(Press-News.org) High levels of the stress hormone cortisol during the third trimester of pregnancy may improve speech and language skills in the first 3 years of a child’s life, according to research presented at the 25th European Congress of Endocrinology in Istanbul. The findings help researchers further understand the role cortisol plays in both fetal and child development.
Language development during early childhood can indicate how well a baby’s nervous system was developed in the womb. Prenatal exposure to cortisol – a steroid hormone that helps the body respond to stress – directs the growth of a fetus and also affects its brain development. However, the effects cortisol has on early language development remain unknown.
In this study, researchers from the Odense University Hospital analysed data on the cortisol levels of 1,093 Danish women during their third trimester of pregnancy and on the speech and language skills of 1,093 Danish children aged 12-37 months, from the Odense Child Cohort. They found that boys exposed to high cortisol levels in the womb could say more words at ages 12-37 months, while girls were better at understanding more words at the age of 12-21 months.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the association between maternal cortisol levels and language development in children over time, also taking offspring sex and maternal educational level into account,” said Dr Anja Fenger Dreyer, who was involved in the study.
She added: “We have had access to a large study cohort, high-quality methods of analysis and relevant covariates, making our study an important contribution to the physiological understanding of prenatal cortisol exposure in fetal maturation and child development.”
The team will next assess whether children exposed to high cortisol in the womb are more likely to have higher intelligence quotient (IQ) scores. Except for the data on maternal cortisol levels and early language development, the Odense Child Cohort also has data on intelligence tests carried out by children aged 7 years old. “Early language development in children is known as a predictor for cognitive function later in life, such as attention, memory and learning, so we want to investigate whether prenatal cortisol exposure is also associated with IQ scores of children aged 7 years old,” said Dr Fenger Dreyer.
--------ENDS-------
Notes for Editors:
For further information about the study, and to arrange an interview with the authors, please contact the ESE press office:
Joanna Williams
Communications Executive
Mob: +44 (0) 7876 824 027
Email: joanna.williams@endocrinology.org
The poster “Maternal cortisol levels in 3rd trimester and early language development, a study of 1,093 mother-child pairs from Odense Child Cohort” will be presented on Saturday 13 May 2023 at the European Congress of Endocrinology at the Halic Congress Center in Istanbul, Turkey. See the full scientific programme here.
The European Society of Endocrinology (ESE) provides a platform to develop and share leading research and best knowledge in endocrine science and medicine. By uniting and representing every part of the endocrine community, we are best placed to improve the lives of patients. With over 5,000 individual members and through the 51 National Societies involved with the ESE Council of Affiliated Societies (ECAS), ESE represents a community of over 20,000 European endocrinologists. We inform policy makers on health decisions at the highest level through advocacy efforts across Europe.
END
Stress hormone during pregnancy may improve early language development in children
2023-05-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Steroids linked to long-lasting heart disease risk and worse quality of life
2023-05-13
Anabolic steroids not only can cause serious side effects during use, such as heart failure and depression, but can continue being harmful years after stopping, according to two studies presented at the 25th European Congress of Endocrinology in Istanbul. These studies, supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation, were carried out by researchers from the Copenhagen University Hospital Rigshospitalet who investigated the impact of anabolic steroids in former users.
Anabolic steroids – synthetic hormones ...
Low levels of vitamin D linked to long COVID
2023-05-13
Long COVID risk has been found to increase with low levels of vitamin D, according to research presented at the 25th European Congress of Endocrinology in Istanbul. The findings suggest that individuals should have their vitamin D levels checked after COVID-19.
Also known as post COVID-19 syndrome, long COVID is a new condition in which the effects of COVID-19 last for more than 12 weeks after contracting the initial infection. Studies have shown that it affects 50-70% of patients previously hospitalised for COVID-19, yet very little is known about the condition. One risk factor for worse outcomes for hospitalised COVID-19 patients, such as intubation and mechanical ventilation ...
Accelerated delivery of transcranial magnetic stimulation is safe and effective
2023-05-12
May 12, 2023 — Accelerated schedules for repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) can be offered to patients experiencing treatment-resistant major depressive disorder (MDD), a group of clinician–researchers and neuroscientists have concluded. The group cautions that such treatment should be proposed only after detailed discussion with patients about acceleration being an alternate form of rTMS scheduling, with documentation of informed consent.
