(Press-News.org) New database offers insight into consequences of language loss
Languages, like animal species, can go extinct. More than half of the world’s approximately 7,000 signed and spoken languages are currently endangered. And without intervention they are likely to become extinct, meaning nobody will speak or sign them any longer.
While language loss is happening across the world, the costs vary strikingly in different places, according to a new study co-authored by Yale linguist Claire Bowern. Regions where all Indigenous language are endangered — including parts of South America and the United States — face the greatest consequences.
The study, recently published in the journal Science Advances, is the first to use Grambank — the world’s largest and most comprehensive database of language structure — to better understand global linguistic diversity and the threat that language loss poses to humanity’s collective knowledge of history, culture, and cognition.
“Grambank allows us to find patterns across many languages and language families in a way that hasn’t been possible at scale until now,” said Bowern, a professor of linguistics in Yale’s Faculty of Arts and Sciences, a member of the international team that built the database, and a senior author of the study.
“It demonstrates the beauty and complexity of language and how languages can be a window into the past. It also shows us how that window is very much under threat.”
The novel database currently covers 2,467 language varieties spanning 215 different language families and 101 isolated languages from all inhabited continents and geographic areas. It captures 195 language properties — including word order, verbal tense, and whether a language features gendered pronouns — allowing researchers to draw comparisons between and across the languages.
“Grambank is like a DNA code of languages,” she said. “We can use it to make comparisons to build language trees or examine how languages that split from a common ancestor differ from each other. We can identify features that are very rare in languages across the globe and figure out which of those features are particularly associated with endangered languages.”
To calculate the potential effects of language loss globally and regionally, the researchers applied a metric called “functional richness,” similar to one used in ecology that measures the number of species occupying niche space in an area. Substituting languages for species, they found that while functional richness would decline only moderately worldwide with the loss of all languages currently under threat, the consequences would vary greatly across regions. Northeast South America, Oregon and Alaska in the United States, and northern Australia — regions where all Indigenous languages are under threat — face the harshest consequences.
The loss of those languages would reduce functional richness to zero in these places, according to the analysis.
“Once linguistic diversity is lost, it’s not easily recovered,” said Bowern, a historical linguist whose work focuses on language change and language documentation in Indigenous Australia. “It will take sustained efforts to document and revitalize endangered languages to avoid a devastating loss to the communities where these languages are part of the cultural fabric and to further prevent the erosion of humanity’s great diversity of languages, which represents an incredible wealth of global human cultural heritage.”
The analysis also revealed that there is a lot more variation across languages than was widely believed and provides important insights into how languages evolve and diversify. For example, the researchers show that genealogy — the gradual changing and splitting of languages over time — plays a larger role in shaping linguistic diversity than does geography, through which languages borrow words and grammatical constructs via contact between people speaking different languages.
Grambank’s developers hope that other researchers will began to use the database to discover new patterns in linguistic diversity, Bowern said.
The project was a collaboration among the Max Planck institutes in Leipzig and Nijmegen, the Australian National University, the University of Auckland, Harvard University, Yale University, the University of Turku, Kiel University, Uppsala University, SOAS at the University of London, and the Endangered Languages Documentation Programme, and more than 100 scholars from around the world.
END
New database offers insight into consequences of language loss
2023-05-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bigger isn’t always better: Size of research teams does not equate to better research outcomes, finds new study
2023-05-10
Having a large research team isn’t linked to producing higher quality research, finds a new study from the University of Surrey which analysed data from 1.4 million academic papers.
Professor Sorin Krammer, lead author of the study and Professor of Strategy and International Business at the University of Surrey, said:
“Despite the prevalence of large teams in research, there is still a lack of a good understanding of how their size and diversity affects their performance.”
“Our ...
The acute problem of chronic disease
2023-05-10
In medicine and science, the term “pathogenesis” describes the origin and development of disease. There is not, however, a broadly accepted term to describe the other half of the equation: the process of healing and recovery.
In a new and far-reaching paper, published May 10, 2023 in the journal Mitochondrion, Robert K. Naviaux, MD, PhD, professor of Medicine, Pediatrics and Pathology at UC San Diego School of Medicine, proposes both a term and, more importantly, outlines the array of processes and players, beginning with cellular mitochondria, that drive the healing process – and whose dysfunction underlies chronic illnesses from diabetes ...
