(Press-News.org) Up to eight percent of the sand in concrete and mortar used to make a single-story house could be replaced with shredded used disposable diapers without significantly diminishing their strength, according to a study published in Scientific Reports. The authors suggest that disposable diaper waste could be used as a construction material for low-cost housing in low- and middle-income countries.
Disposable diapers are usually manufactured from wood pulp, cotton, viscose rayon, and plastics such as polyester, polyethylene, and polypropylene. The majority are disposed of in landfill or by incineration.
Siswanti Zuraida and colleagues prepared concrete and mortar samples by combining washed, dried, and shredded disposable diaper waste with cement, sand, gravel, and water. These samples were then cured for 28 days. The authors tested six samples containing different proportions of diaper waste to measure how much pressure they could withstand without breaking. They then calculated the maximum proportion of sand that could be replaced with disposable diapers in a range of building materials that would be needed to construct a house with a floorplan area of 36 square metres that complies with Indonesian building standards.
The authors found that disposable diaper waste could replace up to ten percent of the sand needed for concrete used to form columns and beams in a three-story house. This proportion increased to 27 percent of sand needed for concrete columns and beams in a single-story house. Up to 40 percent of the sand needed for mortar in partition walls can be replaced with disposable diapers, compared to nine percent of the sand in mortar for floors and garden paving. Together, up to eight percent of the sand in all of the concrete and mortar building materials required to build a single-story house with a floorplan of 36 square metres can be replaced with disposable diaper waste — equivalent to 1.7 cubic metres of waste.
The authors note that wider implementation of their findings would require the involvement of stakeholders in government and waste treatment in developing processes for the large-scale collection, sanitising, and shredding of diaper waste. Additionally, building regulations would need to be modified to allow the use of diaper waste as a construction material.
###
Article details
Application of non-degradable waste as building material for low-cost housing
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-32981-y
Corresponding Author:
Siswanti Zuraida
The University of Kitakyushu, Japan
Email: b0dbb409@eng.kitakyu-u.ac.jp; siswanti.zuraida@gmail.com
Please link to the article in online versions of your report (the URL will go live after the embargo ends): https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-32981-y
END
Engineering: The house that diapers built
2023-05-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Why do Japanese teachers seem unready to teach critical thinking in classrooms?
2023-05-18
Globally, critical thinking (CT) is regarded as a highly desirable cognitive skill that enables a person to question, analyze, and assess an idea or theory from multiple perspectives. CT has become an integral and mandatory part of global educational curricula, but its definition varies across contexts and cultural backgrounds.
To assess the implementation of CT, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) conducts the Teaching and Learning International Survey (TALIS). In a 2018 survey (TALIS 2018), only 12.6% of lower secondary ...
Boosting solar cell energy capture efficiency with a fullerene-derivative interlayer
2023-05-18
Solar cells are a critical component to the transition to renewable energy sources, and enhanced power conversion efficiency (PCE), or amount of power captured with a given amount of sunlight, increases the practicality of solar power in a society with high energy demands. Perovskite solar cells that use all-inorganic perovskite light-absorbing materials are more thermally stable than organic-inorganic hybrid counterparts, but suffer from lower PCE. Researchers have overcome this hurdle in all-inorganic perovskite solar cells ...
Children’s Cancer Research Fund backs cutting-edge leukemia research at UVA
2023-05-18
Children’s Cancer Research Fund has awarded $250,000 to an innovative new approach to treating leukemia – blood cancer – being developed at UVA Cancer Center.
The grant to John H. Bushweller, PhD, of the University of Virginia School of Medicine, is part of the national nonprofit’s efforts to accelerate the development of new and better treatments for difficult-to-treat cancers.
“This funding makes it possible to continue developing a novel approach to treatment for a form of pediatric leukemia with a very poor prognosis,” said Bushweller, of UVA’s Department of Molecular Physiology and Biological Physics. “For ...
