(Press-News.org) PISCATAWAY, NJ—Getting many adolescents and young adults to stop using e-cigarettes may be as simple as doing away with flavored versions of the product, according to new research in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs. This study suggests that a large majority of current users may discontinue their use if the product became available in the tobacco version only.
“The restriction of the availability for certain e-cigarette e-liquid flavors has been considered by various regulatory agencies,” says senior study author Alayna P. Tackett, Ph.D., assistant professor at the Center for Tobacco Research at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. “Our team was interested in surveying youth and young adults to understand their thoughts on what choices they might make should regulatory policies only allow menthol and/or tobacco flavors in e-cigarette e-liquid products.”
Tackett and her colleagues used a national convenience sample of 1,414 e-cigarette users between ages 14 and 21. All had used the product at least once per day in the 30 days before completing the survey. They were asked about which flavors they typically use (the options were tobacco, menthol, cool mint, fruit ice and fruit/sweet).
When asked what they would do if a hypothetical federal regulation meant that tobacco and menthol-flavored e-liquids were the only options available, 38.8% of respondents said they would discontinue e-cigarette use. That number jumped to 70.8% if tobacco became the only option. Adolescents and young adults who preferred vaping fruit or sweet flavors were most sensitive to either restricted scenario compared with other flavor preferences.
Tackett also found it interesting that adolescents and young adults using flavors with cooling additives (such as fruit ice) reported higher odds of discontinuing use under a tobacco-only product standard, compared with menthol flavor users, indicating an important distinction between these groups. (Fruit ice are e-cigarette flavors that have a fruit base characterizing flavor with a cooling additive such as menthol or a synthetic cooling agent.)
“In this sample of adolescents and young adults, it appears that non-tobacco flavors may be important for their interest in and continued use of e-cigarettes,” she said.
It is unknown if the current self-reported intentions would extend to actual behavior in the natural environment and how this may impact use or uptake of other tobacco products. Future research might benefit from examining this scenario in areas or states that have enacted a flavor restriction policy, as well as from using a more representative sample (the convenience sample used was majority White and majority female).
Cigarette smoking remains the leading cause of preventable death in the United States. Tackett says preventing use of e-cigarettes among young people is a crucial goal for public health, but she also points to the potential impact of e-cigarette regulation on adults who smoke and have begun using e-cigarettes as an alternative to quitting altogether.
“Many adults prefer using non-tobacco flavors to switch from combustible cigarettes to e-cigarettes,” says Tackett. “Flavor restriction policies should consider the best ways to protect public health while also supporting adults who are interested in choosing potentially less harmful alternatives to combustible cigarettes.”
-----
Sidhu, N. K., Lechner, W. V., Cwalina, S. N., Whitted, L., Smiley, S. L., Barrington-Trimis, J. L., Cho, J., Wagener, T. L., Leventhal, A. M., &. Tackett, A. P. Adolescent and young adult response to hypothetical e-liquid flavor restrictions. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 84, 303–308. doi:10.15288/jsad.21-00466
-----
For interview requests with Dr. Alayna P. Tackett, please contact Amanda Harper at Amanda.Harper2@osumc.edu.
-----
The Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs is published by the Center of Alcohol & Substance Use Studies at Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey. It is the oldest substance-related journal published in the United States.
-----
The Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs considers this press release to be in the public domain. Editors may publish this press release in print or electronic form without legal restriction. Please include a byline and citation.
-----
To view the public domain, stock-photo database of alcohol, tobacco and other drug-related images compiled by the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, please visit www.jsad.com/photos.
END
Restricting flavored e-cigarettes may reduce their use among teens and young adults: Study
2023-05-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Alumna named BioOne Ambassador for doctoral work in biological sciences
2023-05-04
Chelsea Kross, a University of Arkansas alumna in biological sciences, earned a 2023 BioOne Ambassador award for her submission “Not all frogs can make it in the city: Using the landscape for targeted conservation,” which summarized research done while working toward her Ph.D.
The award recognizes early career researchers in biological, ecological and environmental sciences who demonstrate creative approaches to science communication.
“Communicating complex research is critically important to fostering public understanding and support for the sciences,” said Lauren Kane, president and CEO of BioOne. “The 2023 BioOne ...
Remote aerobic walking exercise training feasible for improving cognitive processing speed in persons with multiple sclerosis
2023-05-04
East Hanover, NJ. May 3, 2023 – Results of a pilot study funded by Kessler Foundation showed that remote aerobic walking exercise training is a feasible and highly promising method for improving cognitive processing speed impairment in fully ambulatory persons with multiple sclerosis (MS). The findings of this single-blind randomized control trial support the design of a randomized, controlled trial in large sample of persons with MS
The study, titled "Feasibility of Remotely Delivered and Supported Aerobic Walking Exercise Training for Cognitive Processing Speed Impairment in Fully Ambulatory Persons with Multiple Sclerosis," (doi: ...
Offering genetic testing at the point of care may increase uptake
2023-05-04
Genetic testing for hereditary cancers, such as breast, colon, pancreatic, and ovarian cancer, helps at-risk individuals understand their familial risk for these diseases and make informed decisions about next steps in care. But fewer than 20 percent of at-risk patients utilize this testing, and even fewer engage in genetic counseling after referral, often due to clinical workflow challenges or barriers to care.
Amid national efforts to increase access to genetic testing, a new study led by a Boston University School of Public Health researcher has identified a streamlined approach in clinical settings that may help advance ...
Early life abuse may be linked to greater risk of adult premature death
2023-05-04
Physical and sexual abuse in childhood and adolescence could be associated with a greater risk of adult premature death (before age 70), finds research published by The BMJ today.
This study extends and refines the existing evidence in this area, and highlights the importance of providing trauma informed care for those who have experienced child abuse, say the researchers.
Early life abuse is a global public health issue because it substantially contributes to child death and a range of long term consequences during adulthood. However, the association of childhood or adolescent abuse with total and cause specific premature death during adulthood ...
New study finds no increased risk of menstrual changes after COVID-19 vaccination
2023-05-04
A Swedish study of nearly 3 million women published by The BMJ today finds no evidence of an increased risk of menstrual changes after covid-19 vaccination.
Weak and inconsistent associations were found between covid-19 vaccination and contact with healthcare for postmenopausal bleeding and were even less consistent for menstrual disturbance and premenstrual bleeding.
These findings do not provide any substantial support for a causal association between covid-19 vaccination and diagnoses related to ...
TSIM introduces online training course for successfully implementing sustainable telehealth services
2023-05-04
The Telehealth Service Implementation Model (TSIM) is set to launch a brand-new online training course for telehealth leaders and teams. TSIM originated at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC), stemming from the successful and groundbreaking work of its successful telehealth team. The MUSC Health Center for Telehealth is one of only two federally designated National Telehealth Centers of Excellence in the country.
All-encompassing in nature, TSIM’s structured framework facilitates the development, implementation and optimization of telehealth services. The pioneers of this unique model aimed to share their knowledge and telehealth best practices with other ...
Durham University receives £9m Wellcome award to transform humanities’ contribution to health research
2023-05-04
-With pictures-
Durham University researchers have been awarded the largest grant ever made by the Wellcome Trust for humanities research.
The £9 million award was announced today (4 May 2023) and will fund a new Discovery Research Platform for Medical Humanities (DRP-MH).
The Discovery Research Platform for Medical Humanities will bring the stories and perspectives of people with lived experience of complex health conditions to the forefront of health research.
The Platform will involve people with lived experience and people from marginalised communities as ...
Severe mental illness linked to low attendance at cancer screening
2023-05-04
People with severe mental illness are less likely to attend cancer screening compared to those who do not have such conditions, according to new research from the University of Surrey and the Office for Health Improvement and Disparities (OHID) at the Department of Health and Social Care.
Funded by OHID and NHS England, with support from Cancer Research UK, the study found disparity in attendance at cancer screening in people with severe mental illness, with the most pronounced disparities being observed for those diagnosed with schizophrenia, followed by those diagnosed with other psychoses and bipolar disorder.
The ...
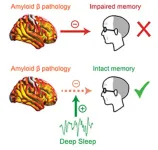
Deep sleep may mitigate Alzheimer’s memory loss, Berkeley research shows
2023-05-04
A deep slumber might help buffer against memory loss for older adults facing a heightened burden of Alzheimer’s disease, new research from the University of California, Berkeley, suggests.
Deep sleep, also known as non-REM slow-wave sleep, can act as a “cognitive reserve factor” that may increase resilience against a protein in the brain called beta-amyloid that is linked to memory loss caused by dementia. Disrupted sleep has previously been associated with faster accumulation of beta-amyloid protein in the brain. However, the new ...
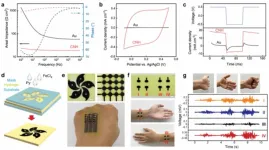
HKU Mechanical Engineering team develops electroconductive hydrogel for biomedical applications
2023-05-04
Synthetic hydrogels show great promise in tissue repair, drug delivery, medical implants, and many other applications. Hydrogels functionalized with electrically conductive components can be used in bioelectronic devices for cardiac or neural interfaces, for applications such as neural prosthetics, cardiac patches, and electronic skin.
A research team led by Dr Lizhi Xu of the Department of Mechanical Engineering in the Faculty of Engineering at the University of Hong Kong (HKU) has recently developed a new type of electroconductive hydrogels with outstanding mechanical strength and manufacturability, creating ...