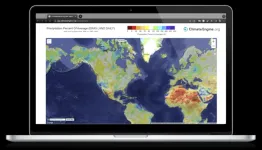
(Press-News.org) The combined use of satellite and climate data has rapidly become critical for scientists and resource managers seeking to accurately assess changes in land cover and land use over time and across space. Unfortunately, processing such vast amounts of data can be time and cost-prohibitive, which is why researchers teamed up with Google and federal agencies to create ClimateEngine.org. Climate Engine’s innovative web application allows scientists, natural resource agencies, and other users to create maps and time series plots that integrate satellite and climate data, providing an indispensable — and free — tool for visualizing complex datasets.
“If you’re trying to study how climate and natural resource management affects the environment, nothing beats the combination of maps and time series for unpacking the data,” says Justin Huntington, Ph.D., Climate Engine project lead and research professor of hydrology at DRI.
First launched in 2016 at the White House Water Summit, ClimateEngine.org is being re-launched with new datasets, support resources, and functionality to increase the capabilities and user-friendliness of the site. Interactive maps and data visualizations produced using decades of satellite data have been a cornerstone of the ClimateEngine.org app, and the new updates will make it easier than ever to use satellite, climate, and forecast data together. These enhanced resources will help Climate Engine’s diverse user community — which includes 12,000+ registered users from public agencies, non-profits, research institutions, and tribal governments — to better use the app to produce charts and maps of environmental indicators such as drought, fire risk, vegetation condition, and agricultural water use.
“As researchers trying to process and visualize many Earth observations together, we understand how difficult it can be to work with these large and disjointed datasets,” Huntington says. “So, we wanted to create a tool that would allow researchers and practitioners to spend more time making discoveries and impact using the best available science.”
The Climate Engine app is unique in that it enables users to visualize and analyze vast amounts of data without the need to code, and results can be downloaded, shared, and recreated with a simple link. It overcomes the computational barriers many research institutions and public agencies face when using large datasets by using Google Earth Engine’s parallel cloud computing platform.
Notable datasets recently added include: 1) ERA5 Ag, which enables calculation of global drought, snowpack, and water demand indicators in near real-time; 2) Rangeland Analysis Platform, a 37-year Landsat dataset of vegetation cover and biomass production for the continental U.S.; and 3) OpenET monthly evapotranspiration, which provides Landsat satellite maps of vegetation water use at field-scale across the Western U.S.
As one of Climate Engine’s primary partners, NOAA’s National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS) uses the Climate Engine Application Programming Interface (API) to automatically create drought datasets shared on Drought.gov.
“Climate Engine is a powerful cloud solution that has enabled NOAA to rapidly create and disseminate critical climate and drought information in ways that were previously impossible,” says Steve Ansari, physical scientist with NOAA’s National Centers for Environmental Information. “The initial Faculty Research Award by Google, followed by funding from NOAA-NIDIS and other federal agencies, has led to a very fruitful and rewarding public-private partnership.” This partnership will continue to produce new datasets, processing capabilities, stakeholder engagement, and web application and API enhancements to advance research, drought monitoring, and early warning.
The Bureau of Land Management (BLM) was also an early supporter of ClimateEngine.org due to the agency’s need to adopt a more data-driven approach to monitoring drought and informing grazing decisions. BLM has positioned itself as a leader in monitoring of federal lands through its investment in ground and satellite-based vegetation monitoring. Among other contributions, the agency supported the development of field-scale trends of drought and vegetation conditions within the Climate Engine web application. BLM is continuing to support trainings and integration of the newest datasets into Climate Engine to provide resource managers with the latest information and science on drought and vegetation conditions.
Moving forward this summer, the ClimateEngine.org team will be adding even more features and functionality to the app, further expanding access to the API, and hosting several public agency webinars and in-person workshops across the Western U.S.
