New lens analysis approach could improve treatments for nearsightedness
Instrumentation recreates properties of the myopic eye to test lenses that prevent visual decline
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed new instruments for rigorously quantifying and comparing the light focusing properties of specialized eyeglass lenses that are used to slow the progression of myopia, or nearsightedness. The information gained with this new approach could help inform future lens designs that are even more effective at preventing visual decline.
Nearsightedness is on the rise around the globe, especially among children. If current trends continue, half of the world’s population will be nearsighted by 2050, according to a report from the Brien Holden Vision Institute in Australia. Although the drivers of this worrisome trend aren’t entirely clear, specialized eyeglass lenses have been shown to keep myopia from getting worse. This is particularly important for children and teens who often experience progression in the condition as their bodies grow.
In Optica, Optica Publishing Group’s journal for high-impact research, researchers from the ZEISS Vision Science Lab at the University of Tübingen, in Germany, and the University of Murcia, in Spain, describe their new instruments, which measure lens performance under real-world viewing conditions. They also report results from measuring the light focusing characteristics of different lenses used to slow myopia progression.
“Insights into the link between the optical properties of myopia progression management lenses and effectiveness in real-world scenarios will pave the way to more effective treatments,” said study author Augusto Arias-Gallego, from the ZEISS Vision Science Lab. “This could help millions of children and is fundamental in understanding the mechanisms by which these lenses work.”
Capturing real-life viewing conditions
Myopia is typically caused when a person’s eyes become slightly elongated. This leads faraway objects to appear blurry because they are focused in front of, rather than onto, the retina. Although traditional eyeglass lenses can correct this blurriness, conventional lenses don’t prevent myopia from getting worse. Myopia progression can increase the likelihood of other eye problems and irreversible blindness.
Lenses that modify retinal signals to reduce myopia progression have been clinically tested and are currently available in the market. Researchers hypothesize that these lenses slow the growth of the eyeball, preventing it from becoming more elongated. These lenses incorporate different types of structures, such as microlenses or microdiffusers, to manipulate the image properties at the peripheral retina while correcting the central vision. However, the optical properties of this relatively new technology have not been extensively studied and compared.
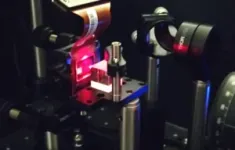
In the new work, the researchers wanted to thoroughly characterize the currently available lenses under real-world viewing conditions. “After exploring the state of the art, we didn’t find a method that could be used to characterize the optical properties of these eyeglass lenses under real viewing conditions,” said Arias-Gallego. “Therefore, we developed a new instrument that can measure the lens’s optical response to different angles of illumination while reproducing the myopic eye’s pupil and refractive errors.”
The new instrument uses an illumination source that is mounted on an arm that rotates around the lens. After the light passes through the lens, a steering rotating mirror guides it toward a spatial light modulator (SLM), which is composed of tiny liquid crystal cells that modify the propagating light with high spatial resolution.
The SLM is the core of the instrument since it reproduces the refractive errors and pupil shape of myopic eyes. This allowed the researchers to reproduce, for the first time, real aberrations produced by different angles of illumination for different myopic eyes while testing the lenses. Those aberrations were programmed as phase maps using the SLM.
Moreover, programmed amounts of defocus can be induced with the SLM, enabling the researchers to conduct a through-focus test. This test captures the image quality within the proximity of a simulated retinal position, shedding light on how the lens interacts with eye elongation signaled at the retina.
The researchers also quantified the lenses’ light scattering properties, which was important because one of the tested lenses is based on contrast reduction by adding scattering. For this, they designed a custom setup that does not require the specialized detectors and moving parts conventionally required for scattering quantification.
Comparing lens properties
“By combining the through-focus results with light-scattering measurements, we were able to accurately characterize several types of eyeglass lenses,” said Arias. “We then compared our measurements for each lens with their reported clinical efficacy for slowing myopia progression. The results raised new questions that need to be studied further while also pointing to potential strategies that could increase the efficacy of future designs.”
