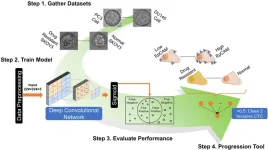
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, May 2, 2023 – Cancer cells that initiate metastasis, or the spread of the disease from its primary location, are different from cancer cells that stay in the original tumor. Distinguishing metastasis-initiating cell types can determine the severity of cancer and help medical practitioners decide on a course of treatment.
In APL Machine Learning, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Texas Tech University developed a deep learning model to classify cancer cells by type. The tool requires only a simple microscope and a small amount of computing power, producing results on par or better than more sophisticated and complex techniques.
“Cancer cells are highly heterogeneous, and recent studies suggest that specific cell subpopulations, rather than the whole, are responsible for cancer metastasis,” said author Wei Li. “Identifying subpopulations of cancer cells is a critical step to determine the severity of the disease.”
Current methods to categorize cancer cells involve advanced instruments, time-consuming biological techniques, or chemical labels.
“The problem with these complicated and lengthier techniques is that they require resources and effort that could be spent exploring different areas of cancer prevention and recovery,” said author Karl Gardner.
Some studies use magnetic nanoparticles to track cancer cells, but attaching these labels could affect the downstream analysis of the cells and integrity of the measurements.
“Our classification procedure does not consist of additional chemicals or biological solutions when taking pictures of the cells,” said Gardner. “It is a ‘label-free’ identification method of metastatic potential.”
The team’s neural network is also simple to use, efficient, and automated. After feeding it an image, the tool converts the data to a probability. A result lower than 0.5 categorizes the cancer as one cell type, while a number higher than 0.5 designates another.
The tool was trained to optimize the accuracy of predictions with a set of images of two cancer cells lines. It reached over 94% accuracy across the data sets used in the study.
Currently, the training data only accounts for single cancer cells. However, research shows that circulating tumor cell clusters are more responsible for the spread of cancer. The authors aim to extend and generalize the model to include both single cells and clusters.
###
The article “Label-free identification of different cancer cells using deep learning-based image analysis” is authored by Karl Gardner, Rutwik Joshi, Md Nayeem Hasan Kashem, Thanh Quang Pham, Qiugang Lu, and Wei Li. It will appear in APL Machine Learning on May 2, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0141730). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0141730.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Machine Learning is an open access journal that features vibrant and timely research for two communities: researchers who use machine learning (ML) and data-driven approaches for physical sciences and related disciplines, and researchers from these disciplines who work on novel concepts, including materials, devices, systems, and algorithms relevant for the development of better ML and AI technologies. See https://pubs.aip.org/aip/aml.
###
END
Classifying cancer cells to predict metastatic potential
Deep learning network analyzes images to categorize cell types accurately and efficiently.
2023-05-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
COVID-19 Mortality by race and ethnicity in metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas
2023-05-02
About The Study: This study found that most of the national decrease in racial and ethnic disparities in COVID-19 mortality between the initial and Omicron waves was explained by increased mortality among non-Hispanic white adults and changes in the geographic spread of the pandemic. These findings suggest that despite media reports of a decline in disparities, there is a continued need to prioritize racial health equity in the pandemic response.
Authors: Andrew C. Stokes, Ph.D., of the Boston University School of Public Health in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For ...
Anti-poverty programs may help reduce disparities in brain development and mental health symptoms in children
2023-05-02
States that provide stronger social safety nets have lower socioeconomic disparities in the brain development and mental health of children 9 to 11 years old, according to research supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) at the National Institutes of Health. The disparity in brain structure between children from high- versus low-income households was more than a third lower in states with greater cash assistance than in those offering less, and the disparity in mental health symptoms was reduced by nearly a half.
The study, published in Nature Communications, ...
Ibogaine inspires new compounds to treat addiction, depression
2023-05-02
Scientists have developed two new drug candidates for potentially treating addiction and depression, modeled on the pharmacology of a traditional African psychedelic plant medicine called ibogaine. At very low doses, these new compounds were able to blunt symptoms of both conditions in mice.