ClimateEngine.org is a collaboration between DRI, University of Merced, Google, and federal partners. The science team includes: DRI researchers Justin Huntington, Britta Daudert, Jody Hansen, Thomas Ott, Kristen O’Shea, Charles Morton, Dan McEvoy, and Eric Jensen, as well as UC Merced researchers Katherine Hegewisch and John Abatzaglou. Find out more about the initiative, partnerships, and updates at ClimateEngine.org and Twitter @ClimateEngOrg, and see the initiative’s peer-reviewed publication.
###
About DRI
The Desert Research Institute (DRI) is a recognized world leader in basic and applied environmental research. Committed to scientific excellence and integrity, DRI faculty, students who work alongside them, and staff have developed scientific knowledge and innovative technologies in research projects around the globe. Since 1959, DRI’s research has advanced scientific knowledge on topics ranging from humans’ impact on the environment to the environment’s impact on humans. DRI’s impactful science and inspiring solutions support Nevada’s diverse economy, provide science-based educational opportunities, and inform policymakers, business leaders, and community members. With campuses in Las Vegas and Reno, DRI serves as the non-profit research arm of the Nevada System of Higher Education. For more information, please visit www.dri.edu.
END
DRI aims to increase scientific access to earth monitoring data with re-launch of ClimateEngine.org
ClimateEngine.org allows researchers and natural resource managers to easily analyze and visualize complex satellite and climate data, helping users understand change in Earth’s landscapes over time
2023-05-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fame-seeking mass shooters more likely to plan ‘surprise’ attacks, and the novelty of their locations and targets brings added fame
2023-05-08
Mass shooters pursuing fame often plan their attacks as “surprises," carefully crafting them in ways that set them apart from previous incidents, which makes them uniquely challenging to prevent.
That is a key finding in a groundbreaking new study from NYU Tandon School of Engineering, about the subset of mass shooters in the U.S. for whom notoriety is a primary objective. The study is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Led by Maurizio Porfiri, NYU Tandon Institute Professor and Director of the Center for Urban Science and ...
UC Irvine scientists develop gene silencing DNA enzyme that can target a single molecule
2023-05-08
NOTE TO EDITORS: PHOTO AVAILABLE AT
https://news.uci.edu/2023/05/08/uc-irvine-scientists-develop-gene-silencing-dna-enzyme-that-can-target-a-single-molecule/
Irvine, Calif., May 8, 2023 — Researchers from the University of California, Irvine have developed a DNA enzyme – or DNAzyme – that can distinguish between two RNA strands inside a cell and cut the disease-associated strand while leaving the healthy strand intact. This breakthrough “gene silencing” technology could revolutionize the development of DNAzymes for treating cancer, infectious diseases and neurological disorders.
DNAzymes ...
Researcher receives prestigious grant to study computer modeling
2023-05-08
Computer models are increasingly used to make decisions that affect nearly every aspect of modern life. This may include how to plan for the sustainable management of environmental resources to responding to pandemics.
And while these models are often based on scientific data and research, they also incorporate subjective values, political interests, and human bias.
With a prestigious national grant, a Virginia Tech researcher will dive into the ways that modeling processes can become more transparent while also incorporating diverse sources of information.
Theodore Lim, an assistant professor ...
Cleanup of inactive Gulf of Mexico wells estimated at $30 billion, UC Davis researchers suggest
2023-05-08
Wetlands, coastal areas and offshore waters near Alabama, Louisiana and Texas have more inactive oil and gas wells than producing ones, and the cost to permanently plug and abandon them could be $30 billion, University of California, Davis, researchers suggest.
A paper published today in the journal Nature Energy examines the cost to plug 14,000 wells that are inactive, have not produced for five years and are unlikely to be reactivated in the Gulf of Mexico region, which is the epicenter of U.S. offshore oil and gas operations.
The wells could pose future environmental and financial risks ...
New research in JNCCN finds telemedicine consistently outperforms in-person visits for cancer care when both are available
2023-05-08
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [May 8, 2023] — New research in the May 2023 issue of JNCCN—Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network from Moffitt Cancer Center finds that telemedicine consistently outperformed in-person visits for both access to care and provider response, according to a long-term study on patient experience. Researchers analyzed survey responses from 39,268 patients across more than 50,000 visits. Telemedicine experiences were compared to in-person visits during and after the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, starting April 1, 2020, and running ...
