(Press-News.org) About The Study: The findings of this study using data for 3.6 million births suggest that the Maternal Vulnerability Index (MVI), a novel county-level index designed to quantify maternal vulnerability to adverse health outcomes, was associated with preterm birth even after adjustment for individual-level confounders. The MVI is a useful measure for county-level preterm birth risk that may have policy implications for counties working to lower preterm rates and improve perinatal outcomes.
Authors: Sara C. Handley, M.D., M.S.C.E., Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.15306)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.15306?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=052523
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
County-level maternal vulnerability and preterm birth
JAMA Network Open
2023-05-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Deep learning for detection and symptom severity assessment of autism spectrum disorder
2023-05-25
About The Study: In this diagnostic study of 45 children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and 50 with typical development, a deep learning system trained on videos acquired using a joint attention–eliciting protocol for classifying ASD versus typical development and predicting ASD symptom severity showed high predictive performance. This new artificial intelligence–assisted approach based predictions on participants’ behavioral responses triggered by social cues. The findings suggest that this method may allow digital measurement of joint attention; however, follow-up studies are necessary for further validation.
Authors: Yu ...
Using AI, scientists find a drug that could combat drug-resistant infections
2023-05-25
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Using an artificial intelligence algorithm, researchers at MIT and McMaster University have identified a new antibiotic that can kill a type of bacteria that is responsible for many drug-resistant infections.
If developed for use in patients, the drug could help to combat Acinetobacter baumannii, a species of bacteria that is often found in hospitals and can lead to pneumonia, meningitis, and other serious infections. The microbe is also a leading cause of infections in wounded soldiers in Iraq and Afghanistan.
“Acinetobacter can survive on hospital doorknobs and equipment ...
Monkey model offers clues for potential widespread HIV cure in people
2023-05-25
PORTLAND, Oregon -- New animal research is helping explain why at least five people have become HIV-free after receiving a stem cell transplant. The study’s insights may bring scientists closer to developing what they hope will become a widespread cure for the virus that causes AIDS, which has infected about 38 million people worldwide.
Published in the journal Immunity, the Oregon Health & Science University-led study describes how two nonhuman primates were cured of the monkey form of HIV after receiving a stem cell transplant. ...
OU professor leading research for next steps in monitoring bat coronaviruses
2023-05-25
Since the emergence of SARS in 2002, coronaviruses have been recognized as potential pandemic threats. This emergence highlights a need for evidence-based strategies to monitor bat coronaviruses. Daniel Becker, Ph.D., a researcher at the University of Oklahoma, is collaborating with other scientists nationwide to determine directions for future research.
Becker, an OU assistant professor of biology, was the senior author of a paper published in Nature Microbiology. The study’s lead author was Lily Cohen, a medical student at the Icahn ...
New framework for defining long COVID highlights twelve signature symptoms
2023-05-25
Long COVID, or Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), includes a wide range of symptoms that present or persist more than 30 days after COVID-19 infection. With over 650 million people globally having been infected with SARS-CoV-2, long COVID represents a significant public health concern that affects quality of life, earnings, and health care costs. To better understand the prevalence and severity of symptoms, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) launched Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery (RECOVER-Adult), ...
Development of a definition of Long COVID
2023-05-25
About The Study: In this analysis of data from 9,764 participants in the RECOVER adult cohort, a prospective longitudinal cohort study, 37 symptoms across multiple pathophysiological domains were identified as present more often in SARS-CoV-2–infected participants at six months or more after infection compared with uninfected participants. A preliminary rule for identifying postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), also known as long COVID, was derived based on a composite symptom score. As a first step to providing a framework for other investigations, iterative refinement that further incorporates other clinical features is needed ...
Identifying the gut bacteria that threaten neonatal babies
2023-05-25
Researchers from the Quadram Institute and University of East Anglia have identified what makes some strains of gut bacteria life-threatening in pre-term babies.
The findings will help identify and track dangerous strains and protect vulnerable neonatal babies.
A major threat to neonatal babies with extremely low birth weight is necrotising enterocolitis (NEC).
Rare in full term babies, this microbial infection exploits vulnerabilities destroying gut tissue leading to severe complications. Two out of five cases are fatal.
One bacterial species that causes especially sudden and severe disease is Clostridium perfringens. These ...
CityU researchers develop a self-supervised AI adaptation framework to enhance sensing accuracy of EMG devices
2023-05-25
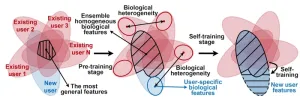
Surface electromyography (EMG) has been widely used to measure the electrical activity of muscles. However, the variability in EMG sensing signals due to biological differences of different users significantly degrades the performance and potential of EMG systems. Recently, researchers from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) developed a deep learning-based framework called EMGSense, which can achieve high sensing performance for new users using AI self-training techniques. This opens a new path for developing more advanced and accurate wearable EMG devices in areas like neurorehabilitation and virtual reality.
This ...
Insilico Medicine receives IND approval for novel AI-designed USP1 inhibitor for cancer
2023-05-25
Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), a generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven clinical stage drug discovery company, today announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved the initial investigational new drug (IND) application for ISM3091 for the treatment of patients with solid tumors. This is Insilico's first oncology program to advance to the clinical validation stage.
The open-label, multicenter Phase I clinical trial of ISM3091 will be conducted simultaneously in the U.S. and China ...
Quantum scientists accurately measure power levels one trillion times lower than usual
2023-05-25
Scientists in Finland have developed a nanodevice that can measure the absolute power of microwave radiation down to the femtowatt level at ultra-low temperatures – a scale trillion times lower than routinely used in verifiable power measurements. The device has the potential to significantly advance microwave measurements in quantum technology.
Measuring extremely low power
Quantum science takes place mostly at ultra-low temperatures using devices called dilution refrigerators. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
Improving data science education using interest‑matched examples and hands‑on data exercises
Sparkling water helps keep minds sharp during long esports sessions
Drone LiDAR surveys of abandoned roads reveal long-term debris supply driving debris-flow hazards
UGA Bioinformatics doctoral student selected for AIBS and SURA public policy fellowship
Gut microbiome connected with heart disease precursor
Nitrous oxide, a product of fertilizer use, may harm some soil bacteria
FAU lands $4.5M US Air Force T-1A Jayhawk flight simulator
SimTac: A physics-based simulator for vision-based tactile sensing with biomorphic structures
Preparing students to deal with ‘reality shock’ in the workplace
Researchers develop beating, 3D-printed heart model for surgical practice
Black soldier fly larvae show promise for safe organic waste removal
People with COPD commonly misuse medications
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
[Press-News.org] County-level maternal vulnerability and preterm birthJAMA Network Open