well-child care.
Authors: Tumaini R. Coker, M.D., M.B.A., of Seattle Children’s Research Institute in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.7197)
Editor’s ...
2023-04-29
About The Study: This case series demonstrated that prostate cancer occurs in transgender women and is not as rare as published case reports might suggest. However, rates were lower than expected based on prior prostate cancer incidence estimates in cisgender male veterans.
Authors: Farnoosh Nik-Ahd, M.D., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.6028)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
2023-04-29
Transgender women keep their prostates even after gender-affirming surgery, but the extent to which they remain at risk of prostate cancer has been unclear.
Now a first of its kind study led by UC San Francisco has estimated the risk at about 14 cases per 10,000 people.
The study drew on 22 years of data from the Veterans Affairs Health System. Although the sample size was necessarily small, it is still the largest study of its kind. It publishes Saturday, April 29, 2023 in the Journal ...
2023-04-29
At least 3,700 out-of-state mental health providers utilized New Jersey’s COVID-19 Temporary Emergency Reciprocity Licensure program to provide mental health services to more than 30,000 New Jersey patients during the first year of the pandemic, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, published in The Journal of Medical Regulation, surveyed health care practitioners who received a temporary license in New Jersey to examine the impact of the temporary licensure program on access to mental health care.
“The New Jersey program enabled patients with ...
2023-04-29
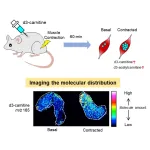
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a way of mapping the distribution of carnitine in skeletal muscle cells. Carnitine is a small compound that helps transport fatty acids and reduce metabolic byproducts. They discovered that slow-type muscle fibers contained the most, and that activity promptly led to rises in acetylcarnitine, a product of the immediate response of carnitine contained in the cell. Their technique promises new insights into how muscle cells work.
Our muscles require ...
2023-04-28
The human body relies heavily on electrical charges. Lightning-like pulses of energy fly through the brain and nerves and most biological processes depend on electrical ions traveling across the membranes of each cell in our body.
These electrical signals are possible, in part, because of an imbalance in electrical charges that exists on either side of a cellular membrane. Until recently, researchers believed the membrane was an essential component to creating this imbalance. But that thought was turned on its head when researchers at Stanford University discovered that similar imbalanced electrical ...
2023-04-28
Astronomers from McGill University are part of an international team that has discovered 25 new sources of repeating fast radio bursts (FRBs), these explosions in the sky that come from far beyond the Milky Way. This discovery brings the total number of confirmed FRB sources to 50. Based on data gathered by the CHIME/FRB collaboration, the new study, published this week in The Astrophysical Journal, may also bring scientists closer to understanding the origins of these mysterious phenomena.
A new way of identifying FRBs
Thanks to the radio telescopes such as those at CHIME, which scan the entire northern sky every day, the number of detected FRBs has grown exponentially in recent years. ...
2023-04-28
The human body relies heavily on electrical charges. Lightning-like pulses of energy fly through the brain and nerves and most biological processes depend on electrical ions traveling across the membranes of each cell in our body.
These electrical signals are possible, in part, because of an imbalance in electrical charges that exists on either side of a cellular membrane. Until recently, researchers believed the membrane was an essential component to creating this imbalance. But that thought was turned on its head when researchers at Stanford University discovered that similar imbalanced electrical charges can exist between microdroplets of water ...
2023-04-28
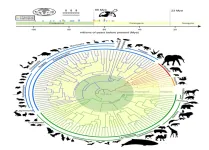
Research led by a team of scientists from the Texas A&M School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences puts to bed the heated scientific debate regarding the history of mammal diversification as it relates to the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs. Their work provides a definitive answer to the evolutionary timeline of mammals throughout the last 100 million years.
The study, published in Science, is part of a series of articles released by the Zoonomia Project, a consortium of scientists from around the globe that is using the largest mammalian genomic dataset in history to determine the evolutionary history of the human genome in the context of mammalian evolutionary history. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers explore why some people get motion sick playing VR games while others don’t