(Press-News.org) New research from Queen Mary University of London shows that only around 13% of global methane emissions are regulated, despite methane emissions causing at least 25% of current global warming.
The global review, published on 19 May in One Earth, also found that little is known about the effectiveness of the policies that exist, with potentially unrepresentative methane emission estimations used rather than actual measurements. Inaccurate estimations can also mean the issue is taken less seriously by decision-makers by masking its severity.
The researchers argue that the lack of regulation and clarity into their impact must urgently be addressed if we are to meet our global climate targets. The review suggests a consistent approach worldwide with robust quantification and reporting could unlock new opportunities to drastically reduce global warming levels.
To meet the Paris Agreement 1.5°C objective, man-made methane emissions should be reduced by at least 40-45% by 2030, compared to the 2020 levels. Methane mitigation is not only a cost-effective strategy to reduce global warming but could also improve the air quality. Today methane emissions are increasing faster than at any time since the 1980s.
This global review of methane policies is the first to systematically look at all major man-made emission sources, agriculture, energy and waste. Researchers focused on 281 policies worldwide, 255 of them currently in force, that aim to monitor and reduce methane emissions examining the geographical coverage, strength and effectiveness of the policies.
90% of identified national policies have been adopted in three regions: North America (39%), Europe (30%) and Asia Pacific (21%). Globally, the research shows there has been a gradual increase in methane policies since 1974. But fossil methane policies, e.g., targeting emissions from coal, oil and gas sectors tend to be less stringent than those targeting biogenic methane sources, especially in the waste sector.
In jurisdictions with fossil methane policies in place, further mitigation opportunities include emissions further along the supply chain e.g. emissions from Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) carrier ships, which were investigated by a team of QMUL researchers led by Dr Balcombe.
One of the main challenges to measuring methane emissions is accurately identifying and quantifying sources. Developing and using technologies such as satellites to monitor methane emissions can help policymakers with measurement, verification, compliance and detection of super-emitters. Introducing policies with greater policy coverage, mitigation solutions including for major sources, and measurable objectives could lead to a significant methane emissions reduction.
Maria Olczak, lead researcher on this project from Queen Mary University of London, said: “Methane reduction is still perceived as a choice rather than a necessary step alongside CO2 reduction to combat global warming. And with so many different sources, there needs to be stronger social support and the political will to act.
“Our review highlights the value of setting policies that are predictable and clear for the industry. They will aid effective investment decisions aligned with the long-term climate mitigation goals, including the decrease in emission intensity and in production across developed and developing economies.”
Dr Paul Balcombe, study author and Senior Lecturer in Chemical Engineering at Queen Mary, said: “It’s shocking to see that most methane emissions aren’t regulated when they contribute heavily to global warming today, although accurately monitoring emissions is not easy. Our chances of reaching global climate targets are slim if this goes unchecked.
“The good news is that there’s an enormous opportunity to limit warming in the short term if we act fast to get on top of methane emissions. We urgently need tighter regulation on better monitoring of methane and concrete actions towards reduction measures.”
Andris Piebalgs, study author, part-time Professor at the Florence School of Regulation and a former EU Commissioner for Energy, said: “Over the last few years, we have seen growing attention to methane thanks to multilateral initiatives such as the International Methane Emissions Observatory and the Global Methane Pledge. The European Union and the US EPA are now working to finalise ambitious regulations targeting methane emissions in the energy sector. I hope that the upcoming COP28 and the first Global Stocktake will make the policymakers across the world realise that methane mitigation is an effective way to enhance their climate commitments.”
END
Scientists urge crackdown on methane emissions with only 13% regulated
2023-05-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Novel gene-editing strategy leverages unusual genetic alteration to block HIV spread in cells
2023-05-19
(Philadelphia, PA) – Genetic alterations that give rise to a rare, fatal disorder known as MOGS-CDG paradoxically also protect cells against infection by viruses. Now, scientists at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University have harnessed this unusual protective ability in a novel gene-editing strategy aimed at eliminating HIV-1 infection with no adverse effects on cell mortality.
The new approach, described online April 28 in the journal Molecular Therapy – Nucleic Acids, is based on a combination of two gene-editing constructs, one that ...
Perceived influence of incentives on COVID-19 vaccination decision-making and trust
2023-05-19
About The Study: This survey study found that although there has been substantial policy attention around incentivizing COVID-19 vaccination, fewer than 1 in 10 vaccinated individuals in a nationally representative sample of U.S. adults reported receiving an incentive. Most vaccinated respondents reported that an incentive did not make a difference in their decision-making to get the COVID-19 vaccine.
