(Press-News.org) A ‘Matter Arising’ paper published in Nature today refutes the findings of a paper by Sala et al on the amount of CO2 released from the seabed by bottom trawling. The paper made significant headlines around the world on release in 2021, as it equated the carbon released by bottom trawling to be of a similar magnitude to the CO2 created by the global airline industry.
In their paper quantifying the carbon benefits of ending bottom trawling, Prof Jan Hiddink of Bangor University’s world-renowned School of Ocean Science and others, explain that the methodology used in the original paper was far too simplistic and vastly overestimates carbon emissions. In calculating the CO2 released by bottom trawling, the paper modelled the amount of carbon that would be disturbed, and they assumed that most of this would be converted into CO2. However, the majority of this organic carbon on the seabed would decompose and be released as CO2 regardless of whether it is disturbed by bottom trawling. Hiddink et al. therefore show that only a very small fraction of seabed carbon reacts to trawling disturbance.
“The carbon benefits of ending bottom trawling have been massively overstated in this paper” Hiddink explains. “While bottom trawling undoubtably disrupts the natural carbon fluxes and disturbs the bottom-dwelling sea life, seabed carbon flows are highly complex and need further research.
Questioning whether the estimates in the paper were realistic, Hiddink reviewed 49 other studies on the measured CO2 differences before and after trawling- and the findings were varied, with 60% of the papers finding no significant effect, 29% finding lower organic carbon and 10 % finding more. If the findings of Sala et al were correct, surely these massive and significant numbers would be reflected in these studies?
Hiddink argues that the Sala paper has confounded the fresh carbon in the top layer, which would be quickly released by natural processes in any case, with the much less reactive carbon stored in the deeper sediment. As the surface layer carbon will be converted to CO2 in any case, assuming it is affected by trawling makes no sense, and massively inflates the estimated CO2 emissions.
HHiddink suggests a figure that is a factor 100 to 1000 times lower than calculated in the Sala paper for the amount of carbon released by trawling would be more appropriate.
“We don’t know enough about what bottom trawling does to seabed carbon stores to be able to make robust global estimates about the effects of bottom trawling.
“Using these figures is worrying, as many governments and others are proposing banning bottom trawling and using the ‘carbon credits’ to offset other activities, but if the carbon emissions are overestimated by several orders of magnitude, we risk increasing overall CO2 emissions while reducing the global food supply.”
END
Paper refutes assertion that effects of bottom trawling on blue carbon can be compared to that of global air travel
Moves to use carbon credits accrued by banning trawling could be directing efforts away from more effective methods
2023-05-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
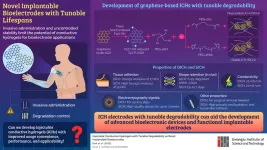
Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology researchers develop injectable bioelectrodes with tunable lifetimes
2023-05-10
Implantable bioelectrodes are electronic devices that can monitor or stimulate biological activity by transmitting signals to and from living biological systems. Such devices can be fabricated using various materials and techniques. But, because of their intimate contact and interactions with living tissues, selection of the right material for performance and biocompatibility is crucial. In recent times, conductible hydrogels have attracted great attention as bioelectrode materials owing to their flexibility, compatibility, and excellent interaction ability. However, the absence ...
Study of cancer metastasis, most common cause of cancer death, gets $35 million boost at Johns Hopkins Medicine
2023-05-10
FOR IMMMEDIATE RELEASE
With a $35 million gift from researcher, philanthropist and race car driver Theodore Giovanis, scientists at Johns Hopkins Medicine will study the biological roots of the most fatal aspect of cancer: how it metastasizes, or spreads, through the body.
The contribution, a 15-year commitment, will establish the Giovanis Institute for Translational Cell Biology, dedicated to studying metastasis. The institute’s researchers aim to make discoveries that reveal common features of metastasis across cancer types, ...
Pandemic stress reshapes the placentas of expectant moms
2023-05-10
WASHINGTON (May 10, 2023) – Elevated maternal stress during the COVID-19 pandemic changed the structure, texture and other qualities of the placenta in pregnant mothers – a critical connection between mothers and their unborn babies – according to new research from the Developing Brain Institute at Children’s National Hospital.
