(Press-News.org) A new study from Swansea University and the University of Cape Town provides the first documented evidence of a cessation in urban space use by a female baboon after giving birth: another example of how wild animals are adaptively responding to urbanisation.
The study, recently published in the journal Ecology & Evolution, used GPS collars to track the movements of 13 chacma baboons in Cape Town, South Africa.
The data revealed that when one collared female gave birth, she stopped using urban space without any significant change in daily distance travelled or social interactions that would be expected with general risk-sensitive behaviour during this time.
Whilst only one baboon gave birth while wearing a GPS-recording tracking collar, the field team observed the same pattern of urban avoidance postpartum in two other non-collared females during the study.
The researchers suggest that such changes in the baboon mothers’ behaviour may reduce the risks newborns might experience in the urban environment. It also presents a valuable insight into how species with slow life history strategies, investing in few offspring with extended parental care, need to adapt their behaviour to cope with changes due to human activity within their lifetime.
Lead researcher Dr Anna Bracken, a former Swansea University PhD student now based at the University of Glasgow, commented: "Urban environments may be risky for baboon mothers and their infants, and this study provides further evidence of how baboons living near these areas are adapting in response to the threats they face."
The team's latest research not only provides an insight into how life history events alter individuals' use of anthropogenic environments, but also can be used to advise on methods for managing the baboon's urban space use.
Dr Andrew King, senior author of the study, said: "These findings have implications for how we manage baboon interactions with human environments. By highlighting how long-lived species with slow life history strategies cope with anthropogenic changes, we can help landowners and decision-makers develop plans to minimise conflict and promote coexistence between humans and wildlife on the urban edge."
This research was funded by South Africa’s National Research Foundation and Swansea University.
Read the paper in full: Postpartum cessation of urban space use by a female baboon living at the edge of the City of Cape Town
END
GPS tracking reveals how a female baboon stopped using urban space after giving birth
2023-05-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tree islands bring biodiversity to oil palm plantations
2023-05-26
Islands of trees in oil palm plantations can significantly increase biodiversity within five years without reducing productivity. This has been shown by an experiment, which has been running for over ten years in Indonesia as part of the Collaborative Research Centre (CRC) "EFForTS" at the University of Göttingen. An international team of researchers led by Göttingen planted experimental islands of trees in plantations on the island of Sumatra to counteract the species loss caused by the ...
Innovative endoscopic imaging system can detect multiple fluorescent tracers
2023-05-26
For patients with solid cancers, endoscopic surgery is one of the primary treatment options to remove tumors. However, there is a high risk of cancer recurrence if even a small number of cancerous cells are left behind after surgical resection. To prevent this from happening, researchers developed fluorescence-guided surgery (FGS). In FGS, patients are injected with a fluorescent probe that preferentially binds to tumor cells, enabling surgeons to easily identify lesions with the help of specialized endoscopes that emit the necessary excitation light.
Unfortunately, tumors can be highly heterogeneous, ...
CHOP researchers show that IgA fine tunes the body’s interactions with microbes
2023-05-26
Philadelphia, May 26, 2023—IgA deficiency is the most common primary immune deficiency worldwide, but its presentation has puzzled physcians and researchers. Some with the disorder present with symptoms like recurrent infections, autoimmune disease, or allergies, whereas others have no symptoms at all and only become aware of their IgA-deficient status through an incidental finding on a blood test. This variability has raised the question among researchers: Why aren’t many of those with IgA deficiency sicker?
A new study by researchers at Children’s ...
Protein-based nano-‘computer’ evolves in ability to influence cell behavior
2023-05-26
HERSHEY, Pa. — The first protein-based nano-computing agent that functions as a circuit has been created by Penn State researchers. The milestone puts them one step closer to developing next-generation cell-based therapies to treat diseases like diabetes and cancer.
Traditional synthetic biology approaches for cell-based therapies, such as ones that destroy cancer cells or encourage tissue regeneration after injury, rely on the expression or suppression of proteins that produce a desired action within a cell. This approach can take time (for proteins ...
Gene therapy rescues hearing for the first time in aged mouse models
2023-05-26
By 2050, one in 10 individuals are expected to live with some form of hearing loss. Of the hundreds of millions of cases of hearing loss affecting individuals worldwide, genetic hearing loss is often the most difficult to treat. While hearing aids and cochlear implants offer limited relief, no available treatment can reverse or prevent this group of genetic conditions, prompting scientists to evaluate gene therapies for alternative solutions.
One of the most promising tools used in these therapies—adeno associated virus (AAV) vectors—has galvanized the hearing-loss community in recent years. ...
The mechanisms behind swallowing
2023-05-26
Sensory cells in the vagus nerve can detect and locate food in the esophagus. Their signals help transport the food onward to the stomach. Signal failure leads to swallowing disorders, say a team led by Carmen Birchmeier at the Max Delbrück Center. They have published their findings in “Neuron.”
Swallowing disorders can have many causes, and they occur more frequently in older people. But neurological diseases such as multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease, and certain medications, can also prevent food moving normally from mouth to stomach. Possible consequences include malnutrition, weight loss, and dehydration.
Now a team led ...
Life through rose-coloured glasses
2023-05-26
Over thousands of years some animals have specialised to live in environments where the sun never shines: giant squid with eyes the size of volleyballs see even in the darkest depths while others, like cave-dwelling olms, have lost the functionality of their eyes completely. But for animals that do not live in these extremes, how do species manage a world that suddenly becomes dark? Lakes that become turbid from algal blooms, agricultural run-off, or other environmental pollutants represent common examples of environmental disturbances that can impact the visual scene that ...
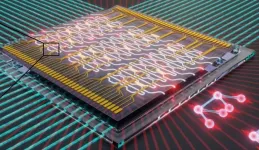
Promising building blocks for photonic quantum simulators
2023-05-26
Researchers at the Niels Bohr Institute have, collaborating with the University of Münster and Ruhr-Universität Bochum, developed new technology capable of processing the enormous amounts of information quantum systems generate. Deterministic single photon light sources, creating quantum bits at extreme rates and speed are now coupled to specially designed, integrated photonic circuits, capable of processing quantum information with adequate speed and quality without degrading the susceptible quantum states. This means that the first steps have been taken towards the development of photonic quantum devices that can, for example, ...
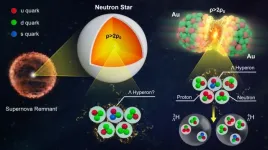
First measurements of hypernuclei flow at RHIC
2023-05-26
UPTON, NY—Physicists studying particle collisions at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) have published the first observation of directed flow of hypernuclei. These short-lived, rare nuclei contain at least one “hyperon” in addition to ordinary protons and neutrons. Hyperons contain at least one “strange” quark in place of one of the up or down quarks that make up ordinary nucleons (the collective name for protons and neutrons). Such strange matter is thought to be abundant in the hearts of neutron stars, which are among the densest, most exotic objects in the universe. While blasting off to neutron stars to study ...
When the cell digests itself: How inherited neurodegenerative diseases develop
2023-05-26
FRANKFURT. A tangle of pockets, tubes and sac-like membrane structures runs through the cells of humans, animals, plants and fungi: the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER for short. In the ER, proteins are manufactured, folded into their three-dimensional structure and modified, lipids and hormones are produced and calcium concentrations in the cell are controlled. In addition, the ER forms the basis for the cellular transport system, feeds misfolded proteins to intracellular disposal and renders toxins that have entered the cell harmless.
In ...