(Press-News.org)
A strong link between the extent of deprivation of local authorities in England and their numbers of children going into the care system through the family courts has been uncovered by researchers at Lancaster University.
The study, available online and due to be published in July 2023 in the journal Children & Society, found that for every one unit increase in the standardized Office for National Statistics’ (ONS) English index of multiple area deprivation, the number of children in care proceedings in English family courts increased by around 70%.
The research team analysed data from the English Children and Family Court Advisory and Support Service (CAFCASS) and area deprivation data from the Office for National Statistics (ONS) from 2015 up until 2019.
The study, ‘Area-deprivation, social care spending and the rates of children in care proceedings in local authorities in England’ was undertaken by Dr Steffi Doebler, Professor Karen Broadhurst, Dr Bachar Alrouh and Dr Linda Cusworth.
The researchers also found that government spending on prevention, such as mother and child support, youth clubs, family help and advice centres, make a difference.
Each £1000 increase in social care spend per child, year and local authority has led to a 12% decrease in the rate of children in compulsory family court proceedings.
Lead author Dr Steffi Doebler says: “Spending on prevention makes a real difference but the benefits are often hidden by the very large impact of deprivation.
“Local authorities in deprived areas are doing their best to support vulnerable families, and they spend more of their budgets on social care than in non-deprived areas.
“But local authorities, especially in the most deprived areas, have been severely affected by austerity cuts over the last 13 years and are scrambling to compensate and afford prevention.”
The study warns that Government funds received by local authorities are not enough to offset the ‘devastating effect’ deprivation has had on families and children.
“We see, in highly deprived areas, the severe long-term harms caused by a decade of austerity,” adds Dr Doebler.
The authors conclude that if the UK government is serious about 'levelling up', it needs to urgently reverse its austerity measures, tackle socioeconomic deprivation in local authorities and invest much more funding in preventative social care.
The study was funded by the Nuffield Family Justice Observatory.
END
JMIR Dermatology—the official journal of the International Society of Teledermatology (ISTD)—and the journal’s guest editors welcome submissions to a special theme issue to coincide with the 10th ISTD World Congress held at the 23rd World Congress of Dermatology on July 4 to 7, 2023, in Singapore.
This theme issue will allow attendees of the ISTD World Congress to share their work with a wider audience by disseminating their work in a well-respected, peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
Teledermatology has been increasingly gaining recognition as a means of delivering dermatological ...
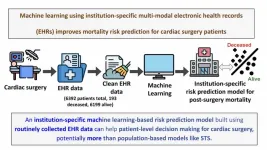
A machine learning-based model that enables medical institutions to predict the mortality risk for individual cardiac surgery patients has been developed by a Mount Sinai research team, providing a significant performance advantage over current population-derived models.
The new data-driven algorithm, built on troves of electronic health records (EHR), is the first institution-specific model for assessing a cardiac patient’s risk prior to surgery, thus allowing health care providers to pursue the best course of action for that individual. The team’s work was described in a study published in The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery ...
Tokyo, Japan – Organic chemistry, the study of carbon-based molecules, underlies not only the science of living organisms, but is critical for many current and future technologies, such as organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays. Understanding the electronic structure of a material’s molecules is key to predicting the material’s chemical properties.
In a study recently published by researchers at the Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo, a machine-learning algorithm was developed to predict the density ...
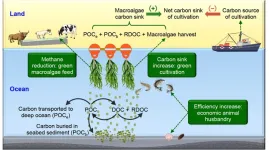
A marine research team led by Professor YAN Qingyun has proposed a method to assess the net carbon sink of marine macroalgae (Gracilaria) cultivation. Then, they calculated the net carbon sink of Gracilaria cultivation in China based on the yield of annual cultivated Gracilaria in the last ten years. Also, the net carbon sink trend of Gracilaria cultivation in the next ten years was predicted by the autoregressive integrated moving average model (ARIMA). Finally, they explored the potential carbon sink increase and methane reduction related to Gracilaria cultivation in China through a scenario analysis.
Their results suggested that the net carbon sink ...
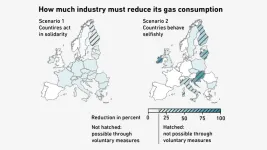
Prior to Putin’s invasion of Ukraine, Europe sourced a great deal of natural gas from Russia. But as a result of EU sanctions on Russia, this supply is no longer there. European countries have scrambled to find and secure new suppliers. But if both the war and these sanctions last into next winter, gas will remain in short supply – especially if next winter is a cold one and people need a lot of gas for heating. There is a distinct possibility that a shortage of gas will mean homes go unheated and will force industry to halt production. As a result, some countries might ...
Korean researchers and an SME have successfully commercialized a light source1) capable of transmitting 25 billion bits per second over long distances for the first time in Korea.
1) Light source: An element that converts electrical signals into optical signals and is manufactured by a compound semiconductor process
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute(ETRI) announced that it has succeeded in commercializing an electro-absorption modulator-integrated laser(EML)2) capable of transmitting data over 30 km at a speed of 25 Gbps with ELDIS Co., Ltd., a III-V semiconductor laser ...
Paris, France, 17 May 2023. The field of coronary drug-coated balloon (DCB) angioplasty looks set to assume growing importance in the years to come and the potential for increased use of these devices in clinical practice is considerable.
DCB catheters became available for coronary use in Europe more than 14 years ago and have become widely used in clinical practice around the world since then. In recent years there has been renewed interest in this therapy linked to the development of novel devices coated with drugs from the limus family and a wider experience in the treatment of de novo lesions. As of today, for coronary use, there are no less ...
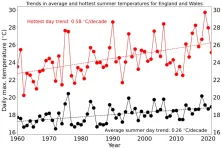
New study analysed data on near-surface air temperatures recorded for North-West Europe over the past 60 years.
The findings show that the maximum temperature of the hottest days is increasing at twice the rate of the maximum temperature of average summer days.
The results highlight the need for urgent action by policy makers to adapt essential infrastructure to the impacts of climate change.
New research led by the University of Oxford has found that climate change is causing the hottest days in North-West Europe to warm at double the rate of average ...
First-generation bioresorbable vascular scaffolds (BVS) may be just as effective as drug-eluting metallic stents, which are currently the standard treatment for heart disease patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
These are significant findings from a global clinical trial led by a researcher from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. The work could lead to advancements and improvements in new BVS technology and future clinical use among interventional cardiologists across the ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Decision-making capabilities of college students – including some graduating this spring – were likely negatively affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, new research suggests.
Students in the small study conducted by researchers at The Ohio State University were less consistent in their decision making during the 2020 fall semester compared to students who had participated in similar research over several previous years.
The researchers compared responses to a hypothetical situation made by students during the pandemic to responses made by students in earlier studies. They found evidence that students in 2020 ...