The findings, published on May 2 in Cell, took inspiration from ibogaine’s impact on the serotonin transporter (SERT), which is also the target of SSRI antidepressants like fluoxetine (Prozac). A team of scientists from UCSF, Yale and Duke universities virtually screened 200 million molecular structures to find ones that blocked SERT in the same way ...
AI helpful in triaging breast masses in low-resource areas
2023-05-02
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Artificial intelligence (AI) can analyze breast mass images from low-cost portable ultrasound machines and accurately identify cancer, according to a study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). This could prove useful for triage in low-resource settings.
Breast lumps are often found accidentally, during breast self-exam or during a breast exam by a medical professional. Breast cancer screening can find cancers in the breast before the lump can be felt.
While cancer screening has been the focus in Western countries, low- and middle-income ...
AI bias may impair radiologist accuracy on mammogram
2023-05-02
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Incorrect advice by an AI-based decision support system could seriously impair the performance of radiologists at every level of expertise when reading mammograms, according to a new study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Often touted as a “second set of eyes” for radiologists, AI-based mammographic support systems are one of the most promising applications for AI in radiology. As the technology expands, there are concerns that it may make radiologists susceptible to automation bias—the tendency of humans ...
Machine translation for cuneiform tablets
2023-05-02
An AI model has been developed to automatically translate Akkadian text written in cuneiform into English. Hundreds of thousands of clay tablets from ancient Mesopotamia, written in cuneiform and dating back as far as 3,400 BCE, have been found by archeologists, far more than could easily be translated by the limited number of experts who can read them. Shai Gordin and colleagues present a new machine learning model that can automatically translate Akkadian cuneiform into English. Two versions of the model were trained. One version translates the Akkadian from representations of the cuneiform signs in Latin ...
Climate reasoning, prior beliefs, and partisanship
2023-05-02
A popular explanation for climate denialism is that humans will adopt beliefs that accord with their political orientation, using their cognitive abilities to explain away identity-inconsistent information in a process called “motivated reasoning.” To test this hypothesis, Bence Bago and colleagues challenged volunteers’ ability to think rationally using time pressure and cognitive loads of varying intensity. The team recruited American participants from Lucid, a website that connects academics with online survey participant pools. The authors found that people who had the ability to deliberate free of cognitive load or time ...
SwRI, UTSA researchers develop new method to synthesize antimalarial drug
2023-05-02
SAN ANTONIO – May 2, 2023 - Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) and The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA) have developed a method to synthesize the highly potent antimalarial drug artemisinin, which could lead to a more cost-effective treatment for malaria. The work, recently featured on the cover of the scientific journal Organic Letters, was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation as well as a grant from the Connecting through Research Partnerships (Connect) program, a joint effort by SwRI and UTSA to enhance scientific collaboration between the two institutions.
In 2021, 247 million cases of malaria led to 619,000 deaths worldwide. The most effective ...
ASBMB calls for better wages and benefits for postdocs
2023-05-02
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology sent recommendations to the National Institutes of Health on April 14 to improve working conditions for postdocs.
The society recommended that the NIH:
Ensure a livable wage, benefits, etc. for postdocs
Require that principle investigators help postdocs craft a training plan
Require that principal investigators complete mentor training programs
Expand programs to create more academic staff scientist positions
Collect data on postdoc career outcomes
“Many of our members who run labs are struggling to recruit and retain qualified postdocs,” Sarina Neote, public affairs director ...
Cooperation benefits from peer-punishment
2023-05-02
A multi-lab replication of a 2006 study supports the role of peer sanction in promoting human cooperation. Cooperation is imperative for society to successfully solve complex problems, including climate change. One approach many groups have adopted is a system of peer sanctions for noncooperators. Such a system incurs costs to participants, who must impose the sanctions, but can allow cooperators to feel more secure that their investments in the shared project will be matched by others. A 2006 study suggested that groups with peer sanctions outgrew and outperformed groups without a peer-sanctioning institution. In light ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
[Press-News.org] Classifying cancer cells to predict metastatic potentialDeep learning network analyzes images to categorize cell types accurately and efficiently.