(Press-News.org) DALLAS – Texas scientists will receive $2.5 million in funding to advance their research thanks to a new prize program from Lyda Hill Philanthropies and TAMEST (Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology). The Hill Prizes, funded by Lyda Hill Philanthropies, will accelerate high-risk, high-reward research ideas with significant potential for real-world impact.
The Prizes will celebrate top Texas innovators and researchers whose work could significantly impact science and society in five categories: Medicine, Engineering, Biological Sciences, Physical Sciences and Technology. A committee of TAMEST members (Texas-based members of the National Academies) will select the recipients. Finalists will be endorsed by a committee of Texas Nobel and Breakthrough Prize Laureates and approved by the TAMEST Board of Directors.
Each of the five prize recipients will receive $500,000 in funding from Lyda Hill Philanthropies to accelerate their work. Prize recipients will be announced and recognized on February 5, 2024, at the opening reception of the TAMEST 2024 Annual Conference in Austin, Texas.
The prizes will recognize exceptional innovators by providing seed funding to advance groundbreaking science and highlight Texas as a premier destination for world-class research. The prizes will help bridge the path from research to business development and further innovations that need additional funding for greater impact. The Hill Prizes will also put recipients in a stronger position to receive more research funding and seek large-scale grants and collaborations.
“Our organization is committed to funding game-changing advances in science and nature and that is exactly what the Hill Prizes’ mission is,” said Lyda Hill, Entrepreneur and Founder of Lyda Hill Philanthropies. “We hope that the funding awarded to these Texas scientists will help enable them to launch their pivotal research into development and continue to make advancements in scientific innovation.”
“By accelerating big ideas through direct research funding, we know the Hill Prizes will help transform the research landscape in Texas and create marketable outcomes from our state’s best scientists,” said TAMEST President Brendan Lee, M.D., Ph.D. (NAM), Baylor College of Medicine. “We look forward to advancing exceptional innovators and the most exciting research in the state thanks to the vision and support of Lyda Hill.”
To qualify as an applicant, researchers must be Texas-based and have started their first independent position at least 15 years ago for all academic categories. For Technology category applicants, researchers must have 25 years of experience since they started their career.
Applicants must have spent the last two years performing research in Texas at an institution within the state and stay active there for at least one year after receiving the prize funding. Institutional approval is required and applications may be submitted by both individuals and teams. More information on prize criteria and eligibility is available in the application guide.
Applications for the Hill Prizes will open on June 27.
View the Hill Prizes Application Guide and visit www.tamest.org/Hill-Prizes for more information on the prizes and nomination process.
About Lyda Hill Philanthropies:
Lyda Hill Philanthropies encompasses the charitable giving for founder Lyda Hill and includes her foundation and personal philanthropy. Her organization is committed to funding transformational advances in science and nature, empowering nonprofit organizations and improving the Texas and Colorado communities. Because Miss Hill has a fervent belief that “science is the answer” to many of life’s most challenging issues, she has chosen to donate the entirety of her estate to philanthropy and scientific research.
About TAMEST:
TAMEST (The Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology) was co-founded in 2004 by the Honorable Kay Bailey Hutchison and Nobel Laureates Michael S. Brown, M.D., and Richard E. Smalley, Ph.D. With more than 335 members, 9 Nobel Laureates and 22 member institutions, TAMEST is composed of the Texas-based members of the three National Academies (National Academy of Medicine, National Academy of Engineering and National Academy of Sciences) and other honorific organizations. TAMEST brings together the state’s brightest minds in medicine, engineering, science and technology to foster collaboration, and to advance research, innovation and business in Texas.
END
New research prizes will give $2.5 million to top scientists in Texas
2023-05-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Morressier joins the fight for science with federated integrity suite for authors and publishers
2023-05-24
Berlin and Washington DC, May 24, 2023 – Morressier announced today an integrity suite that will be offered as part of its end-to-end platform, designed to increase the quality of and trust in the outputs of scientific research.
Pre-flight checks for authors will flag potential quality issues, check for completeness of submissions, and provide recommendations for improvements in areas such as language.
Publishers using the Morressier platform now have access to a powerful suite of automated tools to help them identify integrity issues early and at scale. Plagiarism detection tools in the Morressier platform, for instance, indicate phrases in submissions that may ...
