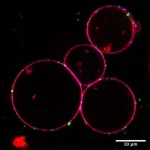
(Press-News.org) A team of researchers at the University of Houston College of Pharmacy is reporting that by manipulating TAK1, a signaling protein that plays an important role in development of the immune system, they can slow down disease progression and improve muscle function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD).
DMD, caused by mutations in dystrophin gene, is an inheritable neuromuscular disorder that occurs in one out of 3,600 male births. DMD patients undergo severe muscle wasting, inability to walk and eventually death in their early thirties due to respiratory failure. The disease is marked by an inflammatory response and death of muscle fibers. Eventually, the muscle fibers are replaced with fat and fibrotic tissue that causes severe muscle weakness.
“Our results suggest that TAK1 (transforming growth factor β-activated kinase1) is a regulator of skeletal muscle mass. By specifically targeting this protein, we can suppress the death of muscle fibers, known as myonecrosis, and slow down disease progression in DMD,” said Ashok Kumar, Else and Philip Hargrove Endowed Professor and chair, Department of Pharmacological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, whose results were published in JCI Insight. “Our research shows that activating TAK1 can stimulate myofiber growth in a model of DMD, with no negative impact on muscle health.”
In a previous breakthrough, Kumar’s team uncovered a surprising fact: TAK1 is essential for maintaining skeletal muscle mass and that activating TAK1 beyond normal levels can enhance skeletal muscle growth.
For this research, supported by the National Institutes of Health, the team designed experiments to reduce or augment the levels of TAK1 protein in skeletal muscle at different stages of disease progression.
“Our experiments demonstrate that depletion of TAK1 activity during peak necrotic phase followed by re-introduction of TAK1 at post-necrotic phase leads to substantial improvement in muscle pathology,” said Anirban Roy, research assistant professor.
The current standard of care for DMD is focused on reducing inflammation with corticosteroids, which modestly reduces disease progression, but has serious side effects.
“Accumulating evidence suggests that regulation of immune response, autophagy, and metabolism along with gene correction therapy can be promising approaches to slow down disease progression in DMD patients,” said Roy.
END
Discovery slows down muscular dystrophy
University of Houston researchers target protein that can slow disease progression, improve muscle function
2023-05-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A novel method to quantify individual limb contributions to standing postural control
2023-05-24
Research question
Can these contributions to standing postural control be quantified from CoP trajectories in neurotypical adults?
Methods
Instantaneous contributions can be negative or larger than one, and integrated contributions sum to equal one. Proof-of-concept demonstrations validated these calculated contributions by restricting CoP motion under one or both feet. We evaluated these contributions in 30 neurotypical young adults who completed two (eyes opened; eyes closed) 30-s trials of bipedal standing. We evaluated the relationships between limb contributions, self-reported limb dominance, and between-limb ...
NASA data could lead to more accurate weather forecasts
2023-05-24
A University of Texas at Arlington civil engineering researcher will use a NASA grant to help forecasters better predict extreme weather events using a variety of existing NASA data sources.
Yu Zhang, associate professor in the Department of Civil Engineering, said the $638,000 grant will use ocean circulation data, atmospheric conditions and current weather information to make longer-range forecasting more reliable. Having a more accurate forecast could help officials make better decisions about the state’s water resources—for example, knowing when to release water from reservoirs.
“Using ...
Digital engineering to reduce risks that lead to brain injuries
2023-05-24
A University of Texas at Arlington engineering researcher who studies traumatic brain injuries has received funding to use computer motion simulation that replicates the movements of a person performing activities that could lead to injury.
The project, funded by a nearly $1 million grant from the Office of Naval Research Defense University Research Instrumentation Program (DURIP), will use real-time data of phantom head and phantom body reactions to ascertain what physical injuries could come from those motions.
Ashfaq Adnan, a UT Arlington professor in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, is leading the project, called “System for Remote ...
