(Press-News.org) A team of astronomers led by the University of Southampton have uncovered the largest cosmic explosion ever witnessed.
The explosion is more than ten times brighter than any known supernova (exploding star) and three times brighter than the brightest tidal disruption event, where a star falls into a supermassive black hole.
The explosion, known as AT2021lwx, has currently lasted over three years, compared to most supernovae which are only visibly bright for a few months. It took place nearly 8 billion light years away, when the universe was around 6 billion years old, and is still being detected by a network of telescopes.
The researchers believe that the explosion is a result of a vast cloud of gas, possibly thousands of times larger than our sun, that has been violently disrupted by a supermassive black hole. Fragments of the cloud would be swallowed up, sending shockwaves through its remnants, as well as into a large dusty ‘doughnut’ surrounding the black hole. Such events are very rare and nothing on this scale has been witnessed before.
Last year, astronomers witnessed the brightest explosion on record - a gamma-ray burst known as GRB 221009A. While this was brighter than AT2021lwx, it lasted for just a fraction of the time, meaning the overall energy released by the AT2021lwx explosion is far greater.
The findings of the research have been published today [Friday, 12 May 2023] in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Discovery
AT2021lwx was first detected in 2020 by the Zwicky Transient Facility in California, and subsequently picked up by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) based in Hawaii. These facilities survey the night sky to detect transient objects that rapidly change in brightness indicating cosmic events such as supernovae, as well as finding asteroids and comets. Until now the scale of the explosion has been unknown.
“We came upon this by chance, as it was flagged by our search algorithm when we were searching for a type of supernova,” says Dr Philip Wiseman, Research Fellow at the University of Southampton, who led the research. “Most supernovae and tidal disruption events only last for a couple of months before fading away. For something to be bright for two plus years was immediately very unusual.”
The team investigated the object further with several different telescopes: the Neil Gehrels Swift Telescope (a collaboration between NASA, the UK and Italy), the New Technology Telescope (operated by the European Southern Observatory) in Chile, and the Gran Telescopio Canarias in La Palma, Spain.
Measuring the explosion
By analysing the spectrum of the light, splitting it up into different wavelengths and measuring the different absorption and emission features of the spectrum, the team were able to measure the distance to the object.
“Once you know the distance to the object and how bright it appears to us, you can calculate the brightness of the object at its source. Once we’d performed those calculations, we realised this is extremely bright,” says Professor Sebastian Hönig from the University of Southampton, a co-author of the research.
The only things in the universe that are as bright as AT2021lwx are quasars - supermassive black holes with a constant flow of gas falling onto them at high velocity.
Professor Mark Sullivan, also of the University of Southampton and another co-author of the paper, explains: “With a quasar, we see the brightness flickering up and down over time. But looking back over a decade there was no detection of AT2021lwx, then suddenly it appears with the brightness of the brightest things in the universe, which is unprecedented.”
What caused the explosion?
There are different theories as to what could have caused such an explosion, but the Southampton-led team believe the most feasible explanation is an extremely large cloud of gas (mostly hydrogen) or dust that has come off course from its orbit around the black hole and been sent flying in.
The team are now setting out to collect more data on the explosion - measuring different wavelengths, including X-rays which could reveal the object’s surface and temperature, and what underlying processes are taking place. They will also carry out upgraded computational simulations to test if these match their theory of what caused the explosion.
Dr Philip Wiseman added: “With new facilities, like the Vera Rubin Observatory’s Legacy Survey of Space and Time, coming online in the next few years, we are hoping to discover more events like this and learn more about them. It could be that these events, although extremely rare, are so energetic that they are key processes to how the centres of galaxies change over time.”
Multiwavelength observations of the extraordinary accretion event AT2021lwx is published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society and is available to read online.
Ends
Notes for editors
Multiwavelength observations of the extraordinary accretion event AT2021lwx will be published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society at 00:01 GMT on Friday 12 May 2023.
A preprint of the paper is available to read at: https://academic.oup.com/mnras/advance-article/doi/10.1093/mnras/stad1000/7115325
For further information and interviews with the following, please contact: Steve Williams, Media Relations, University of Southampton. press@soton.ac.uk 023 8059 3212:
Dr Philip Wiseman, University of Southampton
Professor Sebastian Hönig, University of Southampton
Professor Mark Sullivan, University of Southampton
Associate Professor Manda Banerji, University of Southampton
Associate Professor Matthew Middleton, University of Southampton
Images
Artist impression of a black hole accretion. Credit John A. Paice.
Images of the Zwicky Transient Facility. Credit Caltech
Images of the New Technology Telescope. Credit European Southern Observatory
The University of Southampton drives original thinking, turns knowledge into action and impact, and creates solutions to the world’s challenges. We are among the top 100 institutions globally (QS World University Rankings 2023). Our academics are leaders in their fields, forging links with high-profile international businesses and organisations, and inspiring a 22,000-strong community of exceptional students, from over 135 countries worldwide. Through our high-quality education, the University helps students on a journey of discovery to realise their potential and join our global network of over 200,000 alumni. www.southampton.ac.uk
The Royal Astronomical Society (RAS), founded in 1820, encourages and promotes the study of astronomy, solar-system science, geophysics and closely related branches of science. The RAS organises scientific meetings, publishes international research and review journals, recognises outstanding achievements by the award of medals and prizes, maintains an extensive library, supports education through grants and outreach activities and represents UK astronomy nationally and internationally. Its more than 4,000 members (Fellows), a third based overseas, include scientific researchers in universities, observatories and laboratories as well as historians of astronomy and others.
www.southampton.ac.uk/news/contact-press-team.page
Follow us on twitter: http://twitter.com/unisouthampton
Like us on Facebook: www.facebook.com/unisouthampton
END
Astronomers reveal the largest cosmic explosion ever seen
2023-05-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
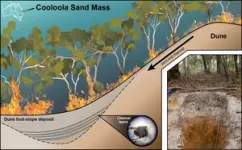
Scientists find fire records inside sand dunes
2023-05-12
A previously unrecognised sedimentary archive in sand dunes could unlock a repository of fire records, a discovery that could expand fire histories across the globe.