In this work, the lenses were characterized using a single wavelength of light to simplify the analysis of the image properties. Because the illumination in real scenarios contains many wavelengths, the researchers are working to adapt the instrument to include sources with varying wavelengths.
Paper: A. Arias, A. Ohlendorf, P. Artal, S, Wahl, “In-depth optical characterisation of spectacle lenses for myopia progression management,” 10, 5 (2023). DOI: 10.1364/OPTICA.486389.
The ZEISS Vision Science Lab is an “Industry on Campus Professorship” workgroup at the University of Tübingen. As part of the Excellence Initiative of the University, new collaborative projects with industry are being launched in the lab, which focuses on application-inspired research in the field of myopia, presbyopia and artificial intelligence.
About Optica
Optica is an open-access journal dedicated to the rapid dissemination of high-impact peer-reviewed research across the entire spectrum of optics and photonics. Published monthly by Optica Publishing Group, the Journal provides a forum for pioneering research to be swiftly accessed by the international community, whether that research is theoretical or experimental, fundamental or applied. Optica maintains a distinguished editorial board of more than 60 associate editors from around the world and is overseen by Editor-in-Chief Prem Kumar, Northwestern University, USA. For more information, visit Optica.
About Optica Publishing Group (formerly OSA)
Optica Publishing Group is a division of Optica (formerly OSA), Advancing Optics and Photonics Worldwide. It publishes the largest collection of peer-reviewed content in optics and photonics, including 18 prestigious journals, the society’s flagship member magazine, and papers from more than 835 conferences, including 6,500+ associated videos. With over 400,000 journal articles, conference papers and videos to search, discover and access, Optica Publishing Group represents the full range of research in the field from around the globe.
Media Contacts:
Aaron Cohen
(301) 633-6773
aaroncohenpr@gmail.com
mediarelations@optica.org
END
New lens analysis approach could improve treatments for nearsightedness
Instrumentation recreates properties of the myopic eye to test lenses that prevent visual decline
2023-05-11
(Press-News.org)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Developing an AI tool to check ARRIVE compliance
2023-05-11
The freely available compliance checker will use natural language processing to automatically assess scientific manuscripts for the information in the ARRIVE Essential 10, a checklist of the most important details to include in any publication describing animal research.
A major factor influencing the reliability and reproducibility of animal experiments is how transparently they are reported. The ARRIVE guidelines help researchers improve the reporting of animal studies by clearly laying out the information that should be included in a manuscript. Reporting animal experiments in line with the ARRIVE guidelines is a requirement ...
Louisiana Cancer Research Center’s “Promising Practices Conference” seeks public and community involvement to help reduce cancer rates in Louisiana
2023-05-11
The Louisiana Cancer Research Center (LCRC) is stepping up its statewide efforts to reduce the state’s extraordinarily high cancer rates by enlisting the help of the public and communities. The LCRC’s newly established Office of Community Outreach and Engagement (OCOE) is convening an all-day “Promising Practices Conference” on Friday, June 2 at Louisiana Tech University and online to highlight the resources and assistance that are available to support better health and wellness throughout Louisiana and strategize on ways to overcome challenges. There is no charge to attend the conference, which is presented by the LCRC in collaboration with ...
High-fat diet ‘turns up the thermostat’ on atherosclerosis
2023-05-11
In a recent study, researchers determined that derivatives of natural emulsifiers such as phospholipids found in high-fat, high-cholesterol diets can promote atherosclerosis via gut bacteria interactions with the immune system. This study could pave the way for targeted interventions for individuals who are at risk for developing heart disease.
Obesity and a high-cholesterol, high-fat diet are both well-established risk factors for atherosclerosis. In fact, obese individuals are two and a half times more likely to develop heart disease. ...
