(Press-News.org) Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified four important signs and symptoms that signal an elevated risk of early-onset colorectal cancer. These red flags may be key to earlier detection and diagnosis of early-onset colorectal cancer among younger adults. The number of young adults with colorectal cancer has nearly doubled in recent years.
Studying de-identified health insurance data on more than 5,000 patients with early-onset colorectal cancer — cancer that occurs before a person turns 50 — the researchers found that in the period between three months and two years before diagnosis, abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, diarrhea and iron deficiency anemia each indicate an increased risk in those under age 50. They found that having a single one of the symptoms almost doubled the risk; having two symptoms increased risk by more than 3.5 times; and having three or more boosted the risk by more than 6.5 times.
The study is published May 4 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
“Colorectal cancer is not simply a disease affecting older people; we want younger adults to be aware of and act on these potentially very telling signs and symptoms — particularly because people under 50 are considered to be at low risk, and they don’t receive routine colorectal cancer screening,” said senior investigator Yin Cao, ScD, an associate professor of surgery in the Public Health Sciences Division, and a research member of Siteman Cancer Center at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Washington University School of Medicine.
“It’s also crucial to spread awareness among primary care doctors, gastroenterologists and emergency medicine doctors,” Cao said. “To date, many early-onset colorectal cancers are detected in emergency rooms, and there often are significant diagnostic delays with this cancer.”
Cao said two symptoms in particular — rectal bleeding and iron deficiency anemia, a condition in which there are not enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen — point to the need for timely endoscopy and follow-up.
In this study, Cao, with first author Cassandra D. L. Fritz, MD, an assistant professor of medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology, and co-first author Ebunoluwa Otegbeye, MD, a general surgery resident, analyzed cases of early-onset colorectal cancer and matched controls using the IBM MarketScan Commercial Database, a big-data tool that provides longitudinal, de-identified information based on health insurance claims data from about 113 million insured adults ages 18 to 64.
“It usually takes about three months to get a diagnosis from the time a person first goes to the doctor with one or more of the red-flag signs and symptoms we’ve identified,” Fritz said. “But in this analysis, we found that some young adults had symptoms for up to two years prior to their diagnoses. That may be part of the reason many of these younger patients had more advanced disease at the time of diagnosis than what we normally see in older people who get screened regularly.”
Individuals born in 1990 have double the risk of colon cancer and four times the risk of rectal cancer compared with young adults born in 1950. That trend has prompted the National Cancer Institute, American Cancer Society, American Gastroenterological Association and other professional societies to prioritize research on identifying risk factors and improving early detection. In 2021, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force lowered the recommended age for colorectal cancer screening from 50 to 45.
Cao, also an associate professor of medicine, leads a research group focused on identifying risk factors and molecular variations in early-onset colorectal cancer. Her group is among the first to report that obesity, prolonged sitting, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, sugar-sweetened beverages and other risk factors may contribute to the rising incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer.
According to the American Cancer Society, although the death rate from colorectal cancer has been dropping for several decades in older adults due to regular colonoscopies and improved treatment, more younger people are diagnosed with the disease at advanced stages, and many are dying of the disease.
Such a shift suggests urgency in recognizing symptoms as early as possible.
“Since the majority of early-onset colorectal cancer cases have been and will continue to be diagnosed after symptom presentation, it is crucial to recognize these red-flag signs and symptoms promptly and conduct a diagnostic work-up as soon as possible,” Cao said. “By doing so, we can diagnose the disease earlier, which in turn can reduce the need for more aggressive treatment and improve patients’ quality of life and survival rates.”
Fritz, CDL. Otegbeye EE, Zong X, Demb J, Nickel KB, Olsen MA, Mutch M, Davidson NO, Gupta S, Cao Y. Red-flag signs and symptoms for earlier diagnosis of early-onset colorectal cancer. The Journal of the National Cancer Institute, May 4, 2023.
The study was funded with support from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the National Cancer Institute and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Grant numbers: UL1 TR002345, T32 DK007130, T32 CA009621, P30 DK52574 and R37 CA246175.
About Washington University School of Medicine
WashU Medicine is a global leader in academic medicine, including biomedical research, patient care and educational programs with 2,800 faculty. Its National Institutes of Health (NIH) research funding portfolio is the third largest among U.S. medical schools, has grown 52% in the last six years, and, together with institutional investment, WashU Medicine commits well over $1 billion annually to basic and clinical research innovation and training. Its faculty practice is consistently within the top five in the country, with more than 1,800 faculty physicians practicing at 65 locations and who are also the medical staffs of Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children’s hospitals of BJC HealthCare. WashU Medicine has a storied history in MD/PhD training, recently dedicated $100 million to scholarships and curriculum renewal for its medical students, and is home to top-notch training programs in every medical subspecialty as well as physical therapy, occupational therapy, and audiology and communications sciences.
END
Red flags indicate risk for early-onset colorectal cancer
Recognizing signs and symptoms earlier could reduce diagnostic delays, improve survival
2023-05-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Reviving exhausted T cells to tackle immunotherapy-resistant cancers
2023-05-04
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – May 03, 2023 – When the cells of our immune system are under constant stress due to cancer or other chronic diseases, the T cells of the immune system shut down in a process called T cell exhaustion. Without active T cells, which kill tumor cells, it’s impossible for our bodies to fight back against cancer. One of the biggest goals of immunotherapy is to reverse T cell exhaustion to boost the immune system’s ability to destroy cancerous cells.