An epigenetic approach to modulating aging with nutrition and exercise
2023-05-10
“In this review, we describe how aging impacts epigenetics and how nutrition and physical exercise can positively impact the aging process, from an epigenetic point of view.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 10, 2023 – A new review paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 8, entitled, “How can we modulate aging through nutrition and physical exercise? An epigenetic approach.”
The World Health Organization predicts that by 2050, 2.1 billion people worldwide ...
APL Photonics selects recipient for 2022 Future Luminary Award
2023-05-10
MELVILLE, N.Y., May 10 – The University of Arizona’s Husain Alqattan is the recipient of the APL Photonics 2022 Future Luminary Award for his work in utilizing pulse shaping and waveform synthesis to control electron motion and open the door for ultrafast electronics that process data at unprecedented speeds.
The winning paper, “Attosecond light field synthesis,” was published in the April 2022 issue of APL Photonics. In it, Alqattan and his team used an attosecond light ...
Using AI to predict important measure of heart performance
2023-05-10
Coronary heart disease is the leading cause of adult death worldwide. The coronary angiography procedure provides the clinical standard diagnostic assessment for nearly all related clinical decision-making, from medications to coronary bypass surgery. In many cases, quantifying left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) at the time of coronary angiography is critical to optimize clinical decision-making and treatment decisions, particularly when angiography is performed for potentially life-threatening acute coronary syndromes (ACS).
Since the left ventricle is the heart’s pumping center, measuring the ejection fraction in the chamber provides critical information about the percentage ...
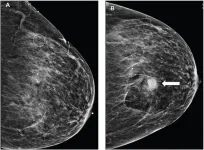
Bleeding after image-guided breast biopsies: Discontinuing vs. maintaining antithrombotic therapy
2023-05-10
Leesburg, VA, May 10, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), frequencies of imaging-apparent and palpable hematoma were not significantly different between patients temporarily discontinuing versus maintaining antithrombotic therapy (AT).
“The findings support safety of continuing AT during breast core-needle biopsy (CNB),” wrote lead researcher Melissa Reichman, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine at New York-Presbyterian ...
Ohio State professor elected to National Academy of Sciences
2023-05-10
COLUMBUS, Ohio - An Ohio State University astronomy professor has been elected to the National Academy of Sciences, one of the highest honors a scientist can receive in the U.S.
David Weinberg, Distinguished University Professor and chair of astronomy, is among 120 new members and 23 international members from 13 countries who were inducted this year in recognition of distinguished and continuing achievement in original research inside their chosen field.
“I have been lucky to have great students and great colleagues throughout ...
New Cleveland Clinic research links immune cell receptors to asthma, inflammatory lung disease
2023-05-10
CLEVELAND - Inhibiting a protein on the surface of immune cells could offer new strategies for treating severe asthma, Cleveland Clinic researchers found.
Researchers discovered a new way a protein called MCEMP1 contributes to severe inflammation in the airway and lungs. The discovery, published in Nature Communications, provides critical information for developing therapeutic interventions to treat long-term lung conditions, including asthma, on a biological level.
The study was conducted in a lab led by Jae Jung, PhD, chair ...
Entangled quantum circuits
2023-05-10
A group of researchers led by Andreas Wallraff, Professor of Solid State Physics at ETH Zurich, has performed a loophole-free Bell test to disprove the concept of “local causality” formulated by Albert Einstein in response to quantum mechanics. By showing that quantum mechanical objects that are far apart can be much more strongly correlated with each other than is possible in conventional systems, the researchers have provided further confirmation for quantum mechanics. What’s special about ...
Simple management steps for a high fertility cycle in your dairy herd
2023-05-10
Philadelphia, May 10, 2023 – The dairy industry has seen a revolution over the past two decades in fertility success within herds. Widely adopted fertility programs are at the heart of this leap forward, along with the industry’s increased understanding—and optimization—of the holistic interactions among the body condition, overall health, and fertility of a dairy cow. In a recent mini-review appearing in a special fertility issue of JDS Communications®, published by Elsevier, researchers from the University of ...