(Press-News.org) Baltimore, MD—New research led by Carnegie’s Yixian Zhen and Minjie Hu reveals how coral cells tag friendly algae before ingesting them, initiating a mutually beneficial relationship. This information could guide next-level coral conservation efforts.
Their work is published in Nature Microbiology.
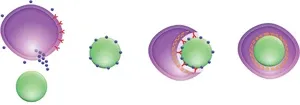
Corals are marine invertebrates that build large exoskeletons from which reefs are constructed. But this architecture is only possible because of a mutually beneficial relationship between the coral and various species of single-celled algae called dinoflagellates that live inside individual coral cells. These algae convert the Sun’s energy into food using a process called photosynthesis and they share some of the nutrients they produce with their coral hosts.
Coral reefs have great ecological, economic, and aesthetic value. Many communities depend on them for food and tourism. Despite this, human activity is putting strain on these fragile communities. Warming oceans, pollution, and acidification all affect this symbiotic relationship.
“Many corals are particularly sensitive to elevated temperatures,” explained Hu. “As oceans heat up, they lose algae, starve due to the lack of nutrients, and die off, a phenomenon called bleaching, because it leaves the coral skeleton looking ghostly white."
For several years, teams of Carnegie researchers, including Zheng and Hu, have been elucidating the molecular and cellular mechanisms underpinning coral-algae symbiosis. Understanding these processes could inform strategies to prevent bleaching and promote coral resilience.
In this new study, the researchers—including Carnegie’s Yun Bai and Xiaobin Zheng—deployed sophisticated bioinformatic and molecular biology tools to reveal the early steps of symbiosis, during which the algae are taken up into the coral. They found a molecule called LePin, which the coral secretes. It is concentrated in the mouth of corals, where it may bind to incoming algae, marking them for uptake into coral cells.
“Understanding how corals tell which algae to take up is an important step in gathering information that will help us mitigate coral bleaching,” Zheng said.
LePin is evolutionarily conserved among soft corals, stony corals, and anemones that perform symbiosis with algae, which means that it could be a good target for efforts to genetically engineer at-risk corals to increase their hardiness in the face of temperature increases.
“Gaining a deeper understanding of LePin could enable us to differentiate how some species of coral are better able to identify and take up heat-resistant algae than others,” Zheng explained. “Once isolated, the LePin sequences that are capable of identifying hardier and more heat-resistant algae could be transplanted into vulnerable coral populations to reduce bleaching events.”
In 2020, Zheng was selected as one of 15 scientists awarded a highly competitive grant from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation to support research on symbiosis in aquatic systems. She has been building on Carnegie’s long-standing tradition of model organism development to understand the molecular mechanisms of endosymbiosis in coral. These efforts illustrate how modern biomedical techniques can be applied to solving urgent ecological challenges—a research priority for Carnegie.
__________________
This work was supported by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
The Carnegie Institution for Science (carnegiescience.edu) is a private, nonprofit organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with three research divisions on both coasts. Since its founding in 1902, the Carnegie Institution has been a pioneering force in basic scientific research. Carnegie scientists are leaders in the life and environmental sciences, Earth and planetary science, and astronomy and astrophysics.
END
Corals mark friendly algae for ingestion—revealing possible conservation target
Understanding how corals tell which algae to take up is an important step in gathering information that will help experts mitigate coral bleaching
2023-05-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
WVU researchers see need to strengthen mental health programs for first responders
2023-05-22
Controlling traumatic situations is synonymous with the daily duties of first responders, yet many mental health programs to combat the increasing stress they encounter are lacking. That’s why West Virginia University researchers are identifying steps policymakers and community members can take to aid front-line workers.
“With elevated risk for suicide and other mental health issues among first responders, we have a significant public health problem,” said Michael Fisher, assistant professor in the WVU School of Public Health ...
Study may explain why high-sugar diets can worsen IBD
2023-05-22
Excess sugar hampers cells that renew the colon’s lining in a mouse model of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to a new study by University of Pittsburgh scientists.
The findings, published in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, could help get to the bottom of why limiting sugary foods can ease symptoms for patients with IBD.
“The prevalence of IBD is rising around the world, and it’s rising the fastest in cultures with industrialized, urban lifestyles, which typically have diets high in sugar,” said senior author Timothy Hand, Ph.D., associate professor of pediatrics and immunology at Pitt’s ...
Identifying the bee’s knees of bumble bee diets
2023-05-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study has identified the bee’s knees of bumble bee dietary options in Ohio and the Upper Midwest.
By viewing almost 23,000 bumble bee-flower interactions over two years, researchers found that these bees don’t always settle for the most abundant flowers in their foraging area – suggesting they have more discerning dietary preferences than one might expect.
Being large, strong and social bees that can fly for long distances, bumble bees are major contributors to pollination, particularly for agriculture – but like other pollinators threatened by habitat ...
TAp63: A new protein drug target for rheumatoid arthritis
2023-05-22
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease characterized by joint deterioration. The clinical outcomes of patients with active RA can be improved using anti-rheumatic medications, such as methotrexate (MTX). Many patients rely on MTX to limit the destructive joint damage and functional disability typical of RA. Although the drug is a folic acid antagonist, its precise mechanisms in RA patients are largely unknown.
Previous research suggests that MTX also affects a type of white blood cell called CD4+ T cells. These cells are believed to play a role in the development of RA—specifically, the balance between the activation of interleukin-17-producing helper T ...
