(Press-News.org) Phosphatases of regenerating liver (PRLs) are a family of enigmatic proteins involved in cell growth and metabolism present in various species. From humans to fruit flies, they play a unique role in the growth of cancerous tumours and the spread of cancer throughout the body. New research emerging from McGill University is contributing to what is known about PRLs, which could potentially become an important tool in the development of cancer-fighting treatments.
Led by Kalle Gehring, a professor in the Department of Biochemistry and founding director of the McGill Centre for Structural Biology, the researchers focused on unravelling the mystery around PRLs. “It's important for us to study PRLs because they are so important in cancer,” said Gehring, “In some cancers such as metastatic colorectal cancer, the proteins are overexpressed up to 300-fold.”
Published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, Prof. Gehring and his colleagues (with data collected at the Canadian Light Source (CLS) at the University of Saskatchewan) confirmed that not only PRLs exist in all kinds of single- and multi-cell animals, but that the role of PRLs in binding magnesium transporters is common among all studied species.
This overexpression of PRLs makes cancer cells more metastatic and drives the spread to other organs. This data could help to further the understanding of how these proteins influence human disease.
“What we learned is that they all bind the magnesium transporters in the same way,” says Gehring. “We're excited because it helps us understand this pathway, and that will reveal new targets for drugs to prevent cancer progression.”
About the study
“Burst kinetics and CNNM binding are evolutionarily conserved properties of phosphatases of regenerating liver” by Kalle Gehring and al. was published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
With files from the Canadian Light Source / Victoria Schramm
END
Tiny proteins found across the animal kingdom play a key role in cancer spread
Discovery about specific proteins shed light on cancer spread
2023-05-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Great inequality in international athletics
2023-05-15
Athletes from less affluent countries need more education on health to prevent injuries during hard training. But, paradoxically, more knowledge can also increase the risk of injury if there is no access to medically trained expertise. This is the conclusion of researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, in a new study on inequality in athletics.
“There were astronomical differences in support resources between juniors from different parts of the world. European competitors had entire medical teams and computer-based analysis programs ...
New DOE portal connects researchers and students with climate science and training opportunities
2023-05-15
The National Virtual Climate Laboratory (NVCL), a comprehensive web portal for climate science projects funded by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science’s Biological and Environmental Research (BER) program, is now available.
The NVCL is a portal for those who have a stake in the climate crisis, such as researchers, students, faculty, and other interested organizations. Portal users will be able to find a wide range of national laboratory experts, programs, projects, activities, ...
Alternating estrogen and anti-estrogen therapies is effective in treating metastatic breast cancer
2023-05-15
LEBANON, NH— Advanced or metastatic estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer is commonly treated with drugs that block the estrogen receptor. However, estrogens that stimulate the receptor can also be effective. Building on their previous studies, researchers at Dartmouth Cancer Center recently concluded a Phase II clinical trial aimed to test the efficacy of alternating between estrogen stimulation and estrogen deprivation in patients with metastatic ER+ breast cancer, and to identify tumor characteristics that predict who might benefit from this strategy. The results, newly published ahead of print in Clinical ...
'Love hormone' guides young songbirds in choice of 'voice coach'
2023-05-15
Oxytocin, the so-called “love hormone,” plays a key role in the process of how a young zebra finch learns to sing by imitating its elders, suggests a new study by neuroscientists at Emory University. Scientific Reports published the findings, which add to the understanding of the neurochemistry of social learning.
“We found that the oxytocin system is involved from an early age in male zebra finches learning song,” says Natalie Pilgeram, first author of the study and an Emory PhD candidate in psychology. “It’s basic science that may lead to insights into the ...
Researchers find compound that combats multidrug-resistant bacteria in less than one hour
2023-05-15
Resistance to antibiotics is a problem that alarms the medical and scientific community. Bacteria resistant to three different classes of antibiotics, known as multi-drug resistant (MDR) bacteria, are far from rare. Some are even resistant to all currently available treatments and are known as pan-drug resistant (PDR). They are associated with dangerous infections and listed by the World Health Organization (WHO) as priority pathogens for drug development with maximum urgency.
An article published in a special issue of the journal Antibiotics highlights a compound with antibacterial activity that presented promising ...
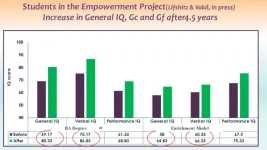
Postsecondary university education improves intelligence of adult students with intellectual disability
2023-05-15
Post-secondary education (PSE) has a potential for improving the IQ of adults with mild intellectual disability (ID), according to a new Bar-Ilan University study.
The study examined the impact of PSE on students with mild ID who study in a university-based program, known as the Empowerment Project, at the Bar-Ilan University Faculty of Education.
The study sample included 24 participants, divided into 12 students with ID who participate in the Empowerment Project and 12 adults with ID with the same background, who did not participate. The results were published in the European Journal of Special Needs Education.
The findings revealed significant IQ improvement ...
With formic acid towards CO2 neutrality
2023-05-15
New synthetic metabolic pathways for fixation of carbon dioxide could not only help to reduce the carbon dioxide content of the atmosphere, but also replace conventional chemical manufacturing processes for pharmaceuticals and active ingredients with carbon-neutral, biological processes. A new study demonstrates a process that can turn carbon dioxide into a valuable material for the biochemical industry via formic acid.
In view of rising greenhouse gas emissions, carbon capture, the sequestration of carbon dioxide from large emission sources, is an ...
Astronomers observe the first radiation belt seen outside of our solar system
2023-05-15
Astronomers have described the first radiation belt observed outside our solar system, using a coordinated array of 39 radio dishes from Hawaii to Germany to obtain high-resolution images. The images of persistent, intense radio emissions from an ultracool dwarf reveal the presence of a cloud of high-energy electrons trapped in the object’s powerful magnetic field, forming a double-lobed structure analogous to radio images of Jupiter’s radiation belts.
“We are actually imaging the magnetosphere of our target by observing the radio-emitting ...
New study reveals widespread presence of environmental DNA in the sky, including allergens and pathogens
2023-05-15
Recently published in PeerJ Life and Environment, researchers successfully use aircraft surveys with novel instrumentation to capture airborne nucleic acids and probe biodiversity in the atmosphere, uncovering surprising findings.
[Clemson, May 2023] - A groundbreaking research article titled "Aircraft Surveys for Air eDNA: Probing Biodiversity in the Sky" unveils a revolutionary approach to studying genetic material in the atmosphere. Scientists have developed a durable and sterilizable probe and supporting system to capture air environmental nucleic acids (eDNA) with full-flow filtration and a high-integrity chamber.
Using this innovative probe, ...
Tetris reveals how people respond to unfair AI
2023-05-15
ITHACA, N.Y. – A Cornell University-led experiment in which two people play a modified version of Tetris revealed that players who get fewer turns perceived the other player as less likable, regardless of whether a person or an algorithm allocated the turns.
Most studies on algorithmic fairness focus on the algorithm or the decision itself, but researchers sought to explore the relationships among the people affected by the decisions.
“We are starting to see a lot of situations in which AI makes decisions on how resources should be distributed among people,” ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
[Press-News.org] Tiny proteins found across the animal kingdom play a key role in cancer spreadDiscovery about specific proteins shed light on cancer spread