(Press-News.org) Astronomers used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to image the warm dust around a nearby young star, Fomalhaut, in order to study the first asteroid belt ever seen outside of our solar system in infrared light. But to their surprise, the dusty structures are much more complex than the asteroid and Kuiper dust belts of our solar system. Overall, there are three nested belts extending out to 14 billion miles (23 billion kilometers) from the star; that’s 150 times the distance of Earth from the Sun. The scale of the outermost belt is roughly twice the scale of our solar system’s Kuiper Belt of small bodies and cold dust beyond Neptune. The inner belts – which had never been seen before – were revealed by Webb for the first time.
The belts encircle the young hot star, which can be seen with the naked eye as the brightest star in the southern constellation Piscis Austrinus. The dusty belts are the debris from collisions of larger bodies, analogous to asteroids and comets, and are frequently described as ‘debris disks.’ “I would describe Fomalhaut as the archetype of debris disks found elsewhere in our galaxy, because it has components similar to those we have in our own planetary system,” said András Gáspár of the University of Arizona in Tucson and lead author of a new paper describing these results. “By looking at the patterns in these rings, we can actually start to make a little sketch of what a planetary system ought to look like – If we could actually take a deep enough picture to see the suspected planets.”
The Hubble Space Telescope and Herschel Space Observatory, as well as the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), have previously taken sharp images of the outermost belt. However, none of them found any structure interior to it. The inner belts have been resolved for the first time by Webb in infrared light. “Where Webb really excels is that we're able to physically resolve the thermal glow from dust in those inner regions. So you can see inner belts that we could never see before,” said Schuyler Wolff, another member of the team at the University of Arizona.
Hubble, ALMA, and Webb are tag-teaming to assemble a holistic view of the debris disks around a number of stars. “With Hubble and ALMA, we were able to image a bunch of Kuiper Belt analogs, and we've learned loads about how outer disks form and evolve,” said Wolff. “But we need Webb to allow us to image a dozen or so asteroid belts elsewhere. We can learn just as much about the inner warm regions of these disks as Hubble and ALMA taught us about the colder outer regions.”
These belts most likely are carved by the gravitational forces produced by unseen planets. Similarly, inside our solar system Jupiter corrals the asteroid belt, the inner edge of the Kuiper Belt is sculpted by Neptune, and the outer edge could be shepherded by as-yet-unseen bodies beyond it. As Webb images more systems, we will learn about the configurations of their planets.
Fomalhaut's dust ring was discovered in 1983 in observations made by NASA's Infrared Astronomical Satellite (IRAS). The existence of the ring has also been inferred from previous and longer-wavelength observations using submillimeter telescopes on Mauna Kea, Hawaii, NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope, and Caltech's Submillimeter Observatory.
“The belts around Fomalhaut are kind of a mystery novel: Where are the planets?” said George Rieke, another team member and U.S. science lead for Webb’s Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), which made these observations. “I think it's not a very big leap to say there's probably a really interesting planetary system around the star.”
“We definitely didn't expect the more complex structure with the second intermediate belt and then the broader asteroid belt,” added Wolff. “That structure is very exciting because any time an astronomer sees a gap and rings in a disk, they say, ‘There could be an embedded planet shaping the rings!’”
Webb also imaged what Gáspár dubs “the great dust cloud,” which may be evidence for a collision occurring in the outer ring between two protoplanetary bodies. This is a different feature from a suspected planet first seen inside the outer ring by Hubble in 2008. Subsequent Hubble observations showed that by 2014 the object had vanished. A plausible interpretation is that this newly discovered feature, like the earlier one, is an expanding cloud of very fine dust particles from two icy bodies that smashed into each other.
The idea of a protoplanetary disk around a star goes back to the late 1700s when astronomers Immanuel Kant and Pierre-Simon Laplace independently developed the theory that the Sun and planets formed from a rotating gas cloud that collapsed and flattened due to gravity. Debris disks develop later, following the formation of planets and dispersal of the primordial gas in the systems. They show that small bodies like asteroids are colliding catastrophically and pulverizing their surfaces into huge clouds of dust and other debris. Observations of their dust provide unique clues to the structure of an exoplanetary system, reaching down to earth-sized planets and even asteroids, which are much too small to see individually.
The team’s results are being published in the journal Nature Astronomy.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory. The Fomalhaut observations utilized the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), which was contributed by NASA and ESA (European Space Agency), with the instrument designed and built by a consortium of nationally funded European Institutes (the MIRI European Consortium) and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in partnership with the University of Arizona. Webb will solve mysteries in our solar system, look beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probe the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA and the Canadian Space Agency.
For more information about Webb, visit:
https://www.nasa.gov/webb
END
Webb looks for Fomalhaut’s asteroid belt and finds much more
2023-05-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UCI researchers discover new drugs with potential for treating world’s leading causes of blindness in age-related and inherited retinal diseases
2023-05-08
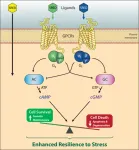
Irvine, CA – May xx, 2023 – In a University of California, Irvine-led study, researchers have discovered small-molecule drugs with potential clinical utility in the treatment of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy (DR), and retinitis pigmentosa (RP).
The study, titled, “Stress resilience-enhancing drugs preserve tissue structure and function in degenerating retina via phosphodiesterase inhibition,” was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“In this study, we introduce a new class of therapeutics called ‘Stress ...
