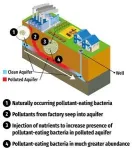
(Press-News.org) University of California, Riverside, chemical and environmental engineering scientists have identified two species of bacteria found in soil that break down a class of stubborn “forever chemicals,” giving hope for low-cost biological cleanup of industrial pollutants.
These bacteria destroy a subgroup of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances, or PFAS, that have one or more chlorine atoms within their chemical structure, Yujie Men, an assistant professor in the Bourns College of Engineering, and her UCR colleagues, reported in the journal Natural Water.
Unhealthful forever chemicals persist in the environment for decades or much longer because of their unusually strong carbon-to-fluorine bonds. Remarkably, the UCR team found that the bacteria cleave the pollutant’s chlorine-carbon bonds, which starts a chain of reactions that destroy the forever chemical structures, rendering them harmless.
“What we discovered is that bacteria can do carbon-chlorine bond cleavage first, generating unstable intermediates,” Men said. “And then those unstable intermediates undergo spontaneous defluorination, which is the cleavage of the carbon-fluorine bond.”
Chlorinated PFAS are a large group in the forever chemical family of thousands of compounds. They include a variety of non-flammable hydraulic fluids used in industry and compounds used to make chemically stable films that serve as moisture barriers in various industrial, packaging, and electronic applications.
The two bacteria species – Desulfovibrio aminophilus and Sporomusa sphaeroides – identified by Men’s group are naturally occurring and are known to live in the subterranean microbiomes where groundwater may be contaminated with PFAS. For expedited cleanups, an inexpensive nutrient, such as methanol, could be injected into groundwater to promote bacterial growth. This would greatly increase the bacteria’s presence to destroy the pollutants more effectively, Men said. If the bacteria are not already present, the contaminated water could be inoculated with one of the bacterium species.
The title of the paper is “Substantial defluorination of polychlorofluorocarboxylic acids triggered by anaerobic microbial hydrolytic dichlorination.” Men is the corresponding author and Bosen Jin, a UCR chemical and environmental engineering graduate student, is the lead author. Other UCR co-authors are postdoc Jinyu Gao; former postdoc Huaqing Liu; former graduate students Shun Che and Yaochun Yu; and Associate Professor Jinyong Liu.
The study expands on earlier work by Men, in which she demonstrated that microbes can breakdown a stubborn class of PFAS called fluorinated carboxylic acids.
Microbes have long been used for biological cleanup of oil spills and other industrial pollutants, including the industrial solvent trichloroethylene or TCE, which Men has studied.
But what’s known about using microorganisms to clean up PFAS is still in its infancy, Men said. Her discovery shows great promise because biological treatments, if effective pollutant-eating microbes are available, are generally less costly and more environmentally friendly than chemical treatments. Pollutant-eating microbes can also be injected into difficult-to-reach locations underground.
Men’s latest PFAS study comes as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is promulgating new regulations to spur cleanups of PFAS-contaminated groundwater sites throughout the nation because these chemicals have been linked to a host of ill health effects, including cancer, kidney disease, and hormone disruptions.
Click here for more information.
END
Biological cleanup discovered for certain “forever chemicals”
Two species of naturally-occurring bacteria found to breakdown chlorinated "forever chemicals," AKA PFAS
2023-05-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cancer survivors who quit smoking have 36% lower cardiovascular risk than continuers
2023-05-31
Sophia Antipolis, 31 May 2023: Cancer patients who continue smoking after their diagnosis have a nearly doubled risk of heart attack, stroke or death due to cardiovascular disease compared with non-smokers, according to research published on World No Tobacco Day in European Heart Journal, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
According to the World Health Organization, there were more than 50.5 million cancer survivors worldwide in 2020.2 Study author Dr. Hyeok-Hee Lee of Yonsei University College ...
More depressed patients than previously estimated could have increased activation of their immune system
2023-05-31
New research from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London has used an assessment of gene expression involved in the immune response to show that there could be more patients with MDD with activated immune systems than research has previously estimated.
By identifying the molecular mechanisms involved in this association, the research could pave the way to better identify those patients with an immune component to their depression which would potentially help to provide more personalised approaches to treatment ...
