(Press-News.org) Researchers from Karolinska Institutet and Sachs’ Children and Youth Hospital in Sweden have mapped the immune system in the gut of children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The results, which were published in Cell Reports Medicine, can be used to design more targeted therapies.
Today, we know relatively little about how the immune system functions in children with IBD and how this differs from adults. About 40 percent of patients, including both children and adults, do not respond to the treatments that are currently available. It is therefore very important to identify biomarkers that can both predict treatment response and help identify new treatment methods.
Understand what happens in the gut
“There is still no cure for inflammatory bowel disease such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis, only symptomatic treatment,” says Jenny Mjösberg, professor of tissue immunology at the Department of Medicine (Huddinge) at Karolinska Institutet. “IBD often first appears in early adulthood, sometimes in childhood. This study is a response to a clinical need to understand why the disease occurs and what happens in the gut in children with IBD.”
Jenny Mjösberg has worked in close collaboration with colleagues at Sachs’ Children and Youth Hospital and Karolinska University Hospital in Sweden to study the intestines of 25 children and eight adults with IBD, as well as ten children and eight adults without IBD. Researchers used flow cytometry and sophisticated single-cell technology, two relatively new techniques that enable the analysis of immune cells from the colon even on small biopsy samples.
Fewer tissue-protective immune cells
The researchers found that pro-inflammatory cell types, such as innate lymphoid cells type 1 (ILC1) and cytotoxic cells, such as T cells and NK cells, were found to a greater extent in children with intestinal inflammation. But they also found that a particular subtype of protective cells – type 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3) – and tissue-resident T cells were present to a lesser degree in the intestinal mucosa of children with IBD.
“Inflammation seems to be linked not only to aggressive cells that drive inflammation, but also to the loss of function in the cells that help maintain a healthy gut,” says Mjösberg. “The treatments that are currently available only aim to suppress inflammation, but it can be just as important to strengthen the tissue-protecting component.”
Children and young people with IBD are also a valuable group to study. They are easier to catch as they just presented with symptoms and thus have not undergone any form of treatment. In addition, they are usually otherwise healthy, are non-smokers and rarely have other confounding health factors. The hope is that the results from this study can be a piece of the puzzle in the development of new treatments.
Individually tailored treatments
“Collaborating on this type of basic clinical research is tremendously important,” says Helena Rolandsdotter, senior consultant at Sachs’ Children and Youth Hospital and researcher at the Department of Clinical Science and Education, Södersjukhuset, at Karolinska Institutet. “Our knowledge of biologic drugs and why they work or don't work is still rather poor. Biomarkers are therefore very important. In the long run, we hope to see more individually tailored treatments. This study is a step in that direction.”
The study was financed by, among others, the European Research Council (ERC starting grant), the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organization (ECCO), The Swedish Research Council, The Swedish Cancer Foundation, The Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research, The Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, Sigrid Jusélius Foundation, and the Finnish Pediatric Research Foundation. The authors declare no competing interests.
Publication: “The single-cell transcriptional landscape of innate and adaptive lymphocytes in pediatric-onset colitis”, Efthymia Kokkinou, Tea Soini, Ram Vinay Pandey, Aline van Acker, Jakob Theorell, Paulo Czarnewski, Egle Kvedaraite, Niels Vandamme, Magda Lourda, Chiara Sorini, Whitney Weigel, Anna Carrasco, Christopher Andrew Tibbitt, Heinrich Schlums, Ulrik Lindforss, Caroline Nordenvall, Malin Ljunggren, Maja Ideström, Mattias Svensson, Jan-Inge Henter Eduardo J. Villablanca, Yenan T. Bryceson, Helena Rolandsdotter, Jenny Mjösberg, Cell Reports Medicine, online 8 May 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101038.
END
Researchers map the immunology of the gut in children with IBD
2023-05-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
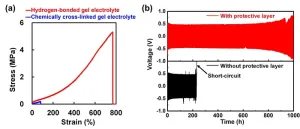
Extending the life of a lithium metal anode using a protective layer made of an extremely tough gel electrolyte
2023-05-09
A National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) research team has succeeded in substantially improving the cycling performance of a lithium metal battery by developing a mechanically very strong polymeric gel electrolyte and integrating it into the battery as a layer to protect the lithium metal anode. This achievement may greatly facilitate efforts to put lithium metal anodes—a potentially very high performance anode material—into practical use.
Today’s society is rapidly transforming through the widespread use of digital technologies, the increasing popularity of electric vehicles and the growing use of renewable energy. These ...
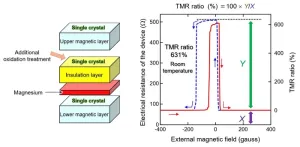
MTJ device with the world’s highest TMR performance developed through precision interfacial control
2023-05-09
The National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) has achieved a tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) ratio of 631% at room temperature, breaking the previous world record which had stood for 15 years. This was accomplished by fine-tuning the interfaces in a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ). This MTJ exhibited very large TMR ratio oscillation effect with a peak-to-valley (PV) difference of 141%. This phenomenon may be exploitable to significantly increase the sensitivity of magnetic sensors and the capacity of magnetoresistive random access ...