SEngine Precision Medicine demonstrates potential of PARIS® Test to find unexpected therapeutic options for treating cancer
2023-05-24
SEngine Precision Medicine, the precision oncology innovator matching patients to medicines based on their own tumor samples, announces the publication of a new case report showing a patient’s remarkable response to an off-label therapy identified by its PARIS® Test. Despite standard-of-care chemotherapy and two surgeries, the patient’s low-grade serous ovarian cancer (LGSOC) was progressing and her prognosis was terminal. But by testing a range of therapies in organoids grown from the patient’s own tumor sample, SEngine’s PARIS® Test identified as ...
Logging on for health: More older adults use patient portals, but access and attitudes vary widely
2023-05-24
Far more older adults these days log on to secure websites or apps to connect with their health information or have a virtual health care appointment, compared with five years ago, a new poll shows.
Overall, 78% of people aged 50 to 80 have used at least one patient portal, up from 51% in a poll taken five years ago, according to findings from the University of Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging. Of those with portal access, 55% had used it in the past month, and 49% have accounts on more than one portal.
But the poll also reveals major disparities, with some groups of older adults less likely to use patient portals, or more likely ...
Life stressors may contribute to multiple sclerosis flares, disability
2023-05-24
A Michigan Medicine-led study finds that stressors across the lifespan — including poverty, abuse and divorce — are associated with worsening health and functional outcomes for people with multiple sclerosis.
Using survey data from more than 700 people with MS, researchers discovered that stressful events occurring both in childhood and adulthood contributed significantly to participants’ level of disability.
The results are published in Brain and Behavior.
“MS is the leading cause of non-traumatic ...
Existing drugs point to first treatment for strokes linked to dementia
2023-05-24
People who experience a type of stroke linked with nearly half of all dementias could be treated for the first time by repurposing two cheap and common drugs, a trial shows.
Researchers found that isosorbide mononitrate and cilostazol, which are already used to treat other heart and circulatory diseases, can safely improve the debilitating outcomes people experience after lacunar stroke.
The two drugs, which were found to be even more effective when used in combination, could be available as a treatment for lacunar strokes within five years, if the results are ...
Long or short menstrual cycles linked to higher risk of CVD including atrial fibrillation
2023-05-24
Research Highlights:
An analysis of data for more than 58,000 women in the U.K. Biobank found that both short (less than 21 days) or long (more than 35 days) menstrual cycles were associated with the development of cardiovascular disease, heart attack or atrial fibrillation (AFib).
Short or long menstrual cycle length was associated with a 19% higher risk of heart disease among those women compared to women with menstrual cycle length between 22 to 34 days.
Irregular menstrual cycle length was associated with a 40% higher risk of atrial ...
Physical activities like a daily, 20-minute walk may help reduce disparities in heart health
2023-05-24
Statement Highlights:
Addressing low levels of physical activity among people in some targeted groups has the potential to improve equity in cardiovascular health.
Physical activity levels are lower among some population groups known to have higher cardiovascular disease risk, including adults who are older, female, Black, have depression, have disabilities, have lower socioeconomic status or live in rural areas.
It’s important to improve resources and opportunities to decrease barriers to physical activity. Physical activity initiatives should engage the community and ...
Cleft lip caused by combination of genes and environment
2023-05-24
A cleft lip or palate arises from the combined effects of genes and inflammatory risk factors experienced during pregnancy, such as smoking or infections, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The study, published in Nature Communications, has revealed for the first time how genetic and environmental factors come together to form a cleft lip or palate in a developing foetus.
Cleft lip, with or without cleft palate, is the most common craniofacial malformation seen at birth, affecting one in 700 live births. It can have devastating ...
Study finds association between long-term exposure to air pollution and severe COVID-19
2023-05-24
A long history of exposure to air pollution is associated with a higher risk of developing severe disease, admission to hospital or an intensive care unit (ICU) and death by COVID‑19 according to a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a research centre supported by the ”la Caixa” Foundation. The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, was based on a large cohort of 4,660,502 adults resident in Catalonia in 2020, the year the Spanish autonomous community had a high incidence of COVID-19.
The ...
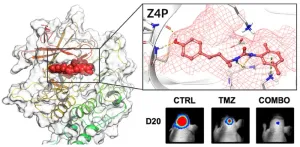
Major progress in curing brain tumours
2023-05-24
Researchers at the University of Gothenburg, working with French colleagues, have successfully developed a method able to kill the aggressive brain tumour glioblastoma. By blocking certain functions in the cell with a docked molecule, the researchers cause the cancer to die of stress.
Cancer cells, especially those that form aggressive tumours, are in one way or another out of control and live a very stressful existence. To manage this stress, the cancer cells hijack mechanisms that the healthy cells use to regulate protein production and process the surplus proteins that they create. Without these hijacked mechanisms, ...