(Press-News.org) Brussels, 1 June 2023 – Today, the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) is excited to share the publication of the first consensus paper by the SISAQOL-IMI Consortium1. The paper provides an overview of the stakeholders’ views on the need for SISAQOL-IMI and the agreed priority set of patient-reported outcome (PRO) objectives that the Consortium will produce international consensus-based recommendations on.
The Setting International Standards in Analysing Patient-Reported Outcomes and Quality of Life Endpoints in Cancer Clinical Trials – Innovative Medicines Initiative (SISAQOL-IMI)2 is an international multidisciplinary consortium, co-led by the EORTC and Boehringer Ingelheim (BI) under a public-private partnership funded by the IMI. Building on the initial SISAQOL work3, this Consortium aims to improve the way patient-reported outcomes (PRO) are used in cancer clinical trials by developing a consensus-based set of best practice recommendations for the design, analysis, presentation, and interpretation of PRO data.
PROs are any outcome reported directly by the patient such as a patient’s description of their disease-related symptoms, treatment side effects, functioning and their impact on their health-related quality of life.4 While PROs are playing an increasingly important role in the decision-making by different stakeholders, there is still a lack of standards and guidance on how PRO data are collected and used in cancer clinical trials.
Dr Madeline Pe, Head of the EORTC Quality of Life Department and Lead author of the paper, highlights the importance of this project, pointing out that: “By developing international multi-stakeholder consensus recommendations, we are able to address the challenges faced by various stakeholders in incorporating PROs in cancer clinical trials.” Anders Ingelgaard, from Boehringer Ingelheim and co-leader of SISAQOL-IMI Work Package 1, adds that: “Improving standards on how we incorporate PRO data in clinical trials will help ensure that the patients’ voice is included in the evaluation of cancer therapies.”
About SISAQOL-IMI
The IMI call on improving standards for PRO analysis recommendations shows how important these standards are in supporting the use of PRO data for optimal drug development and device approval by regulators and HTA bodies, and for the communication between clinicians and patients for the purposes of shared decision making. The SISAQOL-IMI Consortium addresses this need by building on the previous work of SISAQOL and extending its coverage to include single-arm studies and defining clinically meaningful difference.
As design, analysis, presentation, and interpretation of PRO data is a complex and multifaceted issue, this Consortium brings together a broad group of esteemed international experts, coming from academia, industry, non-profit/cancer organisations, small to mid-size enterprises or contract research organisations (CRO), regulators, health technology assessment (HTA) bodies, and patient organisations. The involvement of patients, caregivers and patient representatives is essential to this effort as their contribution will ensure the recommendation statements and their use remain relevant to the patient community.
As Kathy Oliver, from the International Brain Tumour Alliance and WECAN, highlights: “When developing the proposal for SISAQOL-IMI, the Consortium made sure that at least two final recommendation documents will be developed: a technical document aimed at statisticians and similar stakeholders, and a plain-language version tailored for use by the patient, caregiver, and clinical communities. This will ensure the recommendations are understandable and meaningful to stakeholders irrespective of their statistical knowledge and methodological background.”
1 Pe M, Alanya A, Falk RS, et al. Setting International Standards in Analyzing Patient-Reported Outcomes and Quality of Life Endpoints in Cancer Clinical Trials-Innovative Medicines Initiative (SISAQOL-IMI): stakeholder views, objectives, and procedures. Lancet Oncol 2023; 24: e270–83. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanonc/article/PIIS1470-2045(23)00157-2/fulltext
2 The SISAQOL-IMI project has received funding from the Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) 2 Joint Undertaking under grant agreement No 945052. The IMI Joint Undertaking (JU) is a public-private partnership (PPP) between the European Union (EU), represented by the European Commission (EC), and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA).
3 Coens, Corneel, Madeline Pe, Amylou C. Dueck, Jeff Sloan, Ethan Basch, Melanie Calvert, Alicyn Campbell et al. “International standards for the analysis of quality-of-life and patient-reported outcome endpoints in cancer randomised controlled trials: recommendations of the SISAQOL Consortium.” The Lancet Oncology 21, no. 2 (2020): e83-e96.
