(Press-News.org) Fungal networks interconnecting trees in a forest is a key factor that determines the nature of forests and their response to climate change. These networks have also been viewed as a means for trees to help their offspring and other tree-friends, according to the increasingly popular “mother-tree hypothesis”. An international group of researchers re-examined the evidence for and against this hypothesis in a new study.
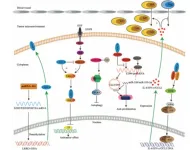
Trees in a forest are interconnected through thread-like structures of symbiotic fungi, called hyphae, which together form an underground network called a mycorrhizal network. While it is well known that the mycorrhizal fungi deliver nutrients to trees in exchange for carbon supplied by the trees, the so-called mother-tree hypothesis implies a whole new purpose of these networks. Through the network, the biggest and oldest trees, also known as mother trees, share carbon and nutrients with the saplings growing in particularly shady areas where there is not enough sunlight for adequate photosynthesis. The network structure should also enable mother trees to detect the ill health of their neighbors through distress signals, alerting them to send these trees the nutrients they need to heal. In this way, mother trees are believed to act as central hubs, communicating with both young seedlings and other large trees around them to increase their chances of survival.
This is a very appealing concept attracting the attention of not only scientists, but also the media, where this hypothesis is often presented as fact. According to the authors of the study just published in New Phytologist, the hypothesis is however hard to reconcile with theory, prompting the researchers to re-examine data and conclusions from publications for and against the mother tree hypothesis.
The study, led by Nils Henriksson at the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, found that the empirical evidence for the mother tree hypothesis is actually very limited and theoretical explanations for the mechanisms are largely lacking. While big trees and their interconnections with their neighbors are still essential for the forest ecosystem, the fungal network does not work as a simple pipeline for resource sharing among trees. This means that apparent resource sharing among trees is more likely to be a result of trading between fungi and trees rather than directed transfer from one tree to another. Very often, this even results in aggravated competition between trees rather than support of seedlings.
“We found that mycorrhizal networks are indeed essential for the stability of many forest ecosystems, but rarely through sharing and caring among trees. Rather, it works like a trading ground for individual trees and fungi, each trying to make the best deal to survive,” explains Oskar Franklin, a study author and a researcher in the Agriculture, Forestry, and Ecosystem Services Research Group of the IIASA Biodiversity and Natural Resources Program. “The forest is not a super organism or a family of trees helping each other. It is a complex ecosystem with trees, fungi, and other organisms, which are all interdependent but not guided by a common purpose.”
“Although the narrative of the mother tree hypothesis is scarcely supported by scientific evidence and is controversial in the scientific community, it has inspired both research and public interest in the complexity of forests. It is vital that the future management and study of forests take the real complexity of these important ecosystems into account,” Franklin concludes.
Reference
Henriksson, N., Marshall, J., Högberg, M.N., Högberg, P., Polle, A., Franklin, O., Näsholm, T. (2023). Re-examining the evidence for the mother tree hypothesis - resource sharing among trees via ectomycorrhizal networks. New Phytologist DOI: 10.1111/nph.18935
New Phytologist is a leading international journal focusing on high quality, original research across the broad spectrum of plant sciences, from intracellular processes through to global environmental change. The journal is owned by the New Phytologist Foundation, a not-for-profit organisation dedicated to the promotion of plant science. https://www.newphytologist.org/
About IIASA:
The International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) is an international scientific institute that conducts research into the critical issues of global environmental, economic, technological, and social change that we face in the twenty-first century. Our findings provide valuable options to policymakers to shape the future of our changing world. IIASA is independent and funded by prestigious research funding agencies in Africa, the Americas, Asia, and Europe. www.iiasa.ac.at
END
Exploring the underground connections between trees
2023-05-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New research sheds light on how human vision perceives scale
2023-05-09
Researchers from Aston University and the University of York have discovered new insights into how the human brain makes perceptual judgements of the external world.
The study, published on 8 May in the journal PLOS ONE, explored the computational mechanisms used by the human brain to perceive the size of objects in the world around us.
The research, led by Professor Tim Meese, in the School of Optometry at Aston University and Dr Daniel Baker in the Department of Psychology at University of York, tells us more about how our visual system can exploit ‘defocus blur’ to infer perceptual scale, but that it does ...
Chinese Medical Journal article reviews role of gene involved in brain functions and disorders
2023-05-09
Leucine-rich repeats containing 4 (LRRC4)—a gene abundantly found in the brain and located on human chromosome 7q31–32—plays a pivotal role in memory formation, autism, spinal cord injury, as well as in determining the malignant potential, development, and progression of glioblastoma (GB), an aggressive cancer involving the brain and/or spinal cord. In a review article published (in volume 136 issue 1 on 5 January 2023, and online on 10 February 2023) in the Chinese Medical Journal, researchers shed light on the ...