Published in Scientific Reports, the findings spotlight the underappreciated link between the mental health of pregnant mothers and the health of the placenta – a critical organ ...
Local Phoenix medical students invited to upcoming medical conference to learn about opportunities in interventional cardiology
2023-05-10
A newly piloted program from the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI), the leading society representing interventional cardiology, hopes to increase access and encourage interest in interventional cardiology early in students' medical careers.
SCAI's Ready to Launch - Careers in Cardiology program is designed to introduce future physicians to the field of interventional cardiology through a half-day program where attendees will get the opportunity to have impactful conversations with nationally recognized interventional cardiologists, learning about training paths, barriers to care and solutions for the future, the importance of health ...
A jumping conclusion: Fossil insect ID’d as new genus, species of prodigious leaper, the froghopper
2023-05-10
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A fossil arthropod entombed in 100-million-year-old Burmese amber has been identified as a new genus and species of froghopper, known today as an insect with prodigious leaping ability in adulthood following a nymphal stage spent covered in a frothy fluid.
Oregon State University researcher George Poinar Jr., an international expert in using plant and animal life forms preserved in amber to learn about the biology and ecology of the distant past, and his co-author, Alex E. Brown, published ...
Allison Institute announces appointment of inaugural members
2023-05-10
HOUSTON ― The James P. Allison Institute at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today announced the appointment of its first members, James P. Allison, Ph.D., Padmanee Sharma, M.D., Ph.D., Jennifer Wargo, M.D., Sangeeta Goswami, M.D., Ph.D., and Kenneth Hu, Ph.D. In addition, Garry Nolan, Ph.D., will join the Allison Institute as an adjunct member.
These members include pioneering researchers who have made notable contributions to science as well as rising stars on the path toward important breakthroughs. This group ...
St. Jude scientist M. Madan Babu elected to the Royal Society of London
2023-05-10
St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital scientist Madan Babu Mohan, Ph.D., Center of Excellence in Data-Driven Discovery director and member of the Department of Structural Biology, has been elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of London. The Royal Society is the oldest scientific academy in continuous existence.
Babu was selected to join the Royal Society for his pioneering data science-based strategies to reveal fundamental principles in biological systems. His scientific accomplishments include determining the molecular mechanisms governing G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling, uncovering the roles of disordered protein regions in biology and disease, ...
Sleep-tracker study finds fatigued officers struggle with investigations
2023-05-10
AMES, IA — Like many first responders, law-enforcement investigators and detectives often struggle with sleep. Late-night shifts, stress, and the 24-hour nature of crime can throw off biological clocks and cut sleep cycles short. Along with the negative health implications, new research indicates officers who are fatigued have a harder time collecting information that could bring justice to victims.
Zlatan Križan, a sleep scientist and psychology professor at Iowa State University, led the study. He ...
Cheese experiments show fungal antibiotics can influence microbiome development
2023-05-10
Washington, DC – Fungi produce metabolites that humans have used to improve health. For example, they secrete penicillin, which is then purified and used as an antibiotic for humans, leading to the development of many other antibiotics. However, the ecology of fungal metabolites in microbial communities is not well understood. In a new study, researchers use cheese rinds to demonstrate that fungal antibiotics can influence how microbiomes develop. The study is published in mBio, an open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
“My lab is interested in how ...
Broad climate change concern in Florida linked with recent extreme weather
2023-05-10
An increasing number of Floridians agree that human actions are causing climate change, including a record number of Florida Republicans, according to a new survey from Florida Atlantic University. This finding reinforces the trend observed in the prior seven Florida Climate Resilience Surveys, conducted by FAU’s Center for Environmental Studies within the Charles E. Schmidt College of Science.
Three main messages emerge from this latest poll. First, climate change is no longer an effective partisan wedge issue. Virtually all respondents (90 percent) ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Paper refutes assertion that effects of bottom trawling on blue carbon can be compared to that of global air travelMoves to use carbon credits accrued by banning trawling could be directing efforts away from more effective methods