(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan – Researchers from the Department of Mechanical Science and Bioengineering at Osaka University have invented a new kind of walking robot that takes advantage of dynamic instability to navigate. By changing the flexibility of the couplings, the robot can be made to turn without the need for complex computational control systems. This work may assist the creation of rescue robots that are able to traverse uneven terrain.
Most animals on Earth have evolved a robust locomotion system using legs that provides them with a high degree of mobility over a wide range of environments. Somewhat disappointingly, engineers who have attempted to replicate this approach have often found that legged robots are surprisingly fragile. The breakdown of even one leg due to the repeated stress can severely limit the ability of these robots to function. In addition, controlling a large number of joints so the robot can transverse complex environments requires a lot of computer power. Improvements in this design would be extremely useful for building autonomous or semi-autonomous robots that could act as exploration or rescue vehicles and enter dangerous areas.
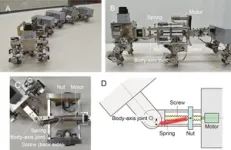
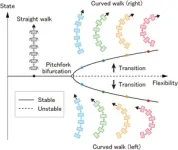
Now, investigators from Osaka University have developed a biomimetic “myriapod” robot that takes advantage of a natural instability that can convert straight walking into curved motion. In a study published recently in Soft Robotics, researchers from Osaka University describe their robot, which consists of six segments (with two legs connected to each segment) and flexible joints. Using an adjustable screw, the flexibility of the couplings can be modified with motors during the walking motion. The researchers showed that increasing the flexibility of the joints led to a situation called a “pitchfork bifurcation,” in which straight walking becomes unstable. Instead, the robot transitions to walking in a curved pattern, either to the right or to the left. Normally, engineers would try to avoid creating instabilities. However, making controlled use of them can enable efficient maneuverability. “We were inspired by the ability of certain extremely agile insects that allows them to control the dynamic instability in their own motion to induce quick movement changes,” says Shinya Aoi, an author of the study. Because this approach does not directly steer the movement of the body axis, but rather controls the flexibility, it can greatly reduce both the computational complexity as well as the energy requirements.
The team tested the robot’s ability to reach specific locations and found that it could navigate by taking curved paths toward targets. “We can foresee applications in a wide variety of scenarios, such as search and rescue, working in hazardous environments or exploration on other planets,” says Mau Adachi, another study author. Future versions may include additional segments and control mechanisms.
###
The article, “Maneuverable and efficient locomotion of a myriapod robot with variable body-axis flexibility via instability and bifurcation,” was published in Soft Robotics at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/soro.2022.0177
END
Robot centipedes go for a walk
Researchers at Osaka University develop a new centipede-like robot and show how its motion can be switched from straight and curved walking, which may assist with search and rescue operations or planetary exploration
2023-05-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How to diagnose and manage depression in adolescents: a new review for clinicians
2023-05-29
How do you diagnose and manage depression in adolescents? A new review published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.220966 aims to help primary care clinicians address this increasingly common, yet under-detected condition, in teenagers.
"Although more than 40% of people with depression experience onset before adulthood, depression remains undetected in many adolescents in Canada, and most are untreated," writes Dr. Daphne Korczak, a psychiatrist with the Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) and the University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, with coauthors. "Clinicians consistently ...
New moms and dads left unprepared for parenthood by government health ‘failures’, report warns
2023-05-27
UK Government’s “outdated” public health messages are leaving new parents in the dark about what to expect after birth
Some parents still smoking or drinking at the start of pregnancy, report by Children’s Alliance warns
Frontline medical staff aren’t passing on key public health messages about pregnancy, authors reveal
Expectant mothers and fathers are being failed by the UK Government’s “outdated” public health plans leaving them unprepared for parenthood, a new report has warned.
The review by Children’s Alliance, with the University of Southampton, found that women and men are unaware of how poor personal health can impact ...
Pediatric Cancer Research Foundation announces 2023 grant recipients to accelerate discovery of new treatments for pediatric cancers
2023-05-26
The Pediatric Cancer Research Foundation (PCRF), a nonprofit focused on transforming pediatric cancer care by accelerating research breakthroughs, today announced the 19 recipients of its 2023 research grants. The researchers will receive $1,730,000 in funding to explore new and safer treatments for pediatric cancers. Of the recipients, six scientists are receiving PCRF funding for the first time.
