(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, May 23, 2023 – Type 1 diabetes affects 46.3 million people worldwide, and the number of people affected increases by about 3% each year. It requires careful calculations of insulin needs and bothersome daily injections to avoid peripheral diseases caused by extremes of high or low blood sugar.
Automated insulin delivery systems, also called artificial pancreases, make diabetes management much less onerous for patients. These systems — with implanted insulin sensors, pumps that deliver insulin inside the body, associated insulin pump controllers, and increasingly sophisticated control algorithms — are rapidly advancing.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Padova, University of Pavia, and Yale University designed a novel algorithm for controlling implanted insulin pumps that accounts for the unique characteristics of individual patients. Their model, tested using an FDA-approved diabetes computer simulation, proves intraperitoneal (within the abdominal cavity) insulin delivery is fast and closely mimics natural physiological insulin delivery.
“Not only is intraperitoneal infusion of insulin much more physiological because you are reproducing the natural physiology, but it simplifies the control problem because you don’t have delays,” author Claudio Cobelli said. “So, this means you can have a very simple, robust controller to handle the everyday situations.”
The current method of automated insulin delivery, which is based on technology called continuous subcutaneous glucose sensors, requires patients to manually enter the number of carbohydrates they consume, announcing their meals to the system before they eat. It is also slow to sense and deliver insulin. These delays, along with the likelihood of errors in manual meal calculations, make the system prone to inaccuracies and increase the prevalence of hyperinsulinemia, a state of high insulin in patients that causes diseases of the large blood vessels.
Using an FDA-accepted simulator designed for continuous subcutaneous insulin delivery, the researchers made modifications to simulate intraperitoneal insulin delivery. They developed a model that can account for individual patient differences and validated a pump control algorithm that does not require meal announcement.
“This is a big plus. It helps with tuning the devices and allows personalization,” Cobelli said. “Different people have different needs, so you need to personalize the algorithms.”
Tying together previous work and current experiments, the researchers successfully showed the similarities between intraperitoneal insulin delivery and the physiology of natural insulin secretion and validated a pump control algorithm that is robust to personalization factors and time variance for breakfast, lunch, and dinner meals.
Their work is part of a multiyear, collaborative European project called “FORGET DIABETES” that aims to rapidly advance automated insulin delivery technologies to the point of clinical trials.
###
The article “In silico design and validation of a time-varying PID controller for an artificial pancreas with intraperitoneal insulin delivery and glucose sensing” is authored by Alberto Dalla Libera, Chiara Toffanin, Martina Drecogna, Alfonso Galderisi, Gianluigi Pillonetto, and Claudio Cobelli. It will appear in APL Bioengineering on May 23, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0145446). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0145446.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Bioengineering is an open access journal publishing significant discoveries specific to the understanding and advancement of physics and engineering of biological systems. See http://aip.scitation.org/journal/apb.
###
END
Artificial pancreas reduces disease management burden for people with diabetes
Intraperitoneal insulin delivery mimics the natural physiology of the pancreas
2023-05-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Electronic noses sniff out volatile organic compounds
2023-05-23
WASHINGTON, May 23, 2023 – Volatile organic compounds are chemicals emitted as gases that can have adverse health effects. They are often found in paints, pharmaceuticals, and refrigerants, among other common products, but they can also act as markers of explosives, insect infestation, food spoilage, and disease.
Tracing VOCs is important for public safety and all “smell” related issues. To this end, in Applied Physics Reviews, from AIP Publishing, Liu et al. introduced a fluid mechanics-based chamber design for an electronic nose (e-nose) that consistently detects ...
Neighborhood income mobility and risk of neonatal and maternal morbidity
2023-05-23
bout The Study: In this study of women living in low-income areas, those who moved to a higher-income area between births experienced less morbidity and death in their second pregnancy, as did their newborns, compared with those who remained in low-income areas between births. Research is needed to determine whether financial incentives or enhancement of neighborhood factors can reduce adverse maternal and perinatal outcomes.
Authors: Joel G. Ray, M.D., M.Sc., of the University of Toronto, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Factors associated with protection from SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infection and disease among vaccinated health care workers
2023-05-23
About The Study: Immunoglobin G and neutralizing antibody titer levels were associated with protection against infection with the Omicron variant and against symptomatic disease in this study that included 2,300 vaccinated health care workers in Israel.
Authors: Gili Regev-Yochay, M.D., of the Sheba Medical Center in Ramat Gan, Israel, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.14757)
Editor’s ...
Prediabetes and fracture risk among midlife women
2023-05-23
About The Study: The findings in this study of nearly 1,700 midlife women without diabetes suggest that prediabetes was associated with risk of fracture. Future research should determine whether treating prediabetes reduces fracture risk.
Authors: Albert Shieh, M.D., of the David Geffen School of Medicine at University of California, Los Angeles, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.14835)
Editor’s ...
Underreporting of quality measures in nursing home ratings
2023-05-23
About The Study: The results of this quality improvement study involving 13,000 nursing homes suggest widespread underreporting of major injury falls and pressure ulcers, and underreporting was associated with the racial and ethnic composition of a facility. Alternative approaches to measuring quality need to be considered.
Authors: Prachi Sanghavi, Ph.D., of the University of Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.14822)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other ...
Boost for the quantum internet
2023-05-23
Quantum networks connect quantum processors or quantum sensors with each other. This allows tap-proof communication and high-performance distributed sensor networks. Between network nodes, quantum information is exchanged by photons that travel through optical waveguides. Over long distances, however, the likelihood of photons being lost increases dramatically. As quantum information cannot simply be copied and amplified, 25 years ago Hans Briegel, Wolfgang Dür, Ignacio Cirac and Peter Zoller, then all at the University of Innsbruck, provided the blueprints for a quantum repeater. These feature light-matter entanglement sources and memories ...
ICUconnect app helped clinicians address unmet palliative care needs across course of ICU care
2023-05-23
Session: C16, The Road to Recovery: Improving Long-Term Outcomes After Critical Illness
Date and Time: 9:24 a.m. ET, Tuesday, May 23, 2023
Location: WEWCC, Room 143 A-C (Street Level)
ATS 2023, Washington, DC – In a randomized controlled trial, ICUconnect helped ICU physicians to reduce unmet palliative care needs of critically ill patients and their families better than standard care did, according to research published at the ATS 2023 International Conference. ICUconnect is a mobile app that enables families to give and receive ...
Hertz Foundation announces 2023 Hertz Fellows
2023-05-23
Pleasanton, Calif., May 23, 2023 — The Fannie and John Hertz Foundation, a nonprofit organization dedicated to empowering the most promising innovators in science and technology, has announced the 2023 Hertz Fellows, 15 remarkable doctoral students in applied science, engineering and mathematics.
By funding their graduate studies for five years, Hertz Fellowships provide each new fellow the freedom to tackle some of the most significant challenges facing our nation and the world today. Their research promises to improve human health, usher in advances in artificial intelligence and quantum technologies that redound to the greater good, yield a deeper understanding of our universe, contribute ...
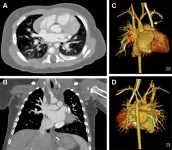
Photon-counting CT offers superior imaging in babies with heart defects
2023-05-23
OAK BROOK, Ill. – A new advanced form of CT imaging called photon-counting computed tomography (PCCT) offers better cardiovascular imaging quality at a similar radiation dose compared to dual-source CT (DSCT) in infants with suspected cardiac heart defects, according to a study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Congenital heart defects are the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the neonatal period, occurring in up to one percent of live births. Of those, approximately 25% are critical defects requiring surgical intervention within the first month after birth. ...
Viral transmission in schools
2023-05-23
Schoolchildren in China, tracked with wearable devices, provide data about close contact behavior that may influence viral transmission, according to a study. Nan Zhang and colleagues fitted wearable trackers on 24 children at a school comprising of primary, middle, and high school students in Jiangsu Province, China. Two volunteers were selected from each grade, 1–12, and asked to sit near the middle of the classroom. For 45 minutes during class and 10 minutes during breaks between two classes, the devices recorded the children’s interpersonal distance, face orientation, relative position (horizontal and vertical), close ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
[Press-News.org] Artificial pancreas reduces disease management burden for people with diabetesIntraperitoneal insulin delivery mimics the natural physiology of the pancreas