EuroPCR 2023 – The interventional cardiovascular community is gathering in Paris to learn, share, and shape the future of patient care worldwide
2023-05-09
EuroPCR, the annual world-leading Course in interventional cardiovascular medicine, has been taking place for over 30 years. It is tailored for all those dedicated to the sharing of knowledge and skills, and improvement of patient care worldwide: interventional cardiologists, cardiac surgeons, imaging specialists, radiologists, nurses, allied professionals and other practitioners, as well as researchers, innovators and industry representatives. The 4-day meeting addresses interventions for coronary and peripheral vessels, for the structural heart including valves, for hypertension, heart failure and stroke, while keeping the community up ...
Spanish courts hand down milder sentences for rapes if they are committed by the victim's partner or ex-partner
2023-05-09
Just four years ago, the Spanish Supreme Court pointed out in a ruling that there is no such thing as a 'conjugal debt'. In other words, a woman is not obliged to satisfy her husband's sexual needs. It may come as a surprise that this point still needs to be made, but the statistics speak for themselves. According to a national survey carried out in 2019, 7.5% of Spanish women over 16 years old have been raped by their partners or ex-partners.
These rapes are usually subject to less attention, and they tend to be "perceived as something less serious". So says Josep Maria Tamarit Sumalla, a full ...
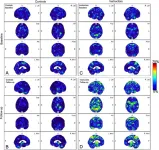
Recurrent brain trauma may increase Alzheimer’s risk
2023-05-09
OAK BROOK, Ill. – New research finds that the brains of otherwise healthy military personnel who are exposed to explosions show an abnormal brain accumulation of amyloid-beta protein—a protein that plays a role in the development of Alzheimer’s disease. The results of the study were published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Research over the last several decades suggests that there might be a relationship between repetitive or severe traumatic ...
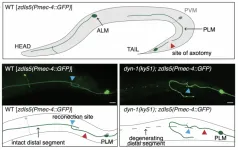
A key protein for repairing broken nerves
2023-05-09
A study explores the role of the dynamin protein DYN-1 in axonal fusion. The axon is a long, thin protrusion of nerve cells that carries electrical impulses. Severed axons can be repaired by a highly efficient regrowth process known as axonal fusion. Previous research has shown that molecules involved in apoptosis—programmed cell death—are also involved in axonal repair. Because dynamin is involved in apoptosis, specifically in the recognition of dying cells, Brent Neumann and colleagues posited that dynamin might also be involved in axonal repair. The team severed axons in the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans, a multicellular nematode worm with just a few hundred ...
Crab populations are crashing. Could losing their sense of smell be one of the important reasons why?
2023-05-09
A new U of T Scarborough study finds that climate change is causing a commercially significant marine crab to lose its sense of smell, which could partially explain why their populations are thinning.
The research was done on Dungeness crabs and found that ocean acidification causes them to physically sniff less, impacts their ability to detect food odours and even decreases activity in the sensory nerves responsible for smell.
“This is the first study to look at the physiological effects of ocean acidification on the sense of smell in crabs,” says Cosima Porteus, an assistant professor in the department of ...
Program Announced for NUTRITION 2023 to be held July 22–25 in Boston
2023-05-09
How do our genes affect what we eat? Can more sustainable diets also improve health? What are the best foods for living longer, fighting cancer, and staying mentally sharp as we age?
You’ll find the answers to these questions and more at NUTRITION 2023, the annual flagship meeting of the American Society for Nutrition. Join us July 22-25 in Boston for an exciting lineup of scientific symposia, educational sessions, hot-topic discussions, and award lectures covering the latest developments in nutrition science.
Get a sneak peek at the ...
NYC Media Lab partners with Verizon to release free immersive educational content available to all US-based educators
2023-05-09
BROOKLYN, NEW YORK (May 9, 2023) — Today, the NYC Media Lab announced the availability of new immersive educational content for all US-based educators. Developed in partnership with Verizon for the $1M Museum Initiative, over 50 augmented reality (AR)- and virtual reality (VR)-focused lesson plans are available on Verizon Innovative Learning HQ (verizon.com/learning)—the free online education portal that brings next-gen learning to all.
Through the $1M Museum Initiative—a nationwide open call for museums and cultural institutions to develop ...
A new theory of what drives partisan conflict and hostility
2023-05-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Partisan conflict can be largely explained as differing views on two crucial tasks of society, according to a new theory developed by a pair of prominent social scientists.
In a new article published yesterday (May 8, 2023) in the journal Psychological Inquiry, Roy Baumeister and Brad Bushman say societies flourish by both amassing and distributing resources.
Conservatives focus on amassing resources, while liberals concentrate on distributing resources. The problem is both sides increasingly tend to disparage the value of what the other side champions, the authors said.
“Both tasks are absolutely essential for society,” ...