Research to improve quality of stroke care is advancing but gaps exist
2023-05-18
INDIANAPOLIS – Every 40 seconds, someone in the U.S. has a stroke. Every 3.5 minutes, someone in the U.S. dies of a stroke. Stroke patients have multifaceted needs, requiring complicated care delivered by multidisciplinary teams.
In the journal Stroke’s annual review of quality improvement advances in stroke care studies, Regenstrief Institute Research Scientist Dawn Bravata, M.D., and colleagues update researchers, clinicians and healthcare administrators on advances in the field, highlighting the challenges of scalability and sustainability.
“Quality improvement exists to ensure that every patient with stroke or at risk of stroke is getting the care ...
High-temperature shock synthesis of high-entropy alloy nanoparticles for catalysis
2023-05-18
High-temperature shock (HTS) is an emerging synthesis method with kinetics-dominated non-equilibrium characteristics, which can achieve an ultrafast heating/cooling rate of ~10^5 K/s and a peak temperature larger than ~3000 K within a time scale of seconds or milliseconds, and is widely used in the preparation of high entropy content, thermodynamic metastable phase and defect-rich materials. Amongst these significant advances, nanoscale high entropy alloys (HEA) are particularly prominent in heterogeneous catalytic reactions with remarkable ...
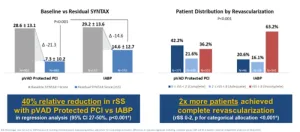
Analysis showcases potential for more complete revascularizations with Impella compared to IABP during HRPCI
2023-05-18
DANVERS, Mass., May 18, 2023 – Abiomed, part of Johnson & Johnson MedTech[1], announces results of a third-party analysis showing that utilizing Impella during high-risk percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) procedures may help physicians achieve a more complete revascularization compared to high-risk PCIs supported using an intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP). Previous studies have shown that a more complete revascularization can lead to longer survival[2],[3], a greater reduction in heart failure and angina symptoms[4], and an improved quality of life for the patient[5].
This analysis shows ...
Novel high-efficiency assay promises rapid mitochondrial disease diagnosis
2023-05-18
The gene ECHS1 encodes for enoyl-CoA hydratase short-chain 1, a mitochondrial enzyme involved in branched-chain amino acid and fatty acid metabolism. Rare inherited mutations in the ECHS1 lead to mitochondrial ECHS1 deficiency, resulting in the disruption of the metabolism of the essential amino acid valine and accumulation of valine intermediates.
In fact, ECHS1 is one of the most common causative genes of mitochondrial diseases. These mutant enzymes also cause brain lesions and severe delays in a child’s psychomotor development, along with elevating blood lactate levels. ECHS1 variants have been reported globally, and many disease-causing ...
A new tool for deforestation detection
2023-05-18
Every second, the planet loses a stretch of forest equivalent to a football field due to
logging, fires, insect infestation, disease, wind, drought, and other factors. In a recently published study, researchers from the U.S. Geological Survey Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center presented a comprehensive strategy to detect when and where forest disturbance happens at a large scale and provide a deeper understanding of forest change.
The study was published on Feb. 28 in the Journal of Remote Sensing.
“Our strategy leads to more accurate land cover ...
To avoid a battery crisis, more of us should share small, lightweight EVs
2023-05-18
Most global scenarios and governmental targets for decarbonizing the transport sector consider battery-powered electric vehicles as a main part of the solution. Enormous amounts of raw materials are needed to build enough batteries and ensure a transition to low-emission vehicles.
Access to lithium is critical, as it is used in all types of EV batteries.
Future demand needs to decrease
“It seems very likely we'll have a shortage. The key lies in the demand. The demand needs to decrease to avoid long-term supply problems,” ...
Space missions set to improve solar storm forecasts
2023-05-18
Satellites launched into outer space could send back improved warnings of dangerous solar storms thanks to a breakthrough in the way scientists use space weather measurements.
Experts from the University of Reading have found that using satellite data that is less reliable but is returned to Earth rapidly can be used to improve the accuracy of solar wind forecasts - which are harmful streams of charged particles sent from the sun - by nearly 50 per cent.
Their research, published today (Thursday, 18 May) in Space Weather, ...