Domestic abuse exposure linked to increased levels of asthma and other atopic diseases
2023-05-06
(Press-News.org) Women who have suffered domestic abuse may have a higher risk of developing atopic diseases including asthma, new research has found.
Published today in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice, the research led by the University of Birmingham found that in analysis of patient records, there were a significantly larger percentage of women who had atopic diseases and had a history of being exposed to domestic abuse and violence compared to those who hadn’t.
Dr Joht Singh Chandan from the University of Birmingham and corresponding author of the study said:
“After adjusting for possible cofounders, our results show women with a recorded exposure to domestic violence and abuse had a 52% increased risk of developing atopic diseases,”
“Domestic violence and abuse is a global issue that disproportionately affects women. We set out to deepen our understanding of the health impacts of domestic violence so evidence-based public health policies can be further developed to address not only domestic violence, but secondary effects like the development of atopic diseases.”
The team of researchers performed a retrospective open cohort study in the United Kingdom, looking at adult women (those aged 18 and older) with a physician recorded exposure to domestic violence and comparing them to women over 18 without a recorded exposure. Patients with pre-existing reports of atopic disease were excluded from the study.
A total of 13,852 women were identified as being exposed to domestic violence and were matched to 49,036 similar women without a reported exposure. In total, 967/13,852 women in the exposed group (incidence rate (IR) 20.10 per 1,000 py) were diagnosed with atopic disease compared to 2,607/49,036 in the unexposed group (IR 13.24 per 1,000 py).
There were limitations to the study. Women in the exposed group were more likely to be a current smoker than women in the unexposed group. Ethnicity data was often lacking in the database and median follow-up for both groups of women was relatively short given the relapsing nature of atopic disease. Researchers hope to address these limitations in future studies.
ENDS
Notes to editor:
The University of Birmingham is ranked amongst the world’s top 100 institutions. Its work brings people from across the world to Birmingham, including researchers, teachers and more than 6,500 international students from over 150 countries.
The University of Birmingham is a founding member of Birmingham Health Partners (BHP), a strategic alliance which transcends organisational boundaries to rapidly translate healthcare research findings into new diagnostics, drugs and devices for patients. Birmingham Health Partners is a strategic alliance between seven organisations who collaborate to bring healthcare innovations through to clinical application:
University of Birmingham
University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust
Birmingham Women's and Children's Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
Aston University
The Royal Orthopaedic Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
Sandwell and West Birmingham Hospitals NHS Trust
West Midlands Academic Health Science Network
Birmingham and Solihull Mental Health NHS Foundation Trust END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-05-06
What:
Twelve people with persistent neurological symptoms after SARS-CoV-2 infection were intensely studied at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and were found to have differences in their immune cell profiles and autonomic dysfunction. These data inform future studies to help explain persistent neurological symptoms in Long COVID. The findings, published in Neurology: Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation, may lead to better diagnoses and new treatments.
People with post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), which includes Long COVID, have a wide range of symptoms, including fatigue, ...
2023-05-06
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – The immune system has a biological telecommunications system — small proteins known as interleukins that send signals among the leukocyte white blood cells to control their defense against infections or nascent cancer. Interleukin-6, or IL-6, is one of these key mediators of inflammation, and it can, as needed, provoke the immune system into attack against pathogens.
However, imbalances of IL-6 — too much or too little — can cause disease, even in the absence of infection. Excess IL-6 is central to the pathogenesis of inflammatory reactions like ...
2023-05-06
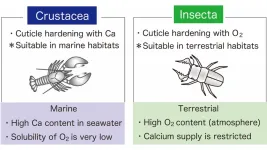
Tokyo, Japan – Scientists from Tokyo Metropolitan University have proposed a hypothesis for why insects are so rare in marine environments. They previously showed that insects evolved a unique chemical mechanism to harden their shells which uses molecular oxygen and an enzyme called multicopper oxidase-2 (MCO2). Now, they argue that this gives them a disadvantage in the sea, while it confers advantages that help them on land, placing MCO2 at the heart of insect eco-evolution.
Insects are some of the most successful organisms on the planet. ...
2023-05-05
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Newly developed “smart” coatings for surgical orthopedic implants can monitor strain on the devices to provide early warning of implant failures while killing infection-causing bacteria, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign researchers report. The coatings integrate flexible sensors with a nanostructured antibacterial surface inspired by the wings of dragonflies and cicadas.
In a new study in the journal Science Advances, a multidisciplinary team of researchers found the coatings prevented infection in live mice and mapped strain in commercial implants applied to sheep spines to warn of various implant or healing failures.
“This ...
2023-05-05
SAN CARLOS, California – A new publication in the May issue of Nature Aging by researchers from Integrated Biosciences, a biotechnology company combining synthetic biology and machine learning to target aging, demonstrates the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to discover novel senolytic compounds, a class of small molecules under intense study for their ability to suppress age-related processes such as fibrosis, inflammation and cancer. The paper, “Discovering small-molecule senolytics with deep neural networks,” authored in collaboration with ...
2023-05-05
Finding a full-time faculty job can be a daunting challenge for doctoral graduates.
University of Cincinnati anthropologist Kathleen Grogan says postdoctoral researchers can benefit from having peers review their applications.
She learned this herself while working as a postdoctoral researcher. She realized that she and other postdocs routinely solicited feedback in an online messaging app dedicated to aspiring scientists.
“I was on the job market and wanted people with broad scientific expertise to look at my stuff,” said Grogan, an assistant professor in UC’s College ...
2023-05-05
LEXINGTON, Ky. (May 5, 2023) — The University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center has been recognized by the National Pancreas Foundation (NPF) as an approved NPF Center of Excellence.
The designation is awarded after a rigorous audit review to determine that an institution's focus is on multidisciplinary treatment of pancreatic cancer, treating the “whole patient” with a focus on the best possible outcomes and an improved quality of life.
“We are honored to receive the NPF designation, which highlight’s Markey’s commitment to multidisciplinary ...
2023-05-05
Researchers at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory captured one of the fastest movements of a molecule called ferricyanide for the first time by combining two ultrafast X-ray spectroscopy techniques. They think their approach could help map more complex chemical reactions like oxygen transportation in blood cells or hydrogen production using artificial photosynthesis.
The research team from SLAC, Stanford and other institutions started with what is now a fairly standard technique: They zapped a mixture of ferricyanide and water with an ultraviolet laser and bright X-rays generated by the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) X-ray free-electron laser. ...
2023-05-05
Providing defendants with legal counsel during their initial bail hearing decreases use of monetary bail and pretrial detention, without increasing the likelihood that defendants fail to appear at the subsequent preliminary hearing, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Researchers found that having legal counsel at bail hearings increased the probability of being released without monetary bail by 21% and reduced the probability that an individual was in jail three days after their bail hearing by 10%.
The analysis, based on a field experiment in Pittsburgh where public defenders were assigned to a limited number of initial bail hearings, is ...
2023-05-05
New Haven, Conn. — When new COVID-19 vaccines were first administered two years ago, public health officials found an increase in cases of myocarditis, an inflammation of the heart muscle, particularly among young males who had been vaccinated with mRNA vaccines. It was unclear, however, what exactly was causing this reaction.
In a new study, Yale scientists have identified the immune signature of these heart inflammation cases.
These findings, published May 5 in the journal Science Immunology, rule out some of the theorized causes of the heart inflammation and suggest potential ways to further ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Domestic abuse exposure linked to increased levels of asthma and other atopic diseases