Scientists use gene-editing technology to produce first calf resistant to major viral disease
2023-05-09
CLAY CENTER, Neb., May 9, 2023 -Scientists have collaborated to produce the first gene-edited calf with resistance to bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV), a virus that costs the U.S. cattle sector billions of dollars annually.
The recent study published in PNAS Nexus results from a collaboration between the USDA’s Agricultural Research Service (ARS), the University of Nebraska–Lincoln (UNL), the University of Kentucky, and industry partners, Acceligen and Recombinetics, Inc.
BVDV is one of the most significant viruses ...
Gene-edited calf may reduce reliance on antimicrobials against cattle disease
2023-05-09
Cattle worldwide face major health threats from a highly infectious viral disease that decades of vaccinations and other precautions have failed to contain. Federal, private-sector and Husker scientists are collaborating on a new line of defense, by producing a gene-edited calf resistant to the virus.
If follow-up research confirms its efficacy, the gene-editing approach offers long-term potential to reduce antimicrobial and antibiotic use in the cattle industry.
The bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) devastates the bovine immune system and can cause severe respiratory and intestinal harm to infected beef and dairy cattle, said veterinary epidemiologist Brian Vander ...
Scientists at uOttawa streamline a widely used chemical reaction, creating new manufacturing opportunities
2023-05-09
A team of scientists from the University of Ottawa has developed an innovative technique to manufacture complex chemical structures from easily accessible substrates, making it one of the simplest and most practical methods for converting alcohols into their arylated equivalents.
This innovative method for performing the reaction, namely the deoxygenative Suzuki-Miyaura arylation of aliphatic alcohols, uses two distinct metal catalysts. Their reaction operates under mild reaction conditions with minimal waste products and is expected to have a significant impact on the creation of new molecules. As a result, it will contribute to advances in pharmaceutical, agrochemical, ...
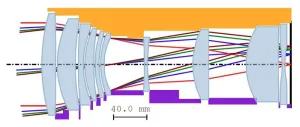
Designing cameras for harsh environments? Be sure to account for lens mount details
2023-05-09
Cameras used in harsh environments must be designed in a way that prevents temperature swings from influencing their optical performance. New research demonstrates that accounting for the exact lens mounting structure used is a critical step in ensuring that lens systems remain robust to temperature changes.
Eric M. Schiesser from Synopsys, Inc. will present the new research at the Optica Design and Fabrication Conference, which will take place 04 – 08 June 2023 in Quebec City, Canada.
“Most optical systems – from the camera in your smartphone to the eyes of the Mars rover - are used over a range of temperatures. To keep the image sharp ...
New study led by Brown researchers sheds light on incidental findings in lung cancer screening
2023-05-09
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University]—When patients receive a low-dose computed tomography screen for lung cancer, doctors can see more than just the lungs. The screening test often picks up abnormalities or potentially “significant incidental findings” (SIFS) not associated with lung cancer. A new study led by Ilana Gareen, an associate professor of epidemiology at the Brown University School of Public Health, and published in JAMA Internal Medicine, highlights the need for proper reporting and management of these findings to reduce mortality, health care costs and unnecessary ...
Single-cell transcriptomic analysis uncovers diverse and dynamic senescent cell populations
2023-05-09
“In summary, single-cell transcriptomic analysis has allowed us to identify the specific populations and the dynamic transition states during senescence initiation and progression.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 9, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 8, entitled, “Single-cell transcriptomic analysis uncovers diverse and dynamic senescent cell populations.”
Senescence is a state of enduring growth arrest triggered by sublethal cell damage. Given that senescent cells actively ...
Variants of MRTFB gene linked to novel neurodevelopmental disorder
2023-05-09
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have linked specific variants or mutations of the gene myocardin-related transcription factor B (MRTFB) with a novel neurodevelopmental disorder. The team reports in the journal Genetics in Medicine that they were able to find variants in this gene in patients whose neurodevelopment disorders had previously gone undiagnosed. The research also revealed that the mutations disrupt the way the MRTFB protein controls other genes in the cell and this cascades to affect hundreds of other genes.
“We identified ...
Change in breast density over time linked to cancer risk
2023-05-09
Many middle-aged and older women get mammograms every one to two years to screen for breast cancer, as recommended by their doctors. A study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis indicates that previous mammograms hold underutilized data that could help identify women at high risk of breast cancer and even reveal which breast is likely to be affected.
When doctors read mammograms, they assess breast density along with signs of cancer, comparing a woman’s previous mammograms to her most recent one to look for worrisome changes. But some changes are difficult to ...