(Press-News.org) The absolute internal quantum efficiency (IQE) of indium gallium nitride (InGaN) based blue light-emitting diodes (LEDs) at low temperatures is often assumed to be 100%. However, a new study from University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Electrical and Computer Engineering researchers has found that the assumption of always perfect IQE is wrong: the IQE of an LED can be as low as 27.5%.
This new research, “Low temperature absolute internal quantum efficiency of InGaN-based light-emitting diodes”, was recently published in Applied Physics Letters.
As ECE associate professor Can Bayram puts it, LEDs are the ultimate lighting source. Since their invention, they have become increasingly popular due to their energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
An LED is a semiconductor that emits light when current flows through the device. It generates photons through the recombination of electrons and holes (carriers), releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light emitted corresponds to the energy of the photon.
InGaN-based blue LEDs enable bright and energy-saving white lighting. The transition to solid-state lighting sources has significantly reduced energy needs and greenhouse gas emissions, but continual efficiency improvements are necessary to hit energy savings goals in the long term. The U.S. Department of Energy’s 2035 roadmap calls for blue LED efficiency to increase from 70% to 90% and furthering energy savings by 450 terawatt hours (TWh) and CO2 emission savings by 150 million metric tons.
Bayram says, “The question is, how can we push this ultimate lighting source further? The answer is by understanding its absolute efficiency, not relative efficiency.” Relative efficiency benchmarks a device with itself, while absolute efficiency allows for comparison across different devices by measuring the efficiency on a commonly shared scale.
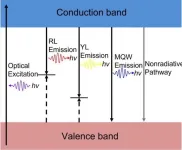
IQE is defined as the ratio of the generated photons to the injected electrons in the active region of the semiconductor and is an important metric to quantify the performance of LEDs. The most widely used method to quantify IQE is by temperature-dependent photoluminescence. In such analyses, it has been assumed that at low temperatures (4, 10, or even 77 Kelvin), there is 100% radiative recombination- meaning producing a photon. At room temperature, because of non-radiative mechanisms- which emit excess energy as heat, rather than photons- the efficiency is significantly lower. The ratio of the two photoluminescence intensities gives a relative efficiency of the LED.
The original assumption has been that at low temperatures, there are no non-radiative recombination- all the loss mechanisms are “frozen”. Bayram and graduate student Yu-Chieh Chiu assert, however, that this assumption may be wrong because non-radiative effects might not in fact be completely frozen out at low temperatures.
In their paper, Bayram and Chiu demonstrate a different method for revealing low temperature absolute IQE of InGaN-based LEDs. Using a “channel-based” recombination model, they report surprising results: the absolute IQE of the LED on traditional sapphire and silicon substrates is 27.5% and 71.1%, respectively- drastically lower than the standard assumption.
To explain these unexpected results, Chiu says that the channel-based recombination model is one of the ways to think about what happens inside the active layer of the LED and how recombination in one channel affects another channel. A channel is a pathway that a carrier may take to recombine radiatively or nonradiatively.
“To determine the efficiency of the blue LED, usually only the blue emission is considered,” Chiu says. “But that ignores the effects of everything else happening inside the device, specifically the non-radiative and defect luminescence channels. Our approach is to get a more holistic view of the device and determine, if there is recombination in the blue channel, how is that affected by the second and third channel(s)?”
As research on the LED continues to advance, it is important to know an absolute efficiency rather than a relative efficiency. Bayram stresses that “the absolute efficiency is very important to the field so that everyone can build on each other’s knowledge rather than each group improving their own efficiency. We need absolute measurements, not just relative measurements.”
To meet the efficiency standards laid out by the DOE, it will be increasingly important to properly quantify the efficiency of LEDs. Even a 1% increase in efficiency will correspond to tons of carbon dioxide savings annually. Chiu says, “By understanding the absolute efficiency, instead of the relative efficiency, that will give us a more accurate picture and allow us to improve devices further by being able to compare them to each other.”
END
Absolute vs. relative efficiency: How efficient are blue LEDs, actually?
LEDs are the ultimate lighting source. Since their invention, they have become increasingly popular due to their energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness
2023-05-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
$4.5M grant to explore link between exercise, slowing down Alzheimer’s
2023-05-26
A $4.5 million groundbreaking grant will fund research to explore a promising link between aerobic exercise and slowing the progression of Alzheimer's disease in a study led by an Arizona State University researcher.
An estimated 6.7 million Americans age 65 and older are living with Alzheimer's disease, according to the Alzheimer’s Association's 2023 report. A $4.5 million groundbreaking grant from the National Institute on Aging will fund research exploring a promising link between aerobic exercise and slowing the progression of Alzheimer's. ...
New study uncovers role of previously unknown protein in obesity and diabetes
2023-05-26
(Boston) – More than 40% of Americans are considered obese, and the trend continues to grow. The treatments or preventive options for obesity and obesity-associated diseases are limited. It is a major national healthcare and public health burden significantly increasing the risk of diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and cancer and is linked to the severity of COVID-19.
A research team from Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine has identified a novel druggable signaling molecule involved in obesity, a previously unknown protein (MINAR2) discovered in 2020 in the laboratory of Associate Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Nader Rahimi, ...
Study finds distinct patterns of pre-existing brain health characteristics in stroke patients
2023-05-26
University of Cincinnati researchers are presenting abstracts at the European Stroke Organization Conference (ESOC) 2023, May 24-26 in Munich, Germany, including the results of the first large-scale assessment of radiological brain health in stroke patients in a population.
Extensive research has helped pinpoint risk factors for initial stroke, but there is limited understanding about what the brains of stroke patients look like on a population level, according to UC’s Achala Vagal, MD, professor of neuroradiology.
“Imaging can be an objective manifestation of the presence ...
Nanorobotic system presents new options for targeting fungal infections
2023-05-26
Infections caused by fungi, such as Candida albicans, pose a significant global health risk due to their resistance to existing treatments, so much so that the World Health Organization has highlighted this as a priority issue.
Although nanomaterials show promise as antifungal agents, current iterations lack the potency and specificity needed for quick and targeted treatment, leading to prolonged treatment times and potential off-target effects and drug resistance.
Now, in a groundbreaking development with far-reaching implications for global ...
Bird brains can flick switch to perceive Earth’s magnetic field
2023-05-26
Earth’s magnetic field, generated by the flow of molten iron in the planet’s inner core, extends out into space and protects us from cosmic radiation emitted by the Sun. It is also, remarkably, used by animals like salmon, sea turtles and migratory birds for navigation.
But how? And why? A new study from researchers at Western’s Advanced Facility for Avian Research (AFAR), home to the world’s first hypobaric climatic wind tunnel for bird flight, explores a brain region called cluster N that migratory birds use to perceive Earth’s magnetic field. The team discovered the region is activated very ...
Food for thought: UH study highlights the role of clean technology in reducing food waste
2023-05-26
Foodservice companies have long struggled with the challenge of what to do with all of their food waste. But researchers at the University of Houston Conrad N. Hilton College of Global Hospitality Leadership are shedding light on how clean technology can help those companies reduce waste and establish long-term sustainability goals.
In a study published in the Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, Tiffany S. Legendre, an associate professor at Hilton College, and her team, interviewed 17 leaders of the country’s largest on-site foodservice providers (e.g., Aramark, Compass and Sodexo), ...
Illinois Tech announced as enrollment partner in NIH’s AI precision nutrition research, largest project of its kind
2023-05-26
CHICAGO—May 26, 2023—Illinois Institute of Technology is one of 14 institutions chosen as an enrollment site for the National Institute of Health’s landmark initiative to advance nutrition research. Nutrition for Precision Health (NPH), powered by the All of Us Research Program, is working to engage 10,000 participants from diverse backgrounds across the United States with the aim of learning about how our bodies respond differently to food.
NPH will use artificial intelligence–based ...
World leader in photonics gives talk at Aston University
2023-05-26
Talk by one of the leading lights in optical communications
Dr. Ming-Jun Li is currently a corporate fellow at Corning Incorporated
He discussed installed optical fibres for ultra-wideband transmission systems.
26 May 2023 | Birmingham, UK
Aston University has hosted one of the leading lights in optical communications and speciality optical fibres at its second international photonics workshop.
Dr. Ming-Jun Li is currently a corporate fellow at Corning Incorporated in the USA and headed ...
GPS tracking reveals how a female baboon stopped using urban space after giving birth
2023-05-26
A new study from Swansea University and the University of Cape Town provides the first documented evidence of a cessation in urban space use by a female baboon after giving birth: another example of how wild animals are adaptively responding to urbanisation.
The study, recently published in the journal Ecology & Evolution, used GPS collars to track the movements of 13 chacma baboons in Cape Town, South Africa.
The data revealed that when one collared female gave birth, she stopped using urban space without any significant change in daily distance travelled or social interactions that would be expected with general risk-sensitive behaviour during this ...
Tree islands bring biodiversity to oil palm plantations
2023-05-26
Islands of trees in oil palm plantations can significantly increase biodiversity within five years without reducing productivity. This has been shown by an experiment, which has been running for over ten years in Indonesia as part of the Collaborative Research Centre (CRC) "EFForTS" at the University of Göttingen. An international team of researchers led by Göttingen planted experimental islands of trees in plantations on the island of Sumatra to counteract the species loss caused by the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
[Press-News.org] Absolute vs. relative efficiency: How efficient are blue LEDs, actually?LEDs are the ultimate lighting source. Since their invention, they have become increasingly popular due to their energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness