(Press-News.org)
Anomaly detectors are used to distinguish differences between normal and abnormal data, which are usually implemented by evaluating and ranking the anomaly scores of each instance. A static unsupervised streaming anomaly detector is difficult to dynamically adjust anomaly score calculation.
To solve the problem, a research team led by Prof. Zhiwen Yu published their new research on 15 April 2023 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
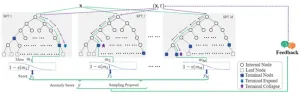
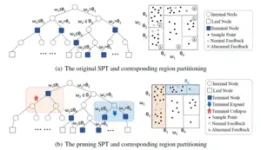
The team proposed a human-machine interactive streaming anomaly detection method, named ISPForest, which can be adaptively updated online under the guidance of human feedback. In particular, the feedback will be used to adjust the anomaly score calculation and structure of the detector, ideally attaining more accurate anomaly scores in the future.
The experimental results demonstrated that the utility of incorporating feedback can improve the performance of anomaly detectors with a few human efforts.
In the research, they analyze the anomaly detection principle of the space partitioning forest model. To improve the original anomaly detector, they add the human feedback mechanism for the detection result during the streaming anomaly detection process. Firstly, in the light of the relationship between forest structure and anomaly score calculation, they construct regional likelihood function and instance likelihood function, respectively, to depict the consistency of the detection results and the human feedback. Then, the parameters and structures of the original anomaly detector are adjusted timely according to the gradient decrease process following the principle of maximum likelihood estimation. Finally, an uncertainty function of the detection results is designed to control the frequency of human-machine interaction.
Experimental results on the effects of feedback reveal that combining anomaly detectors with human feedback is meaningful for adapting to a dynamic environment, and the performance of the detector is improved promptly with a small increase in labor costs. Future work can consider the extension of the method and explore the time-series anomaly detection under the feedback mechanism.
###
Research Article, Published: 15 April 2023
Qingyang LI, Zhiwen YU, Huang XU, Bin GUO. Human-machine interactive streaming anomaly detection by online self-adaptive forest. Front. Comput. Sci., 2023, 17(2): 172317, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-022-1270-y
About Frontiers of Computer Science (FCS)
FCS was launched in 2007. It is published bimonthly both online and in print by HEP and Springer. Prof. Zhi-Hua Zhou from Nanjing University serves as the Editor-in-Chief. It aims to provide a forum for the publication of peer-reviewed papers to promote rapid communication and exchange between computer scientists. FCS covers all major branches of computer science, including: architecture, software, artificial intelligence, theoretical computer science, networks and communication, information systems, multimedia and graphics, information security, interdisciplinary, etc. The readers may be interested in the special columns "Perspective" and "Excellent Young Scholars Forum".
FCS is indexed by SCI(E), EI, DBLP, Scopus, etc. The latest IF is 2.669. FCS solicits the following article types: Review, Research Article, Letter.
END
Sons of women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are three times more likely to develop obesity, according to a study published in Cell Reports Medicine. According to the researchers from Karolinska Institutet the findings highlight a previously unknown risk of passing PCOS-related health problems across generations through the male side of a family.
PCOS is caused by the ovaries producing too much of the sex hormone testosterone. The disease affects around 15 per cent of women of childbearing age worldwide and is a condition that ...
Embargoed for release: Friday, May 5, 2023, 11:00 AM ET
Key points:
Among those diagnosed with non-small cell lung cancer—the most common form of lung cancer—current smokers had 68% higher mortality and former smokers had 26% higher mortality compared to never smokers
The longer a patient had gone without smoking pre-diagnosis, the more improved their odds of survival were
The study is one of few to examine mortality not just among current and never smokers, but also among former smokers—enabling more robust findings about the impacts ...
About The Study: In this study of patients with non–small cell lung cancer, quitting smoking early was associated with lower mortality following a lung cancer diagnosis, and the association of smoking history with overall survival may have varied depending on clinical stage at diagnosis, potentially owing to the differing treatment regimens and efficacy associated with smoking exposure following diagnosis. Detailed smoking history collection should be incorporated into future epidemiological and clinical studies to improve lung cancer ...
About The Study: The findings of this study of 766 patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection suggest that patient-reported perceived cognitive deficits in the first 4 weeks of SARS-CoV-2 infection are associated with post–COVID-19 condition (PCC; colloquially known as long COVID) symptoms and that there may be an affective component to PCC in some patients. The underlying reasons for PCC merit additional exploration.
Authors: Neil Wenger, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of California, Los Angeles, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.11974)
Editor’s ...
Adolescents and young adults with advanced heart disease are at high risk of dying in the hospital, often require invasive treatment and experience significant symptoms that impact their quality of life.
And while most of their parents prefer that decision making about their treatment and care options remain between parents and physicians, many young people want to be actively involved in medical decisions affecting them, a new study suggests.
“As a pediatric psychologist, I have found that healthcare communication is one of the most critical – yet most underappreciated ...
People who perceived that they had cognitive difficulties such as memory problems during COVID were more likely to have lingering physical manifestations of the disease than people who did not report cognitive issues, new UCLA research suggests.
More than one in three people experiencing long COVID symptoms perceived such cognitive deficits, which have been found to be related to anxiety and depression.
The findings indicate that psychological issues such as anxiety or depressive disorders may ...
A research team led by Dr. WANG Liang from the Institute of Psychology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has found that right hippocampal theta power hierarchically encodes the distance between the current position and a goal destination.
The study was published online on May 5 in Current Biology.
Successful navigation to a goal is crucial for animals in nature as well as for humans in modern life. Computational models show that goal-directed navigation computes the Euclidean distance to the goal. Multi-scale representation of goal distance is extremely efficient and less susceptible to interference from background noise than single-scale coding. ...
The language used to communicate fertility awareness should be more empathetic and target both men and women, finds a new study involving UCL researchers.
The review, published in Human Reproduction Open, gives five recommendations on how to promote fertility awareness in a more positive way.
While education about fertility is not intrinsically controversial, finding the right language to address the topic can be difficult – with the risk of causing negative effects such as anxiety, culpability, and stigma.
After reviewing previous studies and literature on the subject, the team were particularly keen to resolve issues around language that could evoke feelings of personal blame, ...
The implementation of effective policies at local and regional level, and the cooperation of all countries in the Mediterranean Sea basin is urgently needed to successfully reverse the environmental problems in this marine area. This is evidenced by a report carried out by the Institute of Environmental Science and Technology of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (ICTA-UAB) presented in the European Parliament by oceanographer Patrizia Ziveri, who stresses the need to urgently fight against the growing pollution caused by marine litter and plastics in the Mediterranean, to improve current legislation and to monitor new pollutants that ...
Two researchers from the University of Bonn have been awarded a Proof of Concept Grant by the European Research Council (ERC) as part of a program designed to help researchers translate their ideas from previous ERC projects into commercial applications. Biologist Prof. Dr. Bernardo S. Franklin from the University Hospital Bonn and physicist Prof. Dr. Simon Stellmer will thus each receive €150,000 over a period of around one year.
Prof. Dr. Bernardo S. Franklin from the Institute for Innate Immunity and the ImmunoSensation2 Cluster of Excellence studies hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), which develop into different blood cells through ...