(Press-News.org) Enzymes are the molecule factories in biological cells. However, which basic molecular building blocks they use to assemble target molecules is often unknown and difficult to measure. An international team including bioinformaticians from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) has now taken an important step forward in this regard: Their AI method predicts with a high degree of accuracy whether an enzyme can work with a specific substrate. They now present their results in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
Enzymes are important biocatalysts in all living cells: They facilitate chemical reactions, through which all molecules important for the organism are produced from basic substances (substrates). Most organisms possess thousands of different enzymes, with each one responsible for a very specific reaction. The collective function of all enzymes makes up the metabolism and thus provides the conditions for the life and survival of the organism.
Even though genes which encode enzymes can easily be identified as such, the exact function of the resultant enzyme is unknown in the vast majority – over 99% – of cases. This is because experimental characterisations of their function – i.e. which starting molecules a specific enzyme converts into which concrete end molecules – is extremely time-consuming.
Together with colleagues from Sweden and India, the research team headed by Professor Dr Martin Lercher from the Computational Cell Biology research group at HHU has developed an AI-based method for predicting whether an enzyme can use a specific molecule as a substrate for the reaction it catalyses.
Professor Lercher: “The special feature of our ESP (“Enzyme Substrate Prediction”) model is that we are not limited to individual, special enzymes and others closely related to them, as was the case with previous models. Our general model can work with any combination of an enzyme and more than 1,000 different substrates.”
PhD student Alexander Kroll, lead author of the study, has developed a so-called Deep Learning model in which information about enzymes and substrates was encoded in mathematical structures known as numerical vectors. The vectors of around 18,000 experimentally validated enzyme-substrate pairs – where the enzyme and substrate are known to work together – were used as input to train the Deep Learning model.
Alexander Kroll: “After training the model in this way, we then applied it to an independent test dataset where we already knew the correct answers. In 91% of cases, the model correctly predicted which substrates match which enzymes.”
This method offers a wide range of potential applications. In both drug research and biotechnology it is of great importance to know which substances can be converted by enzymes. Professor Lercher: “This will enable research and industry to narrow a large number of possible pairs down to the most promising, which they can then use for the enzymatic production of new drugs, chemicals or even biofuels.”
Kroll adds: “It will also enable the creation of improved models to simulate the metabolism of cells. In addition, it will help us understand the physiology of various organisms – from bacteria to people.”
Alongside Kroll and Lercher, Professor Dr Martin Engqvist from the Chalmers University of Technology in Gothenburg, Sweden, and Sahasra Ranjan from the Indian Institute of Technology in Mumbai were also involved in the study. Engqvist helped design the study, while Ranjan implemented the model which encodes the enzyme information fed into the overall model developed by Kroll.
Original publication:
Alexander Kroll, Sahasra Ranjan, Martin K. M. Engqvist, Martin J. Lercher, The substrate scopes of enzymes: a general prediction model based on machine and deep learning. Nature Communications (2023).
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-38347-2
END
AI predicts the function of enzymes
Bioinformatics: Publication in Nature Communications
2023-05-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Video games and education: five steps for choosing the perfect classroom game
2023-05-22
Minecraft is officially the most played video game in history. Despite been 12 years old, the public does not seem to have lost interest: over 175 million people play Minecraft at least once a month. The number of players of this open-world or sandbox building game, which provides virtually unlimited possibilities for creation, keeps growing, and this is to a great extent thanks to its educational potential. According to Microsoft data, Minecraft Education Edition has over 35 million game licences. And this is just one of the many ways in which it can be ...
Ukraine hospital improving emergency cardiovascular care during national crisis
2023-05-22
The Clinical Hospital of Emergency Services, a municipal hospital serving the community of Dnipro, in Ukraine, is the first in the country to take part in the American College of Cardiology’s Global Quality Solutions program. The hospital joins the program in an effort to improve heart attack care by reducing heart attack related deaths and saving lives in their community.
“When the war started, myself and others on my team decided to stay at work to do our best to help our people, soldiers, neighbors and relatives to survive. But we decided it was not enough to only maintain, but that ...
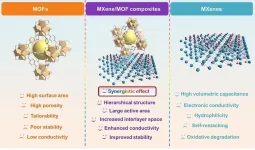
Metal−organic frameworks meet MXene: New opportunities for electrochemical application
2023-05-22
They published their work in Energy Material Advances.
"The investigation of MXene/MOF hybrid materials with high electrochemical performance is important," said paper author Huan Pang, professor with the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University. "Currently, MXene/MOF hybrid materials have received increasing attention in energy-related fields."
Pang explained the motivations for designing MXene/MOF hybrid materials. Firstly, MXenes with numerous negatively charged surface groups can be employed as a valid substrate to support the growth of MOFs, thus not ...
A guide through the genome
2023-05-22
Plants show enormous variety in traits relevant to breeding, such as plant height, yield and resistance to pests. One of the greatest challenges in modern plant research is to identify the differences in genetic information that are responsible for this variation. A research team led by the "Crop Yield" working group at the Institute for Molecular Physiology at Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) and the Carnegie Institution of Science at Stanford has now developed a method to identify precisely these special differences in genetic information. Using the example of maize, they demonstrate the great potential of their method in the journal Genome Biology and present ...
How plants use sugar to produce roots
2023-05-22
Along with sugar reallocation, a basic molecular mechanism within plants controls the formation of new lateral roots. An international team of plant biologists has demonstrated that it is based on the activity of a certain factor, the target of rapamycin (TOR) protein. A better understanding of the processes that regulate root branching at the molecular level could contribute to improving plant growth and therefore crop yields, according to research team leader Prof. Dr Alexis Maizel of the Centre for Organismal Studies at Heidelberg University.
Good root growth ensures that plants can absorb sufficient ...
Dirty air linked with premature death in patients with heart failure
2023-05-22
Prague, Czechia – 22 May 2023: Heart failure patients are at increased risk of dying from their condition on polluted days and up to two days afterwards, according to research presented today at Heart Failure 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“The findings indicate that reducing air pollution has the potential to prevent worsening heart failure,” said study author Dr. Lukasz Kuzma of the Medical University of Bialystok, Poland. “Protecting ...
Eu3+-Bi3+ codoping double perovskites for single-component white-light-emitting diodes
2023-05-22
They published their work on May. 15 in Energy Material Advances.
"With lead-halide perovskites reaching a mature research stage approaching product marketing, concerns remain about the materials' stability and the toxicity of lead-based salts." said paper author Hongwei Song, professor at College of Electronic Science and Engineering, Jilin University. Double perovskites with Cs2AgInCl6 composition, often doped with various elements, have been in the spotlight owing to their intriguing optical properties, namely, ...
ROS-Industrial Americas Consortium celebrates 10th annual meeting at Automate 2023
2023-05-22
San Antonio, Texas – May 22 ,2023 – The ROS-Industrial Americas Consortium, a project dedicated to advancing open-source robotics for manufacturing and industry, will celebrate its 10th anniversary on May 25 at its annual meeting in Detroit.
The event will correspond with the Automate 2023 show, the largest automation showcase in North America, creating an exciting atmosphere for ROS-Industrial members to reflect on the organization’s history while also setting the stage for innovation in the years to come.
The ROS-Industrial open-source project began as a collaboration among Yaskawa Motoman Robotics, Southwest Research Institute ...
ETRI lays the groundwork for convenient and safe drone flight
2023-05-22
The lack of a single communication standard among drone makers has made it difficult for information to be shared between drones, but a Korean research team has found a solution.
The Korea Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) announced that four contributions related to the ‘Unmanned Aircraft Area Network’ were established as international standards at the International Organization for Standardization (ISO*) meeting in Vienna, Austria.
* ISO/IEC JTC1/SC6(communication and information exchange between systems)
The technology ...
The diagnosis of heart failure is more often missed than made especially for women
2023-05-22
Prague, Czechia – 22 May 2023: The diagnosis of heart failure is usually missed, denying patients treatments that could improve wellbeing and reduce mortality. That’s the finding from a late breaking science presentation today at Heart Failure 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“For patients with heart failure, lifestyle advice, medicines and devices can improve symptoms, reduce morbidity and prolong life but this requires someone ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
[Press-News.org] AI predicts the function of enzymesBioinformatics: Publication in Nature Communications