(Press-News.org) About The Study: The findings of this cross-sectional analysis of 2,200 individuals with sickle cell disease (SCD) suggest that employment status, sex, age, and depression are associated with pain frequency. Depression screening for these patients is warranted, especially among those experiencing higher pain frequency and severity. Comprehensive treatment and pain reduction must consider the full experiences of patients with SCD, including impacts on mental health.
Authors: Kelly M. Harris, Ph.D., C.C.C.-S.L.P., of the Washington University in St. Louis School of Medicine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.14070)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.14070?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=051823
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Examining mental health, education, employment, and pain in sickle cell disease
JAMA Network Open
2023-05-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
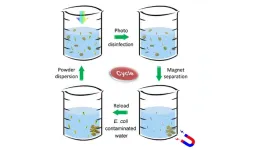
New non-toxic powder uses sunlight to quickly disinfect contaminated drinking water
2023-05-18
At least 2 billion people worldwide routinely drink water contaminated with disease-causing microbes.
Now Stanford University scientists have invented a low-cost, recyclable powder that kills thousands of waterborne bacteria per second when exposed to ordinary sunlight. The discovery of this ultrafast disinfectant could be a significant advance for nearly 30 percent of the world’s population with no access to safe drinking water, according to the Stanford team. Their results are published in a May 18 study in Nature Water.
“Waterborne diseases are responsible for 2 million deaths annually, the majority in children under the age of 5,” said study ...
Some climate-smart agricultural practices may not be so smart
2023-05-18
-Several practices being promoted as climate smart could lead to land use spillovers that change their net impact on climate
-Most evidence is that cover cropping with rye, as done in the US, causes a yield loss. We show that the land use spillovers can then negate most of the climate benefit of cover cropping.
-The method and data we used were made available (as an R package) so that others can apply the same approach to other questions related to land use spillovers END ...
Keeping California’s oil in the ground will improve health but affect jobs
2023-05-18
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — As society reckons with climate change, there’s a growing call to keep fossil fuels right where they are, in the ground. But the impact of curtailing oil production will depend on the policies we implement to achieve this.
An interdisciplinary team of researchers investigated the carbon emissions, labor and health implications of several policies to reduce oil extraction, with a special focus on how the effects vary across different communities in California. Their results, published in Nature Energy, ...
Biodiversity discovery: Unknown species ("dark taxa") drive insect diversity
2023-05-18
Biodiversity loss ranks among the top three risks to humanity, as stated in the 2023 World Economic Forum Global Risks Report. Understanding biodiversity's basic building blocks is essential to monitor changes, identify influencing factors, and implement appropriate policies. However, much of terrestrial animal diversity, including insects, remains unknown or "dark taxa."
For example, the global biodiversity information portal GBIF has nine times more information on birds than insects and arthropods, despite birds only accounting ...
Climate change to push species over abrupt tipping points
2023-05-18
Climate change is likely to abruptly push species over tipping points as their geographic ranges reach unforeseen temperatures, finds a new study led by a UCL researcher.
The new Nature Ecology & Evolution study predicts when and where climate change is likely to expose species across the globe to potentially dangerous temperatures.
The research team from UCL, University of Cape Town, University of Connecticut and University at Buffalo analysed data from over 35,000 species of animals (including mammals, amphibians, reptiles, birds, corals, fish, cephalopods and plankton) and seagrasses from every continent and ocean basin, alongside climate projections running up to 2100.
The ...
Engineering: The house that diapers built
2023-05-18
Up to eight percent of the sand in concrete and mortar used to make a single-story house could be replaced with shredded used disposable diapers without significantly diminishing their strength, according to a study published in Scientific Reports. The authors suggest that disposable diaper waste could be used as a construction material for low-cost housing in low- and middle-income countries.
Disposable diapers are usually manufactured from wood pulp, cotton, viscose rayon, and plastics such as polyester, polyethylene, and polypropylene. ...
Why do Japanese teachers seem unready to teach critical thinking in classrooms?
2023-05-18
Globally, critical thinking (CT) is regarded as a highly desirable cognitive skill that enables a person to question, analyze, and assess an idea or theory from multiple perspectives. CT has become an integral and mandatory part of global educational curricula, but its definition varies across contexts and cultural backgrounds.
To assess the implementation of CT, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) conducts the Teaching and Learning International Survey (TALIS). In a 2018 survey (TALIS 2018), only 12.6% of lower secondary ...
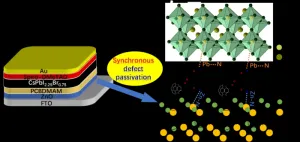
Boosting solar cell energy capture efficiency with a fullerene-derivative interlayer
2023-05-18
Solar cells are a critical component to the transition to renewable energy sources, and enhanced power conversion efficiency (PCE), or amount of power captured with a given amount of sunlight, increases the practicality of solar power in a society with high energy demands. Perovskite solar cells that use all-inorganic perovskite light-absorbing materials are more thermally stable than organic-inorganic hybrid counterparts, but suffer from lower PCE. Researchers have overcome this hurdle in all-inorganic perovskite solar cells ...
Children’s Cancer Research Fund backs cutting-edge leukemia research at UVA
2023-05-18
Children’s Cancer Research Fund has awarded $250,000 to an innovative new approach to treating leukemia – blood cancer – being developed at UVA Cancer Center.
The grant to John H. Bushweller, PhD, of the University of Virginia School of Medicine, is part of the national nonprofit’s efforts to accelerate the development of new and better treatments for difficult-to-treat cancers.
“This funding makes it possible to continue developing a novel approach to treatment for a form of pediatric leukemia with a very poor prognosis,” said Bushweller, of UVA’s Department of Molecular Physiology and Biological Physics. “For ...
Research to improve quality of stroke care is advancing but gaps exist
2023-05-18
INDIANAPOLIS – Every 40 seconds, someone in the U.S. has a stroke. Every 3.5 minutes, someone in the U.S. dies of a stroke. Stroke patients have multifaceted needs, requiring complicated care delivered by multidisciplinary teams.
In the journal Stroke’s annual review of quality improvement advances in stroke care studies, Regenstrief Institute Research Scientist Dawn Bravata, M.D., and colleagues update researchers, clinicians and healthcare administrators on advances in the field, highlighting the challenges of scalability and sustainability.
“Quality improvement exists to ensure that every patient with stroke or at risk of stroke is getting the care ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
[Press-News.org] Examining mental health, education, employment, and pain in sickle cell diseaseJAMA Network Open