(Press-News.org) Older buildings tend to leak heat through their walls, requiring much more energy to maintain a comfortable temperature in summer or winter. Those constructed prior to the late 1970s rarely meet today’s more rigorous energy standards. And yet they account for large proportion of the buildings standing today. In the US, about 44% of the residential building stock was built before 1970 and about half of the commercial buildings that exist today were built before the 1980s, which creates a significant need for energy retrofitting to reduce environmental impact. A new industry-academic collaboration between Jefferson and Lightweight Manufacturing will tackle this problem over the coming year by designing textile-based modular “skins” that can easily and inexpensively cover a building’s façade to improve insulation and energy efficiency.
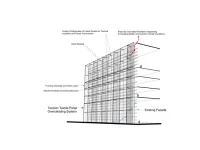
“The concept of using stretched fabrics as spatial cover is an old one,” says associate professor of architecture, Dr. Kihong Ku, who’s leading this new partnership to develop what’s called a building overclad. “Teepees and yurts are historical examples of utilizing the tensile strength of fabrics for their lightweight protective properties. We are trying to take advantage of the scientific and engineering developments in functional textiles to bring more sustainable solutions to an urgent architectural problem.”
Overclad approaches have challenges. For example, Exterior Insulation and Finishing Systems (EIFS), or insulated metal panels, can offer reliable thermal insulation over existing masonry or concrete walls. However, when working with these systems, issues such as condensation may require more extensive recladding which ends up being costly and disruptive to daily building use and operations.
Together with Lightweight Manufacturing, Dr. Ku’s team plans to develop fabric-based overclad panels that can be applied to a building’s exterior. The system would help improve the building’s thermal insulation, while retaining light transmission and airflow. “We are looking at functional textiles with all of these properties so that the building envelope can be sealed,” says Dr. Ku. “However, because we plan to create modular panels, it’s also possible to have portions that leave windows uncovered, or covered with transparent foil material such as ETFE, a sort of translucent plastic sheeting used as an exterior wall.” The panels, designed for mid- and high-rise buildings, would use existing structures as support and be fixed using minimally invasive approaches to avoid compromising the existing waterproofing layer.
Dr. Brian George, director of engineering programs at Jefferson, will lend textile engineering expertise to the project, along with an architecture graduate student, and two undergraduate students who will engage in research and development of the system and its market analysis.
The project won funding through a $69,000 Pennsylvania Department of Economic Development grant, which aims to connect PA industry and manufacturing with local universities for their research expertise and brain trust.
“We are excited to be able to support this research project with Thomas Jefferson University, which aims to utilize tensioned fabric facade systems to make existing buildings more energy efficient and extend their useful life,” says Dirk Cos, president of Lightweight Manufacturing.
By the end of the year, the group hopes to have the prototype fabric and frame system ready to test for resistance to wind and weathering, as well as energy performance. The team will work with fabric producers to identify fabrics that can withstand high levels of sun, wind, rain and general weathering in order to hopefully last twenty or more years. "We may need to get creative to create something that can last as long as roof shingles," says Dr. George.
END
New project to design building skins to retrofit energy-inefficient structures
Researchers will develop prototype modular panels and test for energy savings, resistance to weathering and market feasibility
2023-05-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Heat-loving marine bacteria can help detoxify asbestos
2023-05-15
Asbestos materials were once widely used in homes, buildings, automobile brakes and many other built materials due to their strength and resistance to heat and fire, as well as to their low electrical conductivity. Unfortunately, asbestos exposure through inhalation of small fiber particles has been shown to be highly carcinogenic.
Now, for the first time, researchers from the University of Pennsylvania have shown that extremophilic bacteria from high temperature marine environments can be used to reduce asbestos’ toxicity. The research is published in ...
First-in-human trial of oral drug to remove radioactive contamination begins
2023-05-15
WHAT:
A first-in-human clinical trial of an experimental oral drug for removing radioactive contaminants from inside the body has begun. The trial is testing the safety, tolerability and processing in the body of escalating doses of the investigational drug product HOPO 14-1 in healthy adults. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, is funding the Phase 1 trial, which is sponsored and conducted by SRI International of Menlo Park, California.
Internal radioactive contamination occurs when radioactive ...
Crushed clams, roaming rays: acoustic tags reveal predator interactions
2023-05-15
Clam leases are designated underwater locations used to produce hard clams of all sizes from littlenecks to chowders. Clam production or aquaculture can be a risky business due in part to unwanted marine intruders. Among them, stealthy and highly mobile rays.
The Indian River Lagoon is one key location used for hard clam (Mercenaria mercenaria) aquaculture operations along Florida’s Atlantic coast. Clam fishermen have anecdotally reported seeing rays in clam leases and suspect that their interactions could result in damaged aquaculture gear and crushed clams. After all, ...
EPA's new PFAS rules don’t account for major source of drinking water contamination
2023-05-15
CAPE COD, MASSACHUSETTS – Earlier this year, the US Environmental Protection Agency proposed maximum allowable levels in drinking water for six PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances) – so-called forever chemicals. But the draft standards do not account for half of the PFAS at contaminated sites across the country.
The findings are from a team led by the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) and are published in the journal Environmental Science & Technology.
PFAS are present in fire retardant foams ...
Communities of color disproportionately exposed to PFAS pollution in drinking water
2023-05-15
Embargoed for release: Monday, May 15, 2023, 8:00 AM ET
Boston, MA – People who live in communities with higher proportions of Black and Hispanic/Latino residents are more likely to be exposed to harmful levels of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in their water supplies than people living in other communities, according to a new study led by researchers from Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. The researchers link this finding to the disproportionate siting of sources of PFAS pollution—such ...
WFIRM bioprinting research makes history when it soars to the ISS
2023-05-15
WINSTON-SALEM, NC – MAY 15, 2023 – The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) will make history this month when the first bioprinted solid tissue constructs soar to the International Space Station (ISS) on board the next all private astronaut mission by commercial space leader Axiom Space.
The Axiom Mission 2 (Ax-2) launch by Houston-based Axiom Space is launching from Florida’s Kennedy Space Center. The crew will conduct extensive scientific research experiments including WFIRM’s vascularized tissue research – which won first place in the NASA Vascular Tissue Challenge in 2021.
Liver ...
Smartphone use goes up in city parks, but down in forests
2023-05-15
While a visit to the great outdoors is a common prescription for reducing screen use, a pioneering new study finds that time outdoors doesn’t always reduce smartphone screentime.
The new research, which tracked smartphone activity of 700 study participants for two years, reveals that participants’ smartphone activity actually increased during visits to city parks and other urban green spaces.
With smartphone use rising worldwide, the study clearly identifies a powerful way to reduce screen time: participants who visited nature reserves or forests saw significant declines in screentime over the first three hours, ...
New study finds the placenta, not only the brain, plays a central role in genetic risk of schizophrenia
2023-05-15
BALTIMORE, Md. (May 15, 2023) – More than 100 genes linked to the risk of schizophrenia seem to cause illness because of their role in the placenta rather than in the developing brain, according to a new study led by the Lieber Institute for Brain Development.
Scientists had generally assumed for over a century that genes for schizophrenia risk were principally, if not exclusively, about the brain. But the latest research, just published in Nature Communications, found that the placenta plays a much more significant role in developing illness than previously known.
“The secret of the genetics of schizophrenia has been hiding in plain ...
Wide-ranging strategies needed to eliminate racial and ethnic inequities in stroke care
2023-05-15
Statement Highlights:
In a review of the latest research, few stroke studies addressed racist policies, such as residential segregation, or social determinants of health, such as neighborhood deprivation, walkability or security; food availability; economic stability; education quality; or employment and health insurance, all of which play a role in stroke incidence, care and outcomes.
The statement summarizes research on interventions to address racial and ethnic disparities in stroke care and outcomes.
Additional research is needed to determine ...
Coastal lights trick coral reefs into spawning earlier than they should
2023-05-15
The light pollution caused by coastal cities can trick coral reefs into spawning outside of the optimum times when they would normally reproduce, a new study has found.
Coral broadcast spawning events – in which lunar cycles trigger the release of eggs on certain nights of the year – are critical to the maintenance and recovery of reefs following mass bleaching and other similar events.
However, using a combination of light pollution data and spawning observations, researchers were able to show for the first time that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
[Press-News.org] New project to design building skins to retrofit energy-inefficient structuresResearchers will develop prototype modular panels and test for energy savings, resistance to weathering and market feasibility