First deaf, Black woman receives her PhD in a STEM discipline
2023-05-08
ST. LOUIS, MO - May 8, 2023 – Graduate student Amie Fornah Sankoh recently stood in front of 150 colleagues family and friends at the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center to defend her thesis, Investigating the Effects of Salicylic acid on Intercellular Trafficking via Plasmodesmata in Nicotiana benthamiana. Upon her successful defense, Dr. Amie Sankoh became the first Deaf, Black woman to receive a PhD in any STEM discipline.
Completing a PhD is a challenging undertaking for anyone; to do so without easy access to the kinds of verbal communication that hearing people ...
Microbubble macrophages track tumors #ASA184
2023-05-08
CHICAGO, May 8, 2023 – Macrophages, a type of white blood cell, defend the body by engulfing and digesting foreign particles, such as bacteria, viruses, and dead cells. The immune cells also tend to accumulate in solid tumors, so tracking them could enable new ways to detect cancer and the earliest stages of metastasis.
As part of the 184th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America, Ashley Alva of the Georgia Institute of Technology will describe how attaching microbubbles to macrophages can create high-resolution and sensitive tracking images useful for disease diagnosis. Her presentation, “Tracking macrophages ...
A cocktail party of 3D-printed robot heads #ASA184
2023-05-08
CHICAGO, May 8, 2023 – Imagine a cocktail party full of 3D-printed, humanoid robots listening and talking to each other. That seemingly sci-fi scene is the goal of the Augmented Listening Laboratory at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. Realistic talking (and listening) heads are crucial for investigating how humans receive sound and developing audio technology.
The team will describe the talking human head simulators in their presentation, “3D-printed acoustic head simulators that talk and move,” on Monday, May 8, at 12:15 p.m. Eastern U.S. in the Northwestern/Ohio State room of the Chicago Marriott Downtown Magnificent Mile Hotel. The talk comes as part of ...
Targeting Mitochondria 2023 will highlight current and future mitochondrial research in October in Berlin
2023-05-08
The World Mitochondria Society is organizing its 14th world conference, Targeting Mitochondria 2023, on October 11-13 at the Steigenberger Hotel Am Kanzleramt, Berlin. Targeting Mitochondria 2023 will address the latest advances and perspectives in mitochondrial research and provide an outlook on future mitochondrial therapies.
Volkmar Weissig, president of the World Mitochondria Society, and Marvin Edeas, president of the scientific committee, said, "This year we will have specific sessions on innovations such as mitochondria in space, exosome-based mitochondrial ...
Uniformity of prey can yield spider-eat-spider world
2023-05-08
A limited menu of prey may weave a tangled food web by emboldening wolf spiders of multiple species to dine on each other and even cannibalize their own, says a study from the University of Nebraska–Lincoln.
Ecologists have long known that predators with otherwise-similar diets can coexist by effectively divvying up the food sources of a community to ease competition and, ideally, leave enough prey for everyone. But analyses of wolf spider species in Nebraska suggest that when the diversity of their mutual prey is lacking, the eight-legged ...
Researchers develop model for how the brain acquires essential omega-3 fatty acids
2023-05-08
Researchers at the UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute at UCLA and the National Institutes of Health have developed a zebrafish model that provides new insight into how the brain acquires essential omega-3 fatty acids, including docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and linolenic acid (ALA). Their findings, published in Nature Communications, have the potential to improve understanding of lipid transport across the blood-brain barrier and of disruptions in this process that can lead to birth defects or neurological conditions. The model may also enable researchers to design drug molecules that are capable of directly ...
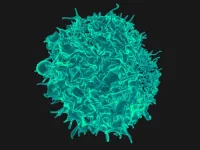
T cells can activate themselves to fight tumors
2023-05-08
When you need a bit of motivation, it often has to come from within. New research suggests cancer-fighting immune cells have found a way to do just that.
Scientists at University of California San Diego have discovered a property of T cells that could inspire new anti-tumor therapeutics. Through a previously undescribed form of cell auto-signaling, T cells were shown to activate themselves in peripheral tissues, fueling their ability to attack tumors.
The study, published May 8, 2023 in Immunity, was led by study first author and postdoctoral fellow Yunlong Zhao, PhD, and co-senior authors Enfu Hui, PhD, professor in the School of Biological Sciences at UC ...
First observational evidence of beaufort gyre stabilization, which could be precursor to huge freshwater release
2023-05-08
Woods Hole, Mass. (Monday, May 8, 2023) - A new study provides the first observational evidence of the stabilization of the anti-cyclonic Beaufort Gyre, which is the dominant circulation of the Canada Basin and the largest freshwater reservoir in the Arctic Ocean.
The study uses a newly extended record of “dynamic ocean topography” satellite data from 2011-2019 provided by two of the co-authors, along with an extensive hydrographic dataset from 2003-2019, to quantify the changing sea surface height ...
Beyond necessity, hearing aids bring enjoyment through music #ASA184
2023-05-08
CHICAGO, May 8, 2023 – For decades, hearing aids have been focused on improving communication by separating speech from background noise. While the technology has made strides in terms of speech, it is still subpar when it comes to music.
In their talk, “Evaluating the efficacy of music programs in hearing aids,” Emily Sandgren and Joshua Alexander of Purdue University will describe experiments to determine the best hearing aids for listening to music. The presentation will take place Monday, May 8, at 11:45 a.m. Eastern U.S. in the Indiana/Iowa room, as part of the 184th Meeting ...