(Press-News.org) Metabolic syndrome with heavy alcohol use may have contributed to recent surge in alcoholic liver disease-related mortality
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-0518
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
A brief research report evaluating the relationship between metabolic syndrome (MetS) and a recent increase in alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) deaths has found that heavy alcohol use and the presence of MetS was associated with a higher risk for advanced liver disease. This association may provide some explanation for the recent surge in alcoholic liver-disease related mortality. The report is published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Mortality from ALD surged from 2009 to 2018 for unclear reasons and despite stable or declining prevalence of alcohol use during that timeframe.
Researchers from University of Southern California Keck School of Medicine and Keck Medicine of USC used NHANES (National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey), a continuous cross-sectional survey, to produce weighted study samples that were representative of the noninstitutionalized U.S. adult population between 1999 and 2018 to examine whether metabolic syndrome (MetS) could be an important contributor to the recent mortality surge from ALD. Participants were divided into 6 subgroups based on alcohol use and MetS: no alcohol use without MetS (n = 7,204); nonheavy alcohol use without MetS (n = 17,475); heavy alcohol use without MetS (n = 805); no alcohol use with MetS (n = 6,818); nonheavy alcohol use with MetS (n = 9,516); and heavy alcohol use with MetS (n = 406). Using logistic regression, the authors estimated marginally adjusted probabilities of advanced liver disease for each subgroup, adjusted for age, sex, and active smoking at 4-year intervals throughout the study period.
The model showed that increasing prevalence of heavy alcohol use with or without MetS did not explain increases in ALD. However, the data did show increases in advanced liver disease with heavy alcohol use with or without MetS, with the greatest increase in advanced liver disease among those with both heavy alcohol use and MetS. A high fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) score (a surrogate for advanced liver disease) was previously associated with 25-fold higher risk for liver-related mortality compared with low FIB-4 score. According to the authors, these findings suggest an increasing interaction effect with MetS and heavy alcohol use that may be contributing to the recent surge in ALD-related mortality, but the reasons are not entirely clear.
Media contacts: For an embargoed PDF, please contact Angela Collom at acollom@acponline.org. To speak with corresponding author Brian P. Lee, MD, MAS, a hepatologist and liver transplant specialist with Kek Medicine of USC, please contact Cynthia Smith at cynthia.smith@med.usc.edu.
END
Metabolic syndrome with heavy alcohol use may have contributed to recent surge in alcoholic liver disease-related mortality
Embargoed News from Annals of Internal Medicine
2023-05-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Low oxygen weight loss trial at Pennington Biomedical open to participants
2023-05-09
BATON ROUGE – Does altitude play a role in weight loss? Why is it easier to lose weight in Colorado versus Louisiana? Researchers at the Pennington Biomedical Research Center are seeking answers to these questions through one of the latest research trials, the “Low Oxygen and Weight Status,” or LOWS study. The LOWS study will determine whether exposure to low oxygen levels in the air, similar to those at higher altitudes, can help individuals with obesity lose weight and improve health.
The LOWS study is now open for participant enrollment. Participants will be randomized to ...
THE LANCET: An estimated one million stillbirths and newborn baby deaths could be prevented each year by implementing low-cost pregnancy interventions in low- and middle-income countries
2023-05-09
Eight low-cost and easily implementable proven interventions for pregnant women in 81 low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) could prevent an estimated 566,000 stillbirths and 5.2 million babies a year from being born preterm or small for gestational age—some with low birth weight—the impacts of which would also affect long-term health and economic output, says a new four-paper Series published in The Lancet.
Additionally, the eight interventions,
multiple micronutrient supplements
balanced protein energy supplements
aspirin
treatment of syphilis
education for smoking cessation
prevention of malaria in pregnancy
treatment ...
Under 40s with mental health problems have elevated risks of heart attack and stroke
2023-05-09
Sophia Antipolis, 9 May 2023: Adults in their 20s and 30s with mental disorders have an up to three-fold elevated likelihood of a heart attack or stroke, according to a study in more than 6.5 million individuals published today in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 Lifestyle behaviours did not explain the excess risk. One in every eight of the 20-to-39-year-old participants had some kind of mental illness including depression, anxiety and insomnia.
