(Press-News.org) A University of Minnesota Twin Cities-led team has developed a first-of-its-kind, breakthrough method that makes it easier to create high-quality metal oxide thin films out of “stubborn” metals that have historically been difficult to synthesize in an atomically precise manner. This research paves the way for scientists to develop better materials for various next-generation applications including quantum computing, microelectronics, sensors, and energy catalysis.
The researchers’ paper is published in Nature Nanotechnology, a peer-reviewed, scientific journal run by Nature Publishing Group.
“This is truly remarkable discovery, as it unveils an unparalleled and simple way for navigating material synthesis at the atomic scale by harnessing the power of epitaxial strain,” said Bharat Jalan, senior author on the paper and a professor and Shell Chair in the University of Minnesota Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science. “This breakthrough represents a significant advancement with far-reaching implications in a broad range of fields. Not only does it provide a means to achieve atomically-precise synthesis of quantum materials, but it also holds immense potential for controlling oxidation-reduction pathways in various applications, including catalysis and chemical reactions occurring in batteries or fuel cells.”
“Stubborn” metals oxides, such as those based on ruthenium or iridium, play a crucial role in numerous applications in quantum information sciences and electronics. However, converting them into thin films has been a challenge for researchers due to the inherent difficulties in oxidizing metals using high-vacuum processes.
The fabrication of these materials has perplexed materials scientists for decades. While some researchers have successfully achieved oxidation, the methods used thus far have been costly, unsafe, or have resulted in poor material quality.
The University of Minnesota researchers’ solution? Give it a stretch.
While attempting to synthesize metal oxides using conventional molecular beam epitaxy, a low-energy technique that generates single layers of material in an ultra-high vacuum chamber, the researchers stumbled upon a groundbreaking revelation. They found that incorporating a concept called "epitaxial strain"—effectively stretching the metals at the atomic level—significantly simplifies the oxidation process of these stubborn metals.
“This enables the creation of technologically important metal oxides out of stubborn metals in ultra-high vacuum atmospheres, which has been a longstanding problem,” said Sreejith Nair, first author of the paper and a University of Minnesota chemical engineering Ph.D. student. “The current synthesis approaches have limits, and we need to find new ways to push those limits further so that we can make better quality materials. Our new method of stretching the material at the atomic scale is one way to improve the performance of the current technology.”
Although the University of Minnesota team used iridium and ruthenium as examples in this paper, their method has the potential to generate atomically-precise oxides of any hard-to-oxidize metal. With this groundbreaking discovery, the researchers aim to empower scientists worldwide to synthesize these novel materials.
The researchers worked closely with collaborators at Auburn University, the University of Delaware, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Argonne National Laboratory, and fellow University of Minnesota Department of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science Professor Andre Mkhoyan’s lab to verify their method.
“When we looked at these metal oxide films very closely using very powerful electron microscopes, we captured the arrangements of the atoms and determined their types,” Mkhoyan explained. “Sure enough, they were nicely and periodically arranged as they should be in these crystalline films.”
This research was funded primarily by the United States Department of Energy (DOE), the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR), and the University of Minnesota’s Materials Research Science and Engineering Center (MRSEC).
In addition to Jalan, Nair, and Mkhoyan, the research team included University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers Zhifei Yang, Dooyong Lee, and Silu Guo; Brookhaven National Laboratory researcher Jerzy Sadowski; Auburn University researchers Spencer Johnson, Ryan Comes, and Wencan Jin; University of Delaware researchers Abdul Saboor and Anderson Janotti; and Argonne National Laboratory researchers Yan Li and Hua Zhou. Parts of the work were carried out at the University of Minnesota’s Characterization Facility.
END
Stretching metals at the atomic level allows researchers to create important materials for quantum, electronic, and spintronic applications
New technique paves the way for easy oxidation of historically “stubborn” metals
2023-05-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI predicts the function of enzymes
2023-05-22
Enzymes are the molecule factories in biological cells. However, which basic molecular building blocks they use to assemble target molecules is often unknown and difficult to measure. An international team including bioinformaticians from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) has now taken an important step forward in this regard: Their AI method predicts with a high degree of accuracy whether an enzyme can work with a specific substrate. They now present their results in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
Enzymes are important biocatalysts in all living cells: They facilitate chemical reactions, through which all molecules ...
Video games and education: five steps for choosing the perfect classroom game
2023-05-22
Minecraft is officially the most played video game in history. Despite been 12 years old, the public does not seem to have lost interest: over 175 million people play Minecraft at least once a month. The number of players of this open-world or sandbox building game, which provides virtually unlimited possibilities for creation, keeps growing, and this is to a great extent thanks to its educational potential. According to Microsoft data, Minecraft Education Edition has over 35 million game licences. And this is just one of the many ways in which it can be ...
Ukraine hospital improving emergency cardiovascular care during national crisis
2023-05-22
The Clinical Hospital of Emergency Services, a municipal hospital serving the community of Dnipro, in Ukraine, is the first in the country to take part in the American College of Cardiology’s Global Quality Solutions program. The hospital joins the program in an effort to improve heart attack care by reducing heart attack related deaths and saving lives in their community.
“When the war started, myself and others on my team decided to stay at work to do our best to help our people, soldiers, neighbors and relatives to survive. But we decided it was not enough to only maintain, but that ...
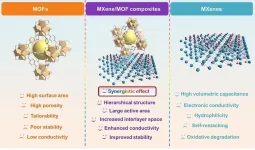
Metal−organic frameworks meet MXene: New opportunities for electrochemical application
2023-05-22
They published their work in Energy Material Advances.
"The investigation of MXene/MOF hybrid materials with high electrochemical performance is important," said paper author Huan Pang, professor with the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University. "Currently, MXene/MOF hybrid materials have received increasing attention in energy-related fields."
Pang explained the motivations for designing MXene/MOF hybrid materials. Firstly, MXenes with numerous negatively charged surface groups can be employed as a valid substrate to support the growth of MOFs, thus not ...
A guide through the genome
2023-05-22
Plants show enormous variety in traits relevant to breeding, such as plant height, yield and resistance to pests. One of the greatest challenges in modern plant research is to identify the differences in genetic information that are responsible for this variation. A research team led by the "Crop Yield" working group at the Institute for Molecular Physiology at Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) and the Carnegie Institution of Science at Stanford has now developed a method to identify precisely these special differences in genetic information. Using the example of maize, they demonstrate the great potential of their method in the journal Genome Biology and present ...
How plants use sugar to produce roots
2023-05-22
Along with sugar reallocation, a basic molecular mechanism within plants controls the formation of new lateral roots. An international team of plant biologists has demonstrated that it is based on the activity of a certain factor, the target of rapamycin (TOR) protein. A better understanding of the processes that regulate root branching at the molecular level could contribute to improving plant growth and therefore crop yields, according to research team leader Prof. Dr Alexis Maizel of the Centre for Organismal Studies at Heidelberg University.
Good root growth ensures that plants can absorb sufficient ...
Dirty air linked with premature death in patients with heart failure
2023-05-22
Prague, Czechia – 22 May 2023: Heart failure patients are at increased risk of dying from their condition on polluted days and up to two days afterwards, according to research presented today at Heart Failure 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“The findings indicate that reducing air pollution has the potential to prevent worsening heart failure,” said study author Dr. Lukasz Kuzma of the Medical University of Bialystok, Poland. “Protecting ...
Eu3+-Bi3+ codoping double perovskites for single-component white-light-emitting diodes
2023-05-22
They published their work on May. 15 in Energy Material Advances.
"With lead-halide perovskites reaching a mature research stage approaching product marketing, concerns remain about the materials' stability and the toxicity of lead-based salts." said paper author Hongwei Song, professor at College of Electronic Science and Engineering, Jilin University. Double perovskites with Cs2AgInCl6 composition, often doped with various elements, have been in the spotlight owing to their intriguing optical properties, namely, ...
ROS-Industrial Americas Consortium celebrates 10th annual meeting at Automate 2023
2023-05-22
San Antonio, Texas – May 22 ,2023 – The ROS-Industrial Americas Consortium, a project dedicated to advancing open-source robotics for manufacturing and industry, will celebrate its 10th anniversary on May 25 at its annual meeting in Detroit.
The event will correspond with the Automate 2023 show, the largest automation showcase in North America, creating an exciting atmosphere for ROS-Industrial members to reflect on the organization’s history while also setting the stage for innovation in the years to come.
The ROS-Industrial open-source project began as a collaboration among Yaskawa Motoman Robotics, Southwest Research Institute ...
ETRI lays the groundwork for convenient and safe drone flight
2023-05-22
The lack of a single communication standard among drone makers has made it difficult for information to be shared between drones, but a Korean research team has found a solution.
The Korea Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) announced that four contributions related to the ‘Unmanned Aircraft Area Network’ were established as international standards at the International Organization for Standardization (ISO*) meeting in Vienna, Austria.
* ISO/IEC JTC1/SC6(communication and information exchange between systems)
The technology ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Stretching metals at the atomic level allows researchers to create important materials for quantum, electronic, and spintronic applicationsNew technique paves the way for easy oxidation of historically “stubborn” metals