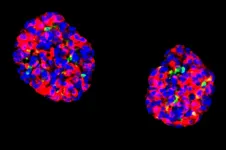
(Press-News.org) May 25, 2023 – A combination of emerging and alternative techniques – microneedling to induce collagen and cupping to increase tissue perfusion – may have a synergistic effect in producing skin rejuvenation, according to an experimental study in the June issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Cupping therapy can be added to microneedling therapy and used to increase certain desired effects on skin," comments lead author Burak Pasinlioğlu, MD, of Kecioren Research and Training Hospital, Ankara, Turkey. "This combination might provide an easy and effective method to improve skin quality in plastic surgery practice."
Experiments look at cellular effects of microneedling plus cupping
Microneedling is a nonsurgical technique that has been used to promote skin regeneration and scar healing. Needles are used to create tiny channels in the skin, with the goal of inducing collagen and other healing factors. "Many studies have demonstrated that microneedling has significant benefits for skin regeneration and scar healing," Dr. Pasinlioğlu and coauthors write.
Cupping is a centuries-old method of alternative medicine that has been shown to produce beneficial effects on the skin. "These effects are similar to those of negative pressure wound therapy, an approach commonly used in plastic surgery," according to the authors. They designed an experimental study to examine the effects of adding cupping therapy to microneedling.
In the study, the researchers performed a single session of microneedling on the skin of anesthetized rats. One group of animals underwent microneedling alone, while the other group underwent microneedling followed by a brief session of cupping. Cupping consisted of applying gentle negative pressure (suction) on the treated skin.
Other animals underwent three sessions of treatment with microneedling, alone or followed by cupping. The goal of the procedures, alone or in combination, was to trigger inflammation and blood supply (vascularization). After four weeks of healing, cellular-level skin changes were compared for rats undergoing microneedling alone or microneedling plus cupping.
Significant increases in skin thickness and collagen levels
The results showed significant improvement in skin thickness. In the outer layer of the skin (epidermis), thickness increased from about 24 micrometers (μm) with one session of microneedling alone to 42 μm with microneedling plus cupping. Cupping was also associated with increased thickness of the dermis, the skin layer beneath the epidermis. There was no further increase in skin thickness with three sessions compared to one session of treatment.
On immunohistochemical studies, microneedling led to greater increases in levels of type 1 collagen within the skin. The ratio of type 1 to type 3 collagen also increased – a high percentage of type 1 collagen is characteristic of younger skin, the researchers note. Percentages of type 1 and 3 collagen were not significantly affected by adding cupping to microneedling.
The preliminary, experimental findings suggest that a combination of microneedling and cupping might provide a useful technique for plastic surgeons seeking to improve on the results of facial rejuvenation procedures. Dr. Pasinlioğlu and coauthors conclude: "[T]he added benefit of negative pressure with microneedling may prove to be an easy and practical method with synergistic effects."
Read [Comparison of the Effects of Skin Microneedling with Cupping Therapy and Microneedling Alone: An Experimental Study]
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers and students in effective decision-making and outcomes across healthcare. We support clinical effectiveness, learning and research, clinical surveillance and compliance, as well as data solutions. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter @WKHealth.
###
About Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
For over 75 years, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery® (http://www.prsjournal.com/) has been the one consistently excellent reference for every specialist who uses plastic surgery techniques or works in conjunction with a plastic surgeon. The official journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery® brings subscribers up-to-the-minute reports on the latest techniques and follow-up for all areas of plastic and reconstructive surgery, including breast reconstruction, experimental studies, maxillofacial reconstruction, hand and microsurgery, burn repair and cosmetic surgery, as well as news on medico-legal issues.
About ASPS
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons is the largest organization of board-certified plastic surgeons in the world. Representing more than 7,000 physician members, the society is recognized as a leading authority and information source on cosmetic and reconstructive plastic surgery. ASPS comprises more than 94 percent of all board-certified plastic surgeons in the United States. Founded in 1931, the society represents physicians certified by The American Board of Plastic Surgery or The Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada.
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (EURONEXT: WKL) is a global leader in professional information, software solutions, and services for the healthcare, tax and accounting, financial and corporate compliance, legal and regulatory, and corporate performance and ESG sectors. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with specialized technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2022 annual revenues of €5.5 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 20,000 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
For more information, visit www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube.
END
Microneedling plus cupping may aid skin rejuvenation
Combination increases skin thickness and collagen levels, reports Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®
2023-05-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists target human stomach cells for diabetes therapy
2023-05-25
Stem cells from the human stomach can be converted into cells that secrete insulin in response to rising blood sugar levels, offering a promising approach to treating diabetes, according to a preclinical study from researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine.
