(Press-News.org) Households whose "heads" score highly for openness and conscientiousness are more likely to make higher charitable donations, according to Chinese study incorporating "Big Five" personality traits
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0284798
Article Title: A study on the influence of personality characteristics on household charitable donation behavior in China
Author Countries: China
Funding: Funding was provided by Shenzhen Key Research Base for Humanities and Social Sciences. The sponsors play an important role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Households whose "heads" score highly for openness and conscientiousness are more likely to make higher charitable donations, according to Chinese study incorporating "Big Five" personality traits
2023-05-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sustainable agriculture is building peace in Colombia
2023-05-17
In areas of Colombia once controlled by guerillas, conflicts over land continue and deforestation has risen considerably. But it’s in these same areas that researchers have found that farmers implementing sustainable land use systems, like agroforestry driven by cocoa (one of the key ingredients of chocolate), has contributed to reducing conflicts.
Deforestation and Conflict
In 2016, the government of Colombia signed a peace treaty with the guerilla group Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC, for its initials in Spanish) and in the following years, forested areas formerly controlled by the FARC saw an influx of other illegal actors, contributing ...
Australian nanomedicine research a ‘milestone’ in the treatment of childhood cancer
2023-05-17
Australian nanomedicine researchers have come up with a new approach to solving a decades-old clinical problem: getting treatment drugs to act selectively on cancer cells in the body. Published this week in the high-impact journal Science Translational Medicine, the research paves the way to safer and more effective treatment options for children with aggressive blood cancers, and potentially other types of cancer as well.
Chemotherapy is the mainstay of treatment for leukaemia, the most common blood cancer in children. However, while chemotherapy can be very effective for certain types of leukaemia, ...
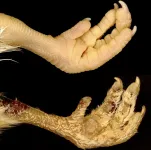
Scales or feathers? It all comes down to a few genes
2023-05-17
Scales, spines, feathers and hair are examples of vertebrate skin appendages, which constitute a remarkably diverse group of micro-organs. Despite their natural multitude of forms, these appendages share early developmental processes at the embryonic stage. Two researchers from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) have discovered how to permanently transform the scales that normally cover the feet of chickens into feathers, by specificially modifying the expression of certain genes. These results, published in the journal Science Advances, open new perspectives for studying mechanisms that have enabled radical evolutionary ...
New study explains how a common virus can cause multiple sclerosis
2023-05-17
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have found further evidence for how the Epstein-Barr virus can trigger multiple sclerosis or drive disease progression. A study published in Science Advances shows that some individuals have antibodies against the virus that mistakenly attack a protein in the brain and spinal cord.
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infects most people early in life and then remains in the body, usually without causing symptoms. The link between EBV and the neurological disease multiple sclerosis (MS) was discovered many years ago and has puzzled ...
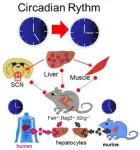
Liver cells control our biological clock
2023-05-17
Organisms rely on a biological clock known as the ‘circadian’ clock to regulate their activity according to the time of day. A central clock, constituted by a group of brain cells — the suprachiasmatic nuclei, or SCN — synchronises the circadian clocks present in all body’s organs, called ‘peripheral’ clocks. Until now, synchronisation of the circadian cycle in mammals was thought to be a one-way mechanism in which the suprachiasmatic nuclei alone synchronized the peripheral ...
Adult friendships can triumph over childhood trauma, even in baboons
2023-05-17
DURHAM, N.C. -- Decades of research show that experiencing traumatic things as a child -- such as having an alcoholic parent or growing up in a tumultuous home -- puts you at risk for poorer health and survival later in life.
But mounting evidence suggests that forging strong social relationships can help mitigate these effects. And not just for people, but for our primate cousins, too.
Drawing on 36 years of data, a new study of nearly 200 baboons in southern Kenya finds that adversity early in life can take years off their lifespan, but strong social bonds with other baboons in adulthood can help ...
Using COVID-19 positive donor hearts may impact post-transplant survival
2023-05-17
Heart transplant recipients receiving organs from active COVID-19 positive donors may have an increased risk of death at six months and one year when compared to those receiving organs from recently recovered COVID-19 patients and COVID-19 negative patients, according to a study published today in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“These early trends should be concerning enough such that heart transplantation centers need to thoroughly evaluate and continue to weigh the risks/benefits of using hearts from active COVID-19 donors,” said Shivank Madan, MD, MHA, lead author of the study and a cardiologist ...
Tick tock – the liver controls the circadian clock
2023-05-17
University of Queensland-led research has revealed liver cells influence the body’s internal circadian clock, which was previously believed to be solely controlled by the brain.
Associate Professor Frédéric Gachon from UQ’s Institute for Molecular Bioscience and Dr Serge Luquet from Université Paris Cité/CNRS in France and their collaborators have demonstrated that mice with transplanted human liver cells had modified circadian rhythms.
Dr Gachon said the ...
University of Colorado data scientists develop rare disease phenopacket standard, tools for global use
2023-05-17
Researchers in the Department of Biomedical Informatics (DBMI) at the University of Colorado School of Medicine have reached a major milestone in developing standards and tools for creating phenopackets that may foster more innovation and advancement in the medical field by allowing health professionals to more easily collect and share data.
A newly-released paper highlights the latest suite of coordinated standards and tools used to collect data related to rare diseases.
The phenopackets, ...
Press Release: ECOG-ACRIN announces the recipients of its 2023 scientific leadership and mentorship awards
2023-05-17
The ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) announces the following cancer researchers as the recipients of the organization’s annual scientific leadership and mentorship awards. Through its Mentoring Program, ECOG-ACRIN formally recognizes outstanding scientific leadership through events and awards that identify, encourage, and recognize investigators in the early years of their careers. The program is expanding in 2023 with the addition of the Remarkable Mentor to Women in Oncology Award.
Young Investigator of the Year
Patrick M. Forde, MBBCh, is the 2023 recipient of the Young Investigator Award, a professional honor to recognize ...