Weigel receives funding for infrastructure development, maintenance and outreach for Heliophysics Application Programmer's Interface (HAPI)
2023-05-22
Robert Weigel, Professor, Physics and Astronomy, received funding for: "Infrastructure Development, Maintenance, and Outreach for the Heliophysics Application Programmer's Interface (HAPI)."
Weigel will facilitate HAPI adoption by upcoming missions by providing targeted instrument team support.
He will create additional HAPI server reference implementations.
He will create a meta-server to facilitate an integrated HAPI ecosystem.
He will create higher-level services that build on the uniformity afforded by HAPI ...
Fossils of a saber-toothed top predator reveal a scramble for dominance leading up to “the Great Dying”
2023-05-22
Two hundred and fifty-two million years ago, Earth experienced a mass extinction so devastating that it’s become known as “the Great Dying.” Massive volcanic eruptions triggered catastrophic climate change, killing off nine out of every ten species and eventually setting the stage for the dinosaurs. But the Great Dying was a long goodbye-- the extinction event took place over the course of up to a million years at the end of the Permian period. During that time, the fossil record shows drama and upheaval as species fought to get a foothold in their changing environments. One animal that exemplifies ...
New method reveals bacterial reaction to antibiotics in five minutes
2023-05-22
“We are confident and hope that this can be one of many tools that doctors need to tackle antibiotic resistance, which is a serious and growing problem,” says principal investigator Vicent Pelechano, associate professor at the Department of Microbiology, Tumor and Cell Biology, Karolinska Institutet.
The method is called 5PSeq, is simple to use, and is based on sequencing the messenger RNA (mRNA) that the bacteria break down as they synthesise proteins. The measurements reveal how the bacteria are affected by different environmental factors, such as antibiotic treatments and other types ...
Uncovering new mechanisms for wheat rust resistance
2023-05-22
Researchers have cloned the wheat rust resistance genes Lr9 and Sr43 and identified that they encode unusual kinase fusion proteins[1][2]. Their research will enable new options for addressing resistance to disease in bread wheat.
Each year about 20 percent of global wheat production is lost to pests and disease, the equivalent of 3,500 grain ships. Breeding resistant cultivars is one of the most economical and environmentally friendly ways to address the problem.
The wild relatives of wheat provide a ...
Importance of neuroscientific evidence for rape trials
2023-05-22
The law should take into consideration neuroscientific evidence that suggests fear and threat can cause victims to become ‘frozen’ in cases of rape or sexual assault, argue UCL experts.
In a comment article, published in Nature Human Behaviour, Professor Patrick Haggard and former UCL undergraduate, Ebani Dhawan, state that victims of sexual assault are often blamed for not fighting or fleeing their attackers.
Thirty per cent of women are thought to experience sexual assault or rape in their lifetime. And, of those who have attended an emergency clinic, 70% reported being “frozen” during ...
Communities should reconsider walking away from curbside recycling, study shows
2023-05-22
Curbside recycling can compensate for the greenhouse gas emissions from garbage destined for landfills, says a new study that encourages towns and cities to continue offering recycling services to meet their climate goals.
The study’s authors took a deep dive into the economic and environmental value of community recycling efforts and compared it to the value of other climate change mitigation practices. They concluded that recycling provides a return on investment similar to or better than environmentally friendly strategies like transitioning to electric vehicles or purchasing green power, which is electricity from clean, renewable energy sources.
“Eliminating ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New ‘scimitar-crested’ Spinosaurus species discovered in the central Sahara
“Cyborg” pancreatic organoids can monitor the maturation of islet cells
Technique to extract concepts from AI models can help steer and monitor model outputs
Study clarifies the cancer genome in domestic cats
Crested Spinosaurus fossil was aquatic, but lived 1,000 kilometers from the Tethys Sea
MULTI-evolve: Rapid evolution of complex multi-mutant proteins
A new method to steer AI output uncovers vulnerabilities and potential improvements
Why some objects in space look like snowmen
Flickering glacial climate may have shaped early human evolution
First AHA/ACC acute pulmonary embolism guideline: prompt diagnosis and treatment are key
Could “cyborg” transplants replace pancreatic tissue damaged by diabetes?
Hearing a molecule’s solo performance
Justice after trauma? Race, red tape keep sexual assault victims from compensation
Columbia researchers awarded ARPA-H funding to speed diagnosis of lymphatic disorders
James R. Downing, MD, to step down as president and CEO of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in late 2026
A remote-controlled CAR-T for safer immunotherapy
UT College of Veterinary Medicine dean elected Fellow of the American Academy of Microbiology
AERA selects 34 exemplary scholars as 2026 Fellows
Similar kinases play distinct roles in the brain
New research takes first step toward advance warnings of space weather
Scientists unlock a massive new ‘color palette’ for biomedical research by synthesizing non-natural amino acids
Brain cells drive endurance gains after exercise
Same-day hospital discharge is safe in selected patients after TAVI
Why do people living at high altitudes have better glucose control? The answer was in plain sight
Red blood cells soak up sugar at high altitude, protecting against diabetes
A new electrolyte points to stronger, safer batteries
Environment: Atmospheric pollution directly linked to rocket re-entry
Targeted radiation therapy improves quality of life outcomes for patients with multiple brain metastases
Cardiovascular events in women with prior cervical high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion
Transplantation and employment earnings in kidney transplant recipients
[Press-News.org] Corals mark friendly algae for ingestion—revealing possible conservation targetUnderstanding how corals tell which algae to take up is an important step in gathering information that will help experts mitigate coral bleaching