“Psychological problems were common in young adults and had strong ...
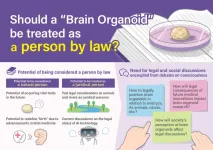
Can tiny brain tissues legally be a person? Researchers say not yet
2023-05-09
Grown in labs, human brain organoids are cultivated from stem cells, feed on nutrient broth and serve as a model of human brain development in miniature. Their growth and structure mimic portions of real brains, allowing scientists to better investigate the origins and potential treatments of neural diseases. How similar are they to actual human brains, though? Are they close enough to be considered people in their own right?
The question is complicated in myriad ethical and moral ways, but researchers based in Japan and Taiwan propose that the legal lens may prove critical when understanding the potential personhood of human ...
Study finds some MND and dementia patients share genetic defects
2023-05-09
New research has discovered that some patients with motor neuron disease (MND) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD) carry the same rare genetic defects that cause other neurodegenerative diseases.
Researchers from the Macquarie University MND Research Centre and The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research have identified the defects in the genomes of some people with non-inherited, or sporadic, MND and FTD.
MND results in the death of the neurons, or motor nerves, connecting the brain and spinal cord to the muscles. These are the cells that control our ability to move, breathe and swallow. The disease ...
Researchers develop interfacial charge modification strategy to enhance photocatalytic water oxidation
2023-05-09
Water oxidation reaction involves a four-electron and four-proton transfer process, which requires an uphill energy transformation and limits the efficiency of the overall photocatalytic water splitting reaction.
Although loading appropriate water oxidation cocatalysts can enhance the performance of water oxidation reactions, the interfacial barrier between the semiconductor and the water oxidation cocatalyst can impede the transfer and utilization of photogenerated charges.
Recently, a research team led by Profs. LI Can and LI Rengui from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) ...
Southwest Rural Health Research Center identifies key health challenges of rural America
2023-05-09
The Southwest Rural Health Research Center at the Texas A&M University School of Public Health has published a peer-reviewed paper detailing Healthy People 2030 priorities that will be most critical for rural America in the upcoming decade. These priorities were identified by rural health stakeholders across the United States. This publication comes ahead of the center’s release of Rural Healthy People 2030 — a continuation of a long-standing tradition of the Southwest Rural Health Research Center in which multidisciplinary authors ...
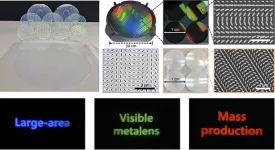
World's first mass production of metalenses for visible wavelengths
2023-05-09
Do you hate the camera bumps on the back of your smartphone? A new optical component called metalens – which was named one of the top 10 future technologies by the World Economic Forum in 2019 – may be the answer. Composed of a nanostructured array, this incredibly thin and lightweight optical device is currently the focus of much attention in the scientific community, even featured in a special issue of Nature Photonics. However, the production of metalenses requires highly precise techniques and can be expensive, posing a challenge for their scalable manufacturing.
In ...
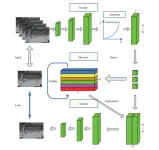
COVAD: Content-oriented video anomaly detection using a self attention-based deep learning model
2023-05-09
Video anomaly detection is a research hotspot in the field of computer vision, attracting many researchers.Video anomaly detection differs from traditional video analysis. Usually, abnormal events occur only in a small percentage of the video pixels and therefore, it is unnecessary to focus on all the video pixels as most of
them are harmless—called “the background”. Therefore, in the video feature extraction process, attention should be focused on a few detectable partial objects. Object detection is very complicated and consumes a significant amount of time during video processing. Therefore, ...
New technique enables in-vivo analysis of protein complexes
2023-05-09
As the executor of life activities, proteins exert their specific biological functions through interactions such as forming protein complexes. The localization effects, crowding effects, and organelle microenvironments within cells are crucial for maintaining the structure and function of protein complexes.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. ZHANG Lihua from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has developed a glycosidic-bond-based mass-spectrometry-cleavable cross-linker, which improves the data ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
[Press-News.org] Metabolic syndrome with heavy alcohol use may have contributed to recent surge in alcoholic liver disease-related mortalityEmbargoed News from Annals of Internal Medicine