For the balance, PCRF funding will support the continuation of ongoing research projects. Grant recipients will conduct their research at top institutions across the U.S, studying various ...
Absolute vs. relative efficiency: How efficient are blue LEDs, actually?
2023-05-26
The absolute internal quantum efficiency (IQE) of indium gallium nitride (InGaN) based blue light-emitting diodes (LEDs) at low temperatures is often assumed to be 100%. However, a new study from University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Electrical and Computer Engineering researchers has found that the assumption of always perfect IQE is wrong: the IQE of an LED can be as low as 27.5%.
This new research, “Low temperature absolute internal quantum efficiency of InGaN-based light-emitting diodes”, was recently published in Applied Physics Letters.
As ECE associate professor Can Bayram puts it, LEDs are the ultimate lighting source. ...
$4.5M grant to explore link between exercise, slowing down Alzheimer’s
2023-05-26
A $4.5 million groundbreaking grant will fund research to explore a promising link between aerobic exercise and slowing the progression of Alzheimer's disease in a study led by an Arizona State University researcher.
An estimated 6.7 million Americans age 65 and older are living with Alzheimer's disease, according to the Alzheimer’s Association's 2023 report. A $4.5 million groundbreaking grant from the National Institute on Aging will fund research exploring a promising link between aerobic exercise and slowing the progression of Alzheimer's. ...
New study uncovers role of previously unknown protein in obesity and diabetes
2023-05-26
(Boston) – More than 40% of Americans are considered obese, and the trend continues to grow. The treatments or preventive options for obesity and obesity-associated diseases are limited. It is a major national healthcare and public health burden significantly increasing the risk of diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and cancer and is linked to the severity of COVID-19.
A research team from Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine has identified a novel druggable signaling molecule involved in obesity, a previously unknown protein (MINAR2) discovered in 2020 in the laboratory of Associate Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Nader Rahimi, ...
Study finds distinct patterns of pre-existing brain health characteristics in stroke patients
2023-05-26
University of Cincinnati researchers are presenting abstracts at the European Stroke Organization Conference (ESOC) 2023, May 24-26 in Munich, Germany, including the results of the first large-scale assessment of radiological brain health in stroke patients in a population.
Extensive research has helped pinpoint risk factors for initial stroke, but there is limited understanding about what the brains of stroke patients look like on a population level, according to UC’s Achala Vagal, MD, professor of neuroradiology.
“Imaging can be an objective manifestation of the presence ...
Nanorobotic system presents new options for targeting fungal infections
2023-05-26
Infections caused by fungi, such as Candida albicans, pose a significant global health risk due to their resistance to existing treatments, so much so that the World Health Organization has highlighted this as a priority issue.
Although nanomaterials show promise as antifungal agents, current iterations lack the potency and specificity needed for quick and targeted treatment, leading to prolonged treatment times and potential off-target effects and drug resistance.
Now, in a groundbreaking development with far-reaching implications for global ...
Bird brains can flick switch to perceive Earth’s magnetic field
2023-05-26
Earth’s magnetic field, generated by the flow of molten iron in the planet’s inner core, extends out into space and protects us from cosmic radiation emitted by the Sun. It is also, remarkably, used by animals like salmon, sea turtles and migratory birds for navigation.
But how? And why? A new study from researchers at Western’s Advanced Facility for Avian Research (AFAR), home to the world’s first hypobaric climatic wind tunnel for bird flight, explores a brain region called cluster N that migratory birds use to perceive Earth’s magnetic field. The team discovered the region is activated very ...
Food for thought: UH study highlights the role of clean technology in reducing food waste
2023-05-26
Foodservice companies have long struggled with the challenge of what to do with all of their food waste. But researchers at the University of Houston Conrad N. Hilton College of Global Hospitality Leadership are shedding light on how clean technology can help those companies reduce waste and establish long-term sustainability goals.
In a study published in the Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, Tiffany S. Legendre, an associate professor at Hilton College, and her team, interviewed 17 leaders of the country’s largest on-site foodservice providers (e.g., Aramark, Compass and Sodexo), ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
[Press-News.org] Robot centipedes go for a walkResearchers at Osaka University develop a new centipede-like robot and show how its motion can be switched from straight and curved walking, which may assist with search and rescue operations or planetary exploration