A look into the heart of cellular waste disposal
2023-05-24
To prevent our body’s cells from overflowing with garbage and to keep them healthy, the waste inside them is constantly being disposed of. This cleaning process is called autophagy. Scientists have now, for the first time, rebuilt the complex nanomachine in the laboratory that starts this process – and it works quite differently from other cellular machines. The researchers’ new insights could help open up new approaches for the treatment of cancer, immune disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases in ...
Designing a next generation hypersonic demonstrator
2023-05-24
Today, large commercial jets fly around 580 mph. The Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird introduced in 1966 is the fastest supersonic jet vehicle in the world, reaching speeds of more than 2,200 mph, nearly four times faster than a commercial jet.
The fastest rocket-powered hypersonic vehicle developed in the late 1960s carrying a human has been the North American X-15, reaching a top speed of 4,520 mph, twice that of the SR-71.
Recently, the U.S. Air Force has awarded a contract to engineer Project Mayhem with the goal to reach 4,603 mph. Now, imagine a vehicle that could fly much faster, maybe even above 6,905 mph, which is beyond nine times the speed of sound.
The University of Texas at Arlington’s ...
Confusion over VAERS: Why the vaccine safety reporting system should be renamed
2023-05-24
PHILADELPHIA – The federal health system for reporting “adverse events” after vaccination, known as VAERS, is designed to assist in the early detection of complications and responsive action. But when the pandemic and advent of new vaccines for Covid-19 turned a spotlight on this formerly little-known system, the flood of web and social media references to it was accompanied by confusion about what the system is and what the reports in it signify.
A new report from the Annenberg Public Policy Center examines misconceptions about the government’s Vaccine Adverse ...
A better way to match 3D volumes
2023-05-24
CAMBRIDGE, MA — In computer graphics and computer-aided design (CAD), 3D objects are often represented by the contours of their outer surfaces. Computers store these shapes as “thin shells,” which model the contours of the skin of an animated character but not the flesh underneath.
This modeling decision makes it efficient to store and manipulate 3D shapes, but it can lead to unexpected artifacts. An animated character’s hand, for example, might crumple when bending its fingers — a motion that resembles how an empty rubber glove deforms rather than the motion of a hand filled with bones, tendons, ...
Chemical Insights Research Institute and the Campus Safety, Health, and Environmental Management Association publish guidance for the safe use of 3D printing in institutions of higher education
2023-05-24
Atlanta (May 24, 2023) - Chemical Insights Research Institute (CIRI) of UL Research Institutes and the Campus Safety, Health, and Environmental Management Association (CSHEMA), announce the publication of, “UL 200B: Guidance Document for Safe Use of 3D Printing for Institutions of Higher Education.”
The availability of 3D printing has fostered creative and innovative learning experiences for many within the large population of students in higher education. There are roughly 17.3 million undergraduates in the U.S. alone. Because 3D printers are affordable compact, and user friendly, they can ...
SWI/SNF complexes “bookmark” cell identity during division
2023-05-24
(Memphis, Tenn.—May 24, 2023) When a cell divides, it retains information about how to grow and instructions about what type of cell to become. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital have gained a new understanding of how these processes can work, revealing a previously unappreciated role for the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex. The study was published today in Nature.
When a cell undergoes differentiation, stem cells (the earliest cells that develop) undergo changes that transform them into a different type of cell, typically one with a more specialized function (such as a skin or muscle cell). As ...
Watching molecules relax in real time
2023-05-24
– By Rachel Berkowitz
Designing the next generation of efficient energy conversion devices for powering our electronics and heating our homes requires a detailed understanding of how molecules move and vibrate while undergoing light-induced chemical reactions. Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have now visualized the distortions of chemical bonds in a methane molecule after it absorbs light, loses an electron, and then relaxes. Their study provides insights into how molecules react to light, which can ultimately be useful for developing new methods ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
[Press-News.org] Discovery slows down muscular dystrophyUniversity of Houston researchers target protein that can slow disease progression, improve muscle function