Supergenes helped bring invasive plant to Norway
2023-05-11
The common ragweed plant (Ambrosia artemisiifolia) has spread rapidly in Europe and has intensified the pollen season for many allergy sufferers. Now the plant has arrived in Norway.
Common ragweed can extend Norway's pollen season into November, but fortunately the species is struggling in this country.
“Common ragweed can be found in Norway, but for now it has no stable populations,” says Vanessa Carina Bieker, a postdoc at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology's (NTNU) ...
How “extracellular chaperones” help remove abnormal proteins
2023-05-11
Proteins tend to fold wrongly and become defective when exposed to stressors such as heat, oxidation, and pH changes. Accumulation of abnormal proteins contributes to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
So, how does the human body deal with such misfolded or defective proteins? It regulates protein networks via a process called ‘proteostasis,’ which prevents protein aggregation and any damage that may result from misfolded protein accumulation inside (intracellular) or outside (extracellular) cells. A set of unique proteins—molecular chaperones—play an essential role in proteostasis: they target and interact with misfolded proteins, maintain their solubility, ...
Therapy sessions benefit mothers, children in homeless shelter
2023-05-11
Short-term therapy sessions with parents and their children in homeless shelters could help improve parenting skills and reduce parental stress and children’s post-traumatic stress symptoms, according to a pilot study published by the American Psychological Association.
Researchers from Florida International University partnered with Lotus House in Miami, one of the largest women’s homeless shelters in the U.S. The study included 144 families (mother and one child) with children from 18 months to 5 years of age. The research was published online in the Journal ...
Sleep apnea associated with increased risk for long COVID
2023-05-11
Sleep apnea may significantly increase the risk for long COVID in adults, according to a study led by the National Institutes of Health’s RECOVER Initiative and supported by NYU Langone Health as home to the effort’s Clinical Science Core (CSC).
As of April 2023, more than 100 million Americans had been infected with the virus that causes COVID-19. As of April the U.S. Government’s Household Pulse survey estimated that about 6 percent of U.S. adults are experiencing symptoms associated with long COVID, including brain fog, fatigue, depression, and sleep problems. ...
A dangerous eye infection from tainted eye drops, months before the CDC’s warning
2023-05-11
HIGHLIGHTS
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a pathogenic and drug-resistant gram-negative bacterium
The CDC advised against using some artificial tear eye drops that were contaminated with the microbe
In November 2022, doctors in Cleveland diagnosed a patient with a corneal ulcer with a P. aeruginosa infection
The patient acquired the infection from tainted eye drops months before the CDC’s February 2023 warning
Washington, DC – In February 2023, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention warned people against using EzriCare eye drops because bottles of the product had ...
Brigham experts provide insights on how Alzheimer’s drug lecanemab slows cognitive decline
2023-05-11
WHO: Dennis Selkoe, MD, co-director of the Ann Romney Center for Neurologic Diseases at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and corresponding author of the paper in Neuron. Andrew Stern, MD, PhD, of the Ann Romney Center for Neurologic Diseases at BWH and first author of the paper in Neuron
WHAT: In a report published in Neuron, a team led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital reveals the structure of the therapeutic target of lecanemab, a drug approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in January 2023 for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. While the ...
Traditional medicine plant could combat drug-resistant malaria
2023-05-11
Much of what is now considered modern medicine originated as folk remedies or traditional, Indigenous practices. These customs are still alive today, and they could help address a variety of conditions. Now reporting in ACS Omega, a team of researchers have identified compounds in the leaves of a particular medicinal Labrador tea plant used throughout the First Nations of Nunavik, Canada, and demonstrated that one of them has activity against the parasite responsible for malaria.
“Labrador tea” refers to multiple, closely related plants — all members of the genus Rhododendron. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] New lens analysis approach could improve treatments for nearsightednessInstrumentation recreates properties of the myopic eye to test lenses that prevent visual decline