Authors: Laura J. Faherty, M.D., M.P.H., M.S.H.P., of the RAND Corporation in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the ...
Estimated pediatric hospitalizations and school absenteeism associated with accelerated COVID-19 bivalent booster vaccination
2023-05-19
About The Study: In this decision analytical model, increased uptake of bivalent booster vaccination among eligible age groups was associated with decreased hospitalizations and school absenteeism in the pediatric population. These findings suggest that although COVID-19 prevention strategies often focus on older populations, the benefits of booster campaigns for children may be substantial.
Authors: Alison P. Galvani, Ph.D., of the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
COVID-19 booster vaccination in early pregnancy and surveillance for spontaneous abortion
2023-05-19
About The Study: In this case-control surveillance study of more than 100,000 pregnancies, COVID-19 booster vaccination in pregnancy was not associated with spontaneous abortion. These findings support the safety of recommendations for COVID-19 booster vaccination, including in pregnant populations.
Authors: Elyse O. Kharbanda, M.D., M.P.H., of HealthPartners Institute in Minneapolis, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.14350)
Editor’s ...
New study finds COVID-19 mRNA booster vaccinations in early pregnancy did not increase miscarriage risk
2023-05-19
HealthPartners Institute researchers have published new data in JAMA Network Open that shows monovalent COVID-19 booster vaccinations administered in early pregnancy (before 20 weeks’ gestation) were not associated with miscarriage. The research adds to the growing understanding about the safety of COVID-19 booster vaccinations among people who are pregnant.
The researchers analyzed data from more than 100,000 pregnancies between six and 19 weeks’ gestation from eight large health systems participating in the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD). The data was collected between Nov. ...
Synthetic biology: proteins set vesicles in motion
2023-05-19
Biophysicists have designed a new cell-like transport system that represents an important milestone on the road to artificial cells.
Creating artificial cells with life-like characteristics out of a minimal set of components is a major goal of synthetic biology. Autonomous motion is a key capability here, and one that is difficult to reproduce in the test tube. A team led by physicist Erwin Frey, Professor of Statistical and Biological Physics at LMU, and Petra Schwille from the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry, has now made ...
New subtypes identified in difficult-to-treat ovarian cancer – Potential for discovering new treatments
2023-05-19
Every year, more than 40,000 women die of ovarian cancer in Europe. Ovarian cancer is a genetically very heterogeneous disease, which makes it exceptionally difficult to study and treat. The prognosis is particularly poor in ovarian high grade serous carcinoma (HGSC), a subtype of ovarian cancer. Less than 40% of patients with this subtype survive five years after their diagnosis.
The researchers were able to classify HGSC tumours into three groups on the basis of genomic changes. The groups differ in the intracellular signalling pathways, the ways in which the tumours grow, and response ...
Hyperpolarization: Multi-million funding for joint Collaborative Research Centre of Leipzig University and Chemnitz University of Technology
2023-05-19
The Collaborative Research Centre, to be known as HYP*MOL, will bring together 29 professors and early career researchers from both universities, as well as other external research partners, to study electron and nuclear spin hyperpolarization in molecular systems.
“This funding is both a cause for celebration and a great incentive for everyone involved,” says Professor Eva Inés Obergfell, Rector of Leipzig University. “Hyperpolarization is an exciting and rapidly evolving field of research. I believe that our research team will contribute new insights that will be appreciated at an international level.” Leipzig University is now involved ...
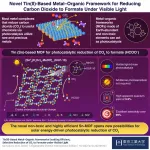
Novel tin-based metal–organic frameworks for reducing carbon dioxide to formate
2023-05-19
The never-ending demand for carbon-rich fuels to drive the economy keeps adding more and more carbon dioxide (CO2) to the atmosphere. While efforts are being made to reduce CO2 emissions, that alone cannot counter the adverse effects of the gas already present in the atmosphere. So, scientists have come up with innovative ways to use existing atmospheric CO2 by transforming it into useful chemicals such as formic acid (HCOOH) and methanol. A popular method for carrying out such conversions is to use visible ...
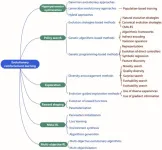
Evolutionary reinforcement learning promises further advances in machine learning
2023-05-19
Evolutionary reinforcement learning is an exciting frontier in machine learning, combining the strengths of two distinct approaches: reinforcement learning and evolutionary computation. In evolutionary reinforcement learning, an intelligent agent learns optimal strategies by actively exploring different approaches and receiving rewards for successful performance. This innovative paradigm combines reinforcement learning's trial-and-error learning with evolutionary algorithms' ability to mimic natural selection, ...