Researchers at Sanford Burnham Prebys studying melanoma have found a new way to make this ...
MD Anderson researchers Helen Piwnica-Worms and Richard Wood elected to National Academy of Sciences
2023-05-03
HOUSTON ― Two researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have been elected to the prestigious National Academy of Sciences (NAS). Helen Piwnica-Worms, Ph.D., professor of Experimental Radiation Oncology, and Richard Wood, Ph.D., professor of Epigenetics and Molecular Carcinogenesis, are recognized for their respective contributions to advancing our understanding of cancer genetics, biochemistry and cell biology.
Piwnica-Worms and Wood are among 120 new members ...
Purdue startup Aerovy Mobility develops cloud software to support infrastructure for electric aircraft
2023-05-03
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – The advanced air mobility sector, which includes electric-powered urban and regional aircraft, may become a $1.5 trillion market by 2040. A new Purdue University-connected startup could benefit airport and vertiport operators and real estate developers looking to establish advanced air mobility technology at existing and potential sites.
Purdue University postgraduate students have launched Aerovy Mobility, a startup company that commercializes cloud-based software solutions to plan and operate infrastructure ...
Retinol disruption and the role of vitamin a metabolism in colon cancer
2023-05-03
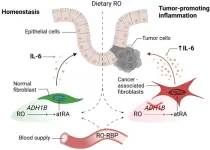
“Retinoids are known to inhibit tumor-promoting IL-6 production.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 3, 2023 – A new research perspective was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on April 26, 2023, entitled, “Disruption of retinol-mediated IL-6 expression in colon cancer-associated fibroblasts: new perspectives on the role of vitamin A metabolism.”
Colon cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignancies and is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. While the tumor microenvironment (TME) supports tumor growth and immune escape through tumor-promoting ...
INRS celebrates the careers of two eminent researchers
2023-05-03
INRS' graduation ceremony will be a wonderful event again this year! In addition to the175 students who will be receiving their master’s or doctorate degrees, two distinguished scholars will be honoured.
During the 2023 ceremony, the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS) is pleased to announce that it will be awarding two honorary doctorates. Researchers Jamal Deen, an expert in electrical engineering and applied physics and a professor at McMaster University, and Mordechai (Moti) Segev, a professor ...
Disparities in telehealth utilization among Medicare beneficiaries
2023-05-03
A new study of telehealth utilization among Medicare beneficiaries in Arkansas showed race/ethnicity and rural/urban disparities. The study, which reported that the association between the number of chronic conditions and telehealth was strongest among White and rural beneficiaries, is published in the peer-reviewed journal Telemedicine and e-Health. Click here to read the article now.
Innovative technologies such as telehealth can improve health care access in underserved areas and in aging populations with growing and complex medical needs. However, the use of telecommunications in clinical settings faces ...
Moffitt researchers develop CAR T cells that fight prostate cancer in bone
2023-05-03
TAMPA, Fla. – Prostate cancer frequently metastasizes to the bone and is incurable. Moffitt Cancer Center researchers are working to identify new treatment options for this subset of patients. In a new article published today in Science Advances, a team of Moffitt scientists demonstrates that chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR T) therapy is an effective antitumor approach in mouse models of bone metastatic prostate cancer.
“Bone metastatic prostate cancer is an incurable disease that significantly impacts patient ...
Journal of Dental Research to publish special issue on aging and oral health
2023-05-03
Alexandria, VA, USA – The International Association for Dental Research (IADR) and American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (AADOCR) have announced the publication in July 2023 of a Special Issue of Journal of Dental Research (JDR) entitled, “Aging and Oral Health.” It will feature Bei Wu, New York University, USA and Ana Paula Vieira Colombo, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil as Guest Editors.
Several articles that will be included in the issue are currently available for viewing Online First at the JDR website, including:
Diabetes, Edentulism, and Cognitive Decline: ...
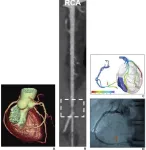
Rapid onsite FFR-CT algorithm helps facilitates clinical adoption
2023-05-03
Leesburg, VA, May 3, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), a high-speed onsite deep-learning based fractional flow reserve (FFR)-CT algorithm yielded excellent diagnostic performance for the presence of hemodynamically significant stenosis, with both high interobserver and intraobserver reproducibility.
“A rapid and accurate onsite approach for determining FFR-CT should address challenges encountered in the clinical ...
How is sleep affected by changing clocks and seasons?
2023-05-03
MINNEAPOLIS – How are you sleeping? A new study has found the transition from daylight saving time to standard time, when one hour is gained overnight, was associated with a brief increase in sleep disorders such as difficulty going to sleep or staying asleep, but there was no such association when an hour is lost in the change from standard time to daylight saving time. The study is published in the May 3, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. It also found a small difference in the amount of sleep people get depending ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
[Press-News.org] Red flags indicate risk for early-onset colorectal cancerRecognizing signs and symptoms earlier could reduce diagnostic delays, improve survival