Galactic bubbles are more complex than imagined, researchers say
2023-05-08
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Astronomers have revealed new evidence about the properties of the giant bubbles of high-energy gas that extend far above and below the Milky Way galaxy’s center.
In a study recently published in Nature Astronomy, a team led by scientists at The Ohio State University was able to show that the shells of these structures – dubbed “eRosita bubbles” after being found by the eRosita X-ray telescope – are more complex than previously thought.
Although they bear a striking similarity in shape to Fermi bubbles, eRosita bubbles are larger and more energetic than their counterparts. Known together as the “galactic ...
Baylor researchers explore effect of Instagram, TikTok on psychological well-being
2023-05-08
Contact: Kelly Craine, Baylor University Media and Public Relations, 254-297-9065
Follow us on Twitter: @BaylorUMedia
WACO, Texas (May 3, 2023) – Instagram and TikTok are two of the fastest-growing social media outlets in the U.S., offering entertainment and connection to a world-wide community with the ease of a finger swipe. Despite their growing popularity, little research has focused on the association between the specific use of Instagram and TikTok and a person’s psychological well-being.
Noted Baylor University smartphone researchers Meredith E. David, Ph.D., ...
Warmer climate could cause Puerto Rico’s frogs to croak #ASA184
2023-05-08
CHICAGO, May 8, 2023 – The coqui frog is one of Puerto Rico’s most iconic animals. It gets its name from its distinctive two-note call, “co-qui,” which can be heard throughout the island every night. The males of the species produce these calls to mark their territory and ward away rivals, but scientists can also use them to study the changing climate.
Peter Narins of the University of California, Los Angeles will describe changes in the calls of the coqui frog over a 23-year period in his talk, “Climate change drives frog call change in Puerto Rico: Predictions and implications.” The presentation will take place Monday, ...
Smallest shifting fastest: Bird species body size predicts rate of change in a warming world
2023-05-08
Photos
Birds across the Americas are getting smaller and longer-winged as the world warms, and the smallest-bodied species are changing the fastest.
That's the main finding of a new University of Michigan-led study scheduled for online publication May 8 in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The study combines data from two previously published papers that measured body-size and wing-length changes in a total of more than 86,000 bird specimens over four decades in North and ...
NSU research into bacteria may lead to new ways of treating infections, improving human health
2023-05-08
FORT LAUDERDALE/DAVIE, Fla. – “Know thy self; know thy enemy” - Sun Tzu
That quote is from centuries ago, but it is applicable in so many ways. One example – new research from Nova Southeastern University (NSU) is understanding human infections and unlocking how bacteria “work together” making these infections much more difficult to treat. But it is understanding this symbiotic relationship – knowing thy enemy – that can lead to better ways to treat various ailments.
This new study was recently published by the scientific journal eLife, and can be found ONLINE.
“There are good bacteria and not so good ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
The world’s largest brain research prize awarded for groundbreaking discoveries on how we sense touch and pain
Magnetofluids help to overcome challenges in left atrial appendage occlusion
Brain-clearing cells offer clues to slowing Alzheimer’s disease progression
mRNA therapy restores fertility in genetically infertile mice
Cloaked stem cells evade immune rejection in mice, pointing to a potential universal donor cell line
Growth in telemedicine has not improved mental health care access in rural areas, study finds
Pitt scientists engineer “living eye drop” to support corneal healing
Outcomes of older adults with advanced cancer who prefer quality of life vs prolonging survival
Lower music volume levels in fitness class and perceived exercise intensity
Of crocodiles, counting and conferences
AERA announces 2026 award winners in education research
Saving two lives with one fruit drop
Photonic chips advance real-time learning in spiking neural systems
[Press-News.org] DRI aims to increase scientific access to earth monitoring data with re-launch of ClimateEngine.orgClimateEngine.org allows researchers and natural resource managers to easily analyze and visualize complex satellite and climate data, helping users understand change in Earth’s landscapes over time