The recommendations are published in a ...
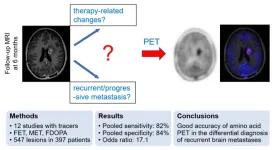
Amino acid PET successfully differentiates recurrent brain metastases, reducing invasive procedures and overtreatment
2023-05-12
Reston, VA—A newly published meta-analysis indicates that amino acid PET can accurately differentiate recurrent or progressive brain metastases from treatment-related changes. A specificity of 84 percent suggests that it may reduce the number of invasive procedures and overtreatment in patients who in fact experience treatment-related changes. This research was published in the May issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Brain metastases occur in 20 to 40 percent of all cancer patients and are most likely ...
Is it too late to change your mind? Study reveals ‘developmental window’ for thinking styles
2023-05-12
Key takeaways
Researchers studied the way different generations in Romania determined the truth of information following the country’s transition from authoritarianism to democracy.
Those who were born and raised after the transition were more likely than older cohorts to compare and evaluate different perspectives before deciding who is right.
The factors associated with the youngest generation’s style of thinking were greater exposure to formal education and social media.
While people change and learn throughout life, experts recognize ...
TVT 2023 late-breaking science announced
2023-05-12
NEW YORK – May 12, 2023 – The Cardiovascular Research Foundation (CRF) announced that TVT: The Structural Heart Summit will feature 15 Late-Breaking Clinical Science studies. An annual meeting featuring cutting-edge research and techniques for structural heart interventions, TVT will take place June 7-10, 2023, at the Phoenix Convention Center – West in Phoenix, Arizona.
TVT has become the epicenter of innovation and collaboration in the structural heart arena over its 16-year history. The meeting brings together world-renowned experts and master operators to help translate novel discoveries into practical therapies for patients with valvular heart disease.
TVT’s ...
UArizona Engineering alum returns to lead School of Mining and Mineral Resources
2023-05-12
Misael Cabrera has been selected through a nationwide search as the inaugural director of the School of Mining and Mineral Resources. The school was created in 2021 and is jointly housed in the College of Engineering and the College of Science, with strong partnerships to additional colleges and centers.
“Our role is to deliver talent and technology through research, but also to change the top-of-mind association with mining. We can create real solutions that both industry and our planet need,” said Cabrera.
Cabrera, who began the position in April, most ...
Researchers track antimicrobial resistance in E. coli isolated from swine
2023-05-12
The spread of drug-resistant microbes has become a global health concern that threatens our ability to treat infections. The widespread use of antimicrobials in livestock, such as swine farms, exacerbates this problem. Therefore, we need surveillance systems to monitor these microbes to support the public health authorities. To this end, researchers have tracked the antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from swine.
Antimicrobials are essential for preventing and treating infections in humans and animals. According to the US Food and Drug Administration, 70% of all antibiotic ...
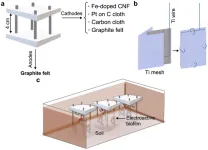
Carbon-based cathodes impact biofilm composition and performance in soil microbial fuel cells
2023-05-12
In the context of increasing energy demands and environmental concerns, renewable energy solutions are crucial for achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. Microbial electrochemical technologies, such as SMFCs, are cost-effective and environmentally friendly, making them an attractive option for green energy systems. SMFCs utilize endogenous microorganisms present in soil to convert organic matter into electricity, offering a sustainable energy source and a self-powered in situ bioremediation strategy for contaminated soils.
Cathode materials play a significant role in the performance of microbial fuel cells. In this study, researchers compared the performance ...
Healthy teeth thanks to the "washing machine effect”
2023-05-12
Ruminants like cows have developed an unusual way of digesting their food: they ingest plants, give them a rough chewing and then swallow the half-chewed mash before regurgitating it repeatedly and continuing to chew. This has clear advantages, as a research team including the University of Göttingen has shown: the regurgitated mushy food contains much less hard grit, sand and dust than the food that they first ingested. This protects the teeth from being ground down during the chewing process. This ...