In the study, which appeared April 27 in Nature Cell Biology, the researchers showed that they could take stem cells obtained from human stomach tissue and reprogram them directly—with strikingly high efficiency—into cells that closely resemble pancreatic insulin-secreting cells known as beta cells. Transplants of small groups of these cells reversed disease signs in a mouse model of diabetes.
“This ...
Sage’s 10-Year Impact Awards recognize research with long-term influence
2023-05-25
For the fourth year, Sage has awarded 10-Year Impact Awards to three research articles that have had a lasting influence over the past decade. The awards are given to the authors of three papers published in Sage Journals in 2012 that have received the most citations in the 10 years since than all other studies published in the same year.
The three winning papers are:
“The Nature and Organization of Individual Differences in Executive Functions: Four General Conclusions” by Akira Miyake and Naomi P. Friedman in Current Directions ...
CU researchers weave deeper understanding of diverse ancestry and gene expression
2023-05-25
Exploring diverse ancestry is a critical factor in furthering medical research.
A new study published in Nature Genetics from researchers in the Department of Biomedical Informatics (DBMI) at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, in partnership with the University of California San Francisco and Stanford University, is the largest of its kind that focuses on ancestry correlations with biomedical traits and the first study to examine the role of genetic variants across diverse ...
Does body contouring increase long-term weight loss after bariatric surgery? New findings
2023-05-25
May 25, 2023 – For patients with massive weight loss after bariatric surgery, subsequent body contouring to remove excess skin is not itself associated with long-term weight loss, reports a study in the June issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"In contrast to previous studies, we found that body contouring ...
Epigenetic mechanisms activated by GHK-Cu increase skin collagen density in clinical trial
2023-05-25
Skin loses collagen and elastin and becomes progressively thinner with age leading to wrinkles, so reversing this age-related loss of skin density is the holy grail of anti-aging treatments. One compound capable of doing that is the naturally occurring peptide GHK-Cu (GHK from glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine bound to a copper ion), which affects 31.2% of the human genes by either activating or deactivating them (based on a criterion of a reduction or increment in gene activity of more than 50%), meaning that it works by ...
Scientists use AI to find promising new antibiotic to fight evasive hospital superbug
2023-05-25
Attention editors: Embargoed by the journal Nature Chemical Biology until Thursday, May 25 at 11 a.m. easter
Hamilton, ON, May 25, 2023 – Scientists at McMaster University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have used artificial intelligence to discover a new antibiotic which could be used to fight a deadly, drug-resistant pathogen that strikes vulnerable hospital patients.
The process they used could also speed the discovery of other antibiotics to treat many other challenging ...
A metabolic process in cancer cells could unlock a possible treatment for glioblastoma
2023-05-25
A study led by researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center has found that targeting a metabolic process in people with a specific genetic mutation could help treat glioblastoma, an aggressive brain cancer.
The genetic alteration — a deletion in a gene called CDKN2A — is present in about 60% of people who have glioblastoma. The mutation causes changes in the way lipids are distributed in cancer cells, which in turn makes the cancer cells vulnerable to being destroyed. The ...
Can sugar and fat influence immune cell responses?
2023-05-25
LA JOLLA, CA—A population of unconventional white blood cells has recently captured the attention of immunologists and clinicians alike. Unlike conventional T cells, which circulate throughout the body in our blood, mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells are largely found in tissues where they provide immune protection against a broad range of diseases.
MAIT cells are highly abundant in humans. Although they make up only 2 percent of the lymphocytes in blood, MAIT cells account for 10 to 40 percent of lymphocytes in the liver, and they are common in tissues such as lungs. Still, much about MAIT cell biology and clinical function remains unknown.
In ...
County-level maternal vulnerability and preterm birth
2023-05-25
About The Study: The findings of this study using data for 3.6 million births suggest that the Maternal Vulnerability Index (MVI), a novel county-level index designed to quantify maternal vulnerability to adverse health outcomes, was associated with preterm birth even after adjustment for individual-level confounders. The MVI is a useful measure for county-level preterm birth risk that may have policy implications for counties working to lower preterm rates and improve perinatal outcomes.
Authors: Sara C. Handley, M.D., M.S.C.E., Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Deep learning for detection and symptom severity assessment of autism spectrum disorder
2023-05-25
About The Study: In this diagnostic study of 45 children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and 50 with typical development, a deep learning system trained on videos acquired using a joint attention–eliciting protocol for classifying ASD versus typical development and predicting ASD symptom severity showed high predictive performance. This new artificial intelligence–assisted approach based predictions on participants’ behavioral responses triggered by social cues. The findings suggest that this method may allow digital measurement of joint attention; however, follow-up studies are necessary for further validation.
Authors: Yu ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Microneedling plus cupping may aid skin rejuvenationCombination increases skin thickness and collagen levels, reports Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®