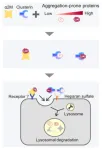
(Press-News.org) Proteins tend to fold wrongly and become defective when exposed to stressors such as heat, oxidation, and pH changes. Accumulation of abnormal proteins contributes to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
So, how does the human body deal with such misfolded or defective proteins? It regulates protein networks via a process called ‘proteostasis,’ which prevents protein aggregation and any damage that may result from misfolded protein accumulation inside (intracellular) or outside (extracellular) cells. A set of unique proteins—molecular chaperones—play an essential role in proteostasis: they target and interact with misfolded proteins, maintain their solubility, and designate them for refolding or degradation. And, while intracellular proteostasis is well understood, extracellular conditions are harsher. Mediating proteostasis in this environment requires specific extracellular molecular chaperones, and the specifics of extracellular proteostasis are yet to be fully understood. Take, for example, an extracellular chaperone, alpha 2-macroglobulin (ɑ2M), an abundant plasma protein. ɑ2M targets defective proteins and is speculated to facilitate the clearance of defective proteins. However, the exact mechanism of how this happens is unknown.
Now, a team of researchers led by Dr. Eisuke Itakura, Associate Professor in the Department of Biology at Chiba University—also including Dr. Ayaka Tomihari and Dr. Mako Kiyota from the Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Chiba University, and Dr. Akira Matsuura from the Graduate School of Science, Chiba University—has identified the substrates that ɑ2M targets for degradation. They also developed a novel assay that detects how ɑ2M mediates the lysosomal degradation of targeted proteins. The group’s findings were published online on March 28, 2023, in Volume 13 of Scientific Reports.
“Thus far, no quantitative method has been available to detect the lysosomal degradation of extracellular proteins. Therefore, we established a fluorescence internalization assay to measure α2M-mediated lysosomal degradation,” says Dr. Itakura.
To devise the assay, the chaperone α2M was tagged with red and green fluorescence proteins (RFP and GFP, or RG) that could be visually detected inside cells. When α2M-RG was internalized into lysosomes, the fluorescence of RFP, but not GFP, was detected. This is because GFP is prone to lysosomal degradation, but RFP is quite resistant. “So, in this assay, if α2M is inducing degradation of misfolded proteins, RFP should accumulate in the cell, producing a red fluorescence,” Dr. Itakura explains. These results were also validated in red blood cell lysates.
The group also probed the significance of why multiple extracellular chaperones exist inside our body by comparing the substrate specificities of α2M and clusterin, another extracellular chaperone. Previously, the group had reported that clusterin also plays a part in the extracellular degradation of proteins like amyloid-beta, the extracellular aggregation of which has been implicated in Alzheimer’s disease. The group found that while α2M and clusterin had overlapping functions, their pathways were not redundant. α2M was seen to recognize the defective proteins more prone to aggregation. According to the researchers, this finding lends credence to the theory that an array of extracellular chaperones cooperates to protect us from the spectrum of misfolded proteins likely to be found in the body.
But what are the long-term implications of this work? Dr. Itakura says, “In the future, elucidating the molecular mechanism of protein degradation by extracellular chaperones may prove useful in treating related diseases, like Alzheimer’s disease. By degrading and removing abnormal proteins that accumulate outside cells, extracellular chaperones have the potential to be a valuable therapeutic tool.”
“If a more detailed relationship between extracellular chaperones and disease can be determined, it may be possible to predict an individual’s condition and the likelihood of developing a particular disease through blood tests,” he concludes.
About Associate Professor Eisuke Itakura
Dr. Eisuke Itakura earned his Ph.D. in 2009 from the Graduate School of Science and Engineering at Saitama University. He has been at Chiba University since 2015, where he is an Associate Professor in the Department of Biology. His research interests span the role of autophagy, lysosomes, endocytosis, and the extracellular environment in the accumulation and clearance of defective proteins. He has published over 35 peer-reviewed articles since 2004.
END
How “extracellular chaperones” help remove abnormal proteins
Researchers discover how wrongly folded proteins occurring outside cells are degraded, thereby preventing them from causing health problems.
2023-05-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Therapy sessions benefit mothers, children in homeless shelter
2023-05-11
Short-term therapy sessions with parents and their children in homeless shelters could help improve parenting skills and reduce parental stress and children’s post-traumatic stress symptoms, according to a pilot study published by the American Psychological Association.
Researchers from Florida International University partnered with Lotus House in Miami, one of the largest women’s homeless shelters in the U.S. The study included 144 families (mother and one child) with children from 18 months to 5 years of age. The research was published online in the Journal ...
Sleep apnea associated with increased risk for long COVID
2023-05-11
Sleep apnea may significantly increase the risk for long COVID in adults, according to a study led by the National Institutes of Health’s RECOVER Initiative and supported by NYU Langone Health as home to the effort’s Clinical Science Core (CSC).