The research, conducted by Dr Nicholas Patton during his PhD at The University of Queensland, has solved a persistent problem facing historians investigating changing fire patterns.
“Knowing how the frequency and intensity of wildfires has changed over time offers scientists a glimpse into Earth’s past landscapes, as well as an understanding of future climate change impacts,” Dr Patton said.
“To reconstruct fire records, researchers usually rely heavily ...
Brain-belly connection: gut health may influence likelihood of developing Alzheimer’s
2023-05-11
Could changing your diet play a role in slowing or even preventing the development of dementia? We’re one step closer to finding out, thanks to a new UNLV study that bolsters the long-suspected link between gut health and Alzheimer’s disease.
The analysis — led by a team of researchers with the Nevada Institute of Personalized Medicine (NIPM) at UNLV and published this spring in the Nature journal Scientific Reports — examined data from dozens of past studies into the belly-brain connection. The results? There’s a strong link between particular kinds of gut bacteria and Alzheimer’s disease.
Between 500 and 1,000 species of bacteria ...
New research from UMass Amherst links changes in land use to water quality and quantity
2023-05-11
AMHERST, Mass. – Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst recently published a study in the journal PLOS Water that focuses on the Sudbury-Assabet and Concord watershed in eastern Massachusetts, and which links hydrological changes, including floods, drought and runoff, to changing patterns of land use.
“We all live in a watershed” says Timothy Randhir, professor of environmental conservation at UMass Amherst and the paper’s senior author. “We’re constantly modifying our landscape, turning what were once forests into ...
UC Irvine study shows traffic-related air pollution in Irvine weakens brain function
2023-05-11
Irvine, Calif., May 11, 2023 – Researchers from the University of California, Irvine have found that exposure to traffic-related air pollution in Irvine led to memory loss and cognitive decline and triggered neurological pathways associated with the onset of Alzheimer’s disease.
“The link between air pollution and Alzheimer’s disease is concerning, as the prevalence of toxicants in ambient air is not just on the rise globally, but also hitting close to home here in Irvine,” said corresponding ...
Bail reform law in New York had negligible effect on increases in crime
2023-05-11
Across the United States, legislators and the public have debated the issue of bail reform, which aims to reduce pretrial jail populations by eliminating cash bail. New York State passed legislation in 2019 to limit the use of money bail and expand pretrial release. In a new study, researchers evaluated the effect of the law on state crime rates, considering the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic. Although rates of murder, larceny, and motor vehicle theft rose after the bail reform law went into effect, none of the increases were statistically significant when compared with a control group. This suggests that the effect of bail reform on crime rate increases was negligible.
The study, ...
The science of attraction: why do we fall for certain people?
2023-05-11
Sometimes life’s most meaningful relationships grow from the briefest of connections. Like when you go to a party and meet someone wearing your favorite band’s T-shirt, or who laughs at the same jokes as you, or who grabs that unpopular snack you alone (or so you thought) love. One small, shared interest sparks a conversation—that’s my favorite, too!—and blossoms into lasting affection.
This is called the similarity-attraction effect: we generally like people who are like us. Now, new findings from a Boston ...
Estimated annual spending on Lecanemab and its ancillary costs in the Medicare program
2023-05-11
About The Study: Lecanemab and associated ancillary services could add an estimated $2 billion to $5 billion annually to Medicare spending with substantial out-of-pocket costs for beneficiaries lacking supplemental coverage, according to a cost analysis using nationally representative survey data. Lecanemab, an antidementia medication with modest clinical benefit, received accelerated Food and Drug Administration approval.
Authors: John N. Mafi, M.D., M.P.H., of the David Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, is the corresponding ...
Kentucky, Tennessee GAME Change team wins NSF Engines Development Award
2023-05-11
LEXINGTON, Ky. (May 11, 2023) — The University of Kentucky, as lead organization, together with partners across Kentucky and Tennessee, has been awarded $1 million from the U.S. National Science Foundation’s Regional Innovation Engines, or NSF Engines, program. This team’s proposal, “Advancing carbon centric circular economy technologies for advanced manufacturing solutions (KY, TN),” is led by a coalition named Generate Advanced Manufacturing Excellence for Change (GAME Change).
The GAME Change team is among the more than 40 unique teams to receive one of the first-ever NSF Engines ...
Study could help solve mystery of the disappearing twins
2023-05-11
Key takeaways
UCLA and Keck Observatory scientists analyzed over a decade’s worth of data about 16 young supermassive stars orbiting the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
Supermassive stars typically are formed in pairs, but the new study found that all 16 of the stars were singletons.
The findings support a scenario in which the supermassive black hole drives nearby stars to either merge or be disrupted, with one of the pair being ejected from the system.
When supermassive stars are born, they’re almost always paired ...
Expansion of cell-to-cell communication drives the early development of pancreatic cancer, new research in mice finds
2023-05-11
Discussions of cancer often stress the genetic mutations that drive disease by altering the normal function of cellular proteins. KRAS, for example, normally acts as an on/off switch for cellular proliferation, but mutations to the gene — common in lung cancer, colorectal cancer and pancreatic cancer — cause that switch to stay on.
Yet mutations are only half of the story.
Interactions between these genetic mutations and external factors, such as tissue injury that leads to inflammation, reshape both cells’ identities and their local environment in ways that foster cancer’s emergence and runaway growth.
In pancreatic cancer, these changes start ...