Shedding light on the complex flow dynamics within the small intestine
2023-05-31
Science is well aware of the important role that gut bacteria and their interactions with the gastrointestinal tract play in our overall health. Villi, tiny finger-like structures that line the inside of the small intestine (SI), are known to interact with the gut bacteria and trigger a protective immune response. Despite researching into the molecular mechanisms underlying these interactions, however, not much is known about the dynamics of liquid flow around the villi.
While computer simulations have aided such observations, ...
UK cardiology societies issue joint policy statement to stamp out bullying, harassment, and discrimination in the specialty
2023-05-31
The British Junior Cardiologists’ Association (BJCA) and the British Cardiovascular Society (BCS) have issued a joint position statement in a bid to stamp out bullying, harassment, discrimination and other “unacceptable” and “unprofessional” behaviours in the specialty.
The statement, published online in the journal Heart, urges every cardiology team member to call out these behaviours to drive culture change.
Endorsed by 19 organisations affiliated with the BCS, the statement represents a specialty-wide response to the issue.
It comes in the wake of evidence suggesting ...
Predominance of young Asian men among large UK case series of laughing gas users
2023-05-31
The largest clinical case series to date of recreational users of nitrous oxide, popularly known as laughing gas, has found a predominance of young men of Asian ethnicity among those with neurological side effects who were seen at hospitals in 3 major cities in England.
This may indicate genetic susceptibility to the nerve damage caused by exposure to the gas, or other, as yet unidentified, social factors, suggest the researchers by way of an explanation for the finding, published online in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
Nitrous oxide is widely used as an anaesthetic in people and animals, ...
Ketamine nasal spray may prove safe and effective treatment for refractory migraine
2023-05-31
Ketamine taken in the form of a nasal spray may prove a safe and effective treatment for refractory chronic migraine, suggests a single centre study, published in the open access journal Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine.
It’s a more convenient alternative to intravenous infusion—the usual method of administration for these patients—but the potential for overuse means that it should be reserved for those in whom other treatment approaches have failed, caution the researchers.
Several clinical trials have shown ...
The clams that fell behind, and what they can tell us about evolution and extinction
2023-05-31
Every so often, life on Earth steps onto a nearly empty playing field and faces a spectacular opportunity. Something major changes—in the atmosphere or in the oceans, or in the organisms themselves —and the existing species begin to branch out into a brand-new world. Scientists are fascinated by this process, because it’s a unique look into evolution at pivotal moments in the history of life.
A new study led by scientists with the University of Chicago examined how bivalves—the group that includes clams, mussels, scallops, and oysters—evolved among many others in the period of rapid evolution known as the Cambrian Explosion. The team found ...
Medical school does not equip new doctors for the real working world, junior doctor warns
2023-05-31
Clinician burnout and overwork are known to adversely affect patient safety and junior doctors may be particularly vulnerable, research suggests.
The UK is facing a crisis in recruitment and retention in medicine, with a recent survey by the British Medical Association reporting that 4 in 10 junior doctors will quit their roles as soon as they find another job.
Considering the immense pressure doctors are under, with their decisions having the potential to shape the course of patients’ illnesses and even their lives, is a balanced and happy life as a doctor still possible?
In a new book released today titled The Bleep Test, junior doctor Luke Austen has combined ...
Unique “bawdy bard” act discovered, revealing 15th-century roots of British comedy
2023-05-31
University of Cambridge media release
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 00:01AM (UK TIME) ON WEDNESDAY 31ST MAY 2023
An unprecedented record of medieval live comedy performance has been identified in a 15th-century manuscript. Raucous texts – mocking kings, priests and peasants; encouraging audiences to get drunk; and shocking them with slapstick – shed new light on Britain’s famous sense of humour and the role played by minstrels in medieval society.
The texts contain the earliest recorded use of ‘red herring’ in English, extremely rare forms of medieval literature, as well as a ...
Saved from extinction, Southern California’s Channel Island Foxes now face new threat to survival
2023-05-31
Tiny foxes — each no bigger than a five-pound housecat — inhabiting the Channel Islands off the coast of Southern California were saved from extinction in 2016. However, new research reveals that the foxes now face a different threat to their survival.
Suzanne Edmands, professor of biological sciences at USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences, and Nicole Adams, who earned her PhD from USC Dornsife in 2019, found that the foxes’ genetic diversity has decreased over time, possibly jeopardizing their survival ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Biological cleanup discovered for certain “forever chemicals”Two species of naturally-occurring bacteria found to breakdown chlorinated "forever chemicals," AKA PFAS