(Press-News.org) Ithaca, NY (May 15, 2023) - Today, the Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI) is taking a significant step forward in its mission to bridge the gap between scientific discovery and real-world application. Thanks to a generous $1M gift from the Cane-Bridge Foundation, BTI has launched an innovative translational program called "Project Vault!" to propel plant science discoveries into applications that tackle global life science challenges.
"The Cane-Bridge Foundation's support is vital to accelerate our mission of advancing scientific progress in areas like global health, food security, and environmental sustainability," remarked Julien Fey, BTI's Director of Technology Transfer.
This substantial gift was made possible by Roberto Cañizares, who serves on BTI's Board of Directors and on the board of the Cane-Bridge Foundation.
BTI President David Stern lauded Project Vault! as a visionary concept that can revolutionize the Institute's impact. "This investment marks a key milestone in BTI's journey toward its centennial in 2024. The initiative will expand our research and offer new avenues of opportunity for early-career scientists," he added.
During a recent ceremony at BTI, Cañizares outlined the purpose of the gift. "We hope to rapidly expand BTI's capacity to translate the Institute's groundbreaking research into real-world solutions," he said. "Our goal is to enable the Institute to take more risks in the pursuit of multiple potential applications to ultimately create a self-sustaining model that supports a research culture delivering continuous societal impact and contributes to its financial strength."
With a BS in Engineering Physics from Cornell University, an MS in Applied Economics, and an MBA from the Johnson College of Business, Cañizares built a successful career as a global business leader, focusing on building companies in emerging markets. Cañizares and his wife Gail, who he met at Cornell, founded the Cane-Bridge Foundation to "Propel Transformative Leaps" in non-profit organizations. Their generous donation and Cañizares' commitment to BTI's Board underscore their belief in the power of scientific research to drive global societal improvement.
Paul Debbie, BTI's Director of Research and New Business Development, expressed gratitude for the Foundation's support. "This donation will significantly enlarge our translational science program, enabling us to deliver beneficial technologies to those we serve, including farmers, healthcare patients, and society."
BTI Board Chair Greg Galvin further emphasized Cañizares' contributions, stating, "Rob brings great enthusiasm and engagement to his role on the BTI Board of Directors. This gift is tangible evidence of Rob's leadership and vision for how BTI can benefit our world."
###
About Cane-Bridge Foundation Founded ten years ago to support quantum leaps in non-profit organizations that are ready to make a major change, it helps selected foundations raise themselves to a higher level. In addition to project funds, Cane-Bridge contributes consulting assistance, including guidance to adapt management processes/practices with demonstrated high effectiveness in private industry.
About BTI Opened in 1924, BTI is an independent life sciences research institution located in Ithaca, New York. Its mission is to improve agriculture, protect the environment, and enhance human health. BTI is committed to inspiring and training the next generation of scientists. For more information, please visit BTIscience.org.
For more information, contact: Mike Carroll, Communications Manager, communications@btiscience.org.
END
Translating science into impact: Cane-Bridge Foundation donates $1M to Boyce Thompson Institute for Innovative Translational Research Program
2023-05-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
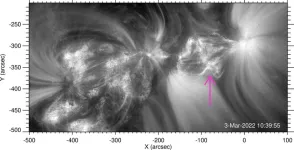
Latest research provides SwRI scientists close-up views of energetic particle jets ejected from the Sun
2023-05-15
SAN ANTONIO — May 15, 2023 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) scientists observed the first close-ups of a source of energetic particles expelled from the Sun, viewing them from just half an astronomical unit (AU), or about 46.5 million miles. The high-resolution images of the solar event were provided by ESA’s Solar Orbiter, a Sun-observing satellite launched in 2020.
“In 2022, the Solar Orbiter detected six recurrent energetic ion injections. Particles emanated along the jets, a signature of magnetic reconnection involving ...
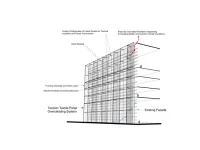
New project to design building skins to retrofit energy-inefficient structures
2023-05-15
Older buildings tend to leak heat through their walls, requiring much more energy to maintain a comfortable temperature in summer or winter. Those constructed prior to the late 1970s rarely meet today’s more rigorous energy standards. And yet they account for large proportion of the buildings standing today. In the US, about 44% of the residential building stock was built before 1970 and about half of the commercial buildings that exist today were built before the 1980s, which creates a significant need for energy retrofitting to reduce environmental impact. A new industry-academic collaboration between Jefferson and Lightweight ...
Heat-loving marine bacteria can help detoxify asbestos
2023-05-15
Asbestos materials were once widely used in homes, buildings, automobile brakes and many other built materials due to their strength and resistance to heat and fire, as well as to their low electrical conductivity. Unfortunately, asbestos exposure through inhalation of small fiber particles has been shown to be highly carcinogenic.
Now, for the first time, researchers from the University of Pennsylvania have shown that extremophilic bacteria from high temperature marine environments can be used to reduce asbestos’ toxicity. The research is published in ...
First-in-human trial of oral drug to remove radioactive contamination begins
2023-05-15
WHAT:
A first-in-human clinical trial of an experimental oral drug for removing radioactive contaminants from inside the body has begun. The trial is testing the safety, tolerability and processing in the body of escalating doses of the investigational drug product HOPO 14-1 in healthy adults. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, is funding the Phase 1 trial, which is sponsored and conducted by SRI International of Menlo Park, California.
Internal radioactive contamination occurs when radioactive ...
Crushed clams, roaming rays: acoustic tags reveal predator interactions
2023-05-15
Clam leases are designated underwater locations used to produce hard clams of all sizes from littlenecks to chowders. Clam production or aquaculture can be a risky business due in part to unwanted marine intruders. Among them, stealthy and highly mobile rays.
The Indian River Lagoon is one key location used for hard clam (Mercenaria mercenaria) aquaculture operations along Florida’s Atlantic coast. Clam fishermen have anecdotally reported seeing rays in clam leases and suspect that their interactions could result in damaged aquaculture gear and crushed clams. After all, ...
EPA's new PFAS rules don’t account for major source of drinking water contamination
2023-05-15
CAPE COD, MASSACHUSETTS – Earlier this year, the US Environmental Protection Agency proposed maximum allowable levels in drinking water for six PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances) – so-called forever chemicals. But the draft standards do not account for half of the PFAS at contaminated sites across the country.
The findings are from a team led by the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) and are published in the journal Environmental Science & Technology.
PFAS are present in fire retardant foams ...
Communities of color disproportionately exposed to PFAS pollution in drinking water
2023-05-15
Embargoed for release: Monday, May 15, 2023, 8:00 AM ET
Boston, MA – People who live in communities with higher proportions of Black and Hispanic/Latino residents are more likely to be exposed to harmful levels of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in their water supplies than people living in other communities, according to a new study led by researchers from Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. The researchers link this finding to the disproportionate siting of sources of PFAS pollution—such ...
WFIRM bioprinting research makes history when it soars to the ISS
2023-05-15
WINSTON-SALEM, NC – MAY 15, 2023 – The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) will make history this month when the first bioprinted solid tissue constructs soar to the International Space Station (ISS) on board the next all private astronaut mission by commercial space leader Axiom Space.
The Axiom Mission 2 (Ax-2) launch by Houston-based Axiom Space is launching from Florida’s Kennedy Space Center. The crew will conduct extensive scientific research experiments including WFIRM’s vascularized tissue research – which won first place in the NASA Vascular Tissue Challenge in 2021.
Liver ...
Smartphone use goes up in city parks, but down in forests
2023-05-15
While a visit to the great outdoors is a common prescription for reducing screen use, a pioneering new study finds that time outdoors doesn’t always reduce smartphone screentime.
The new research, which tracked smartphone activity of 700 study participants for two years, reveals that participants’ smartphone activity actually increased during visits to city parks and other urban green spaces.
With smartphone use rising worldwide, the study clearly identifies a powerful way to reduce screen time: participants who visited nature reserves or forests saw significant declines in screentime over the first three hours, ...
New study finds the placenta, not only the brain, plays a central role in genetic risk of schizophrenia
2023-05-15
BALTIMORE, Md. (May 15, 2023) – More than 100 genes linked to the risk of schizophrenia seem to cause illness because of their role in the placenta rather than in the developing brain, according to a new study led by the Lieber Institute for Brain Development.
Scientists had generally assumed for over a century that genes for schizophrenia risk were principally, if not exclusively, about the brain. But the latest research, just published in Nature Communications, found that the placenta plays a much more significant role in developing illness than previously known.
“The secret of the genetics of schizophrenia has been hiding in plain ...