4 European Medicines Agency OWP. European Medicines Agency Reflection Paper on the use of patient reported outcome (PRO) measures in oncology studies [Draft]. 2014.
About EORTC
The European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) is a non-governmental, non-profit organisation, which unites clinical cancer research experts, throughout Europe, to define better treatments for cancer patients to prolong survival and improve quality of life. Spanning from translational to large, prospective, multi-centre, phase III clinical trials that evaluate new therapies and treatment strategies as well as patient quality of life, its activities are coordinated from EORTC Headquarters, a unique international clinical research infrastructure, based in Brussels, Belgium.
About the Quality of Life Group
The Quality of Life Group (QLG) strives to improve health-related quality of life (HRQoL) of cancer patients, through dedicated research and the use of HRQoL measures within cancer clinical trials and clinical practice. HRQoL constitutes an important aspect of cancer research and care: it gives a voice to patients, putting their experience at the forefront. The QLG is part of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC).
For further information, please visit the QLG website.
END
SISAQOL-IMI: Setting standards for the use of patient-reported outcome data in cancer trials
Publication of the first consensus paper by the SISAQOL-IMI Consortium
2023-06-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
First soil map of terrestrial and blue carbon highlights need for conservation
2023-06-01
New Curtin University research has identified the most carbon-rich soils in Australia are in areas that are most threatened by human activities and climate change, including Eucalypt and mangrove forests, and woodland and grassland areas that cover large parts of the country’s interior.
Lead researcher Dr Lewis Walden from Curtin’s Soil & Landscape Science in the School of Molecular and Life Sciences said the findings highlighted the need to protect key terrestrial and coastal marine ecosystems, which play an important contributing role in national strategies to mitigate climate change.
“Using multiscale machine ...
Tiny video capsule shows promise as an alternative to endoscopy
2023-06-01
For Embargoed Release: June 1, 2023 at 9:00 am Eastern Time USA
Media Contacts: Kathy Fackelmann, kfackelmann@gwu.edu
WASHINGTON (June 1, 2023)—While ingestible video capsule endoscopes have been around for many years, the capsules have been limited by the fact that they could not be controlled by physicians. They moved passively, driven only by gravity and the natural movement of the body. Now, according to a first-of-its-kind research study at George Washington University, physicians can remotely drive a miniature video ...
National Comprehensive Cancer Network joins collaboration to improve standards in cancer care for Vietnam
2023-06-01
PHILADELPHIA, UNITED STATES & HANOI, VIETNAM [June 1, 2023] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—a not-for-profit alliance of leading cancer centers in the United States—today announced the signing of a Memo of Understanding (MOU) with Vietnam National Cancer Hospital (“K Hospital”) and the Vietnam Cancer Association to work together to improve standards for cancer care throughout the country. Five delegates from NCCN visited Hanoi May 24-26 to sign the MOU and pilot the creation of NCCN Harmonized Guidelines™ for Vietnam.
“We are honored to collaborate with in-country experts to develop and validate Vietnamese harmonizations ...
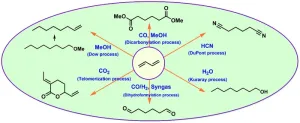
Industrially applied and relevant transformations of 1,3-butadiene using homogeneous catalysts
2023-06-01
The use of 1,3-butadiene as a cheap and abundant raw material for new applications has attracted more interest in recent decades, specifically in the chemical industry. The review covers several important homogeneously catalyzed processes and technologies that are currently used or have the potential to produce fine and bulk chemicals from 1,3-butadiene. This article focuses specifically on the application of homogeneous catalysts and presents representative examples for the readers. For example, palladium-catalyzed telomerization of 1,3-butadiene offers versatile platform chemicals for ...
Ticks prove resilient to extreme temperatures
2023-06-01
PULLMAN, Wash. — Tick season is here, along with the increased danger of Lyme disease, and it turns out the tiny arachnids are even tougher than scientists previously thought.
A recent study in Ecological Monographs shows blacklegged ticks (Ixodes scapularis) are actually really good at surviving extreme cold and heat in nature. Previous lab research suggests