As of April 2023, more than 100 million Americans had been infected with the virus that causes COVID-19. As of April the U.S. Government’s Household Pulse survey estimated that about 6 percent of U.S. adults are experiencing symptoms associated with long COVID, including brain fog, fatigue, depression, and sleep problems. ...
A dangerous eye infection from tainted eye drops, months before the CDC’s warning
2023-05-11
HIGHLIGHTS
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a pathogenic and drug-resistant gram-negative bacterium
The CDC advised against using some artificial tear eye drops that were contaminated with the microbe
In November 2022, doctors in Cleveland diagnosed a patient with a corneal ulcer with a P. aeruginosa infection
The patient acquired the infection from tainted eye drops months before the CDC’s February 2023 warning
Washington, DC – In February 2023, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention warned people against using EzriCare eye drops because bottles of the product had ...
Brigham experts provide insights on how Alzheimer’s drug lecanemab slows cognitive decline
2023-05-11
WHO: Dennis Selkoe, MD, co-director of the Ann Romney Center for Neurologic Diseases at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and corresponding author of the paper in Neuron. Andrew Stern, MD, PhD, of the Ann Romney Center for Neurologic Diseases at BWH and first author of the paper in Neuron
WHAT: In a report published in Neuron, a team led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital reveals the structure of the therapeutic target of lecanemab, a drug approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in January 2023 for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. While the ...
Traditional medicine plant could combat drug-resistant malaria
2023-05-11
Much of what is now considered modern medicine originated as folk remedies or traditional, Indigenous practices. These customs are still alive today, and they could help address a variety of conditions. Now reporting in ACS Omega, a team of researchers have identified compounds in the leaves of a particular medicinal Labrador tea plant used throughout the First Nations of Nunavik, Canada, and demonstrated that one of them has activity against the parasite responsible for malaria.
“Labrador tea” refers to multiple, closely related plants — all members of the genus Rhododendron. ...
ESO telescope reveals hidden views of vast stellar nurseries
2023-05-11
Using ESO’s Visible and Infrared Survey Telescope for Astronomy (VISTA), astronomers have created a vast infrared atlas of five nearby stellar nurseries by piecing together more than one million images. These large mosaics reveal young stars in the making, embedded in thick clouds of dust. Thanks to these observations, astronomers have a unique tool with which to decipher the complex puzzle of stellar birth.
“In these images we can detect even the faintest sources of light, like stars far less massive than the Sun, revealing objects that no one has ever seen before,” says Stefan Meingast, an astronomer at the University of Vienna in Austria and lead author ...
Majority of nurses attribute well-being struggles to staffing shortages
2023-05-11
Cross Country Healthcare, Inc. (NASDAQ: CCRN), a market-leading, tech-enabled workforce solutions platform and advisory firm, in collaboration with Florida Atlantic University, today announced the results of its annual survey of nursing professionals and students.
The study found that although nurses are passionate about doing meaningful work and earning a good income, only one-third of nurses plan to remain in the profession for the foreseeable future, and about one-fourth plan to leave in just one to two years from now. The survey, conducted in collaboration with FAU’s Christine E. Lynn College of Nursing, found ...
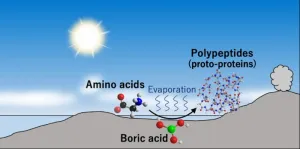
Researchers uncover how primordial proteins formed on prebiotic earth
2023-05-11
How did catalytic organic polymers emerge on prebiotic Earth? Answering this essential question will unlock key understandings in the origin of life.
A team of scientists at Tohoku University have recently found a potential environment for the reaction that produced catalytic organic polymers. To do so, they dried down amino acid solutions containing boric acid and found that boric acid catalyzes polypeptide synthesis under neutral and acidic conditions. The longest peptides formed in the experiments were 39 monomer-long glycine polypeptides under a neutral condition.
Previous studies ...
Women with hardened arteries may need stronger treatment to prevent heart attacks than men
2023-05-11
Barcelona, Spain – 11 May 2023: Postmenopausal women with clogged arteries are at higher risk of heart attacks than men of similar age, according to research presented at EACVI 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC),1 and published in European Heart Journal - Cardiovascular Imaging.2 The study in nearly 25,000 adults used imaging techniques to examine the arteries and followed patients for heart attacks and death.
“The study suggests that a given burden of atherosclerosis ...
A potential pathway to improved stroke recovery
2023-05-11
Osaka, Japan – Ischemic stroke, caused by a blockage of blood flow to the brain, is a common cause of death and disability. Treatments are urgently needed to improve patient outcomes, because recovery currently depends largely on the timely injection of a blood clot-dissolving drug. Priorities for therapy include limiting inflammation at the ischemic site and rebuilding neuronal connections damaged by the stroke. However, a molecule that can achieve these therapeutic effects has remained elusive.
In a study to be published in Stroke, researchers from Osaka University provide new hope for patients. They have identified ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] How “extracellular chaperones” help remove abnormal proteinsResearchers discover how wrongly folded proteins occurring outside cells are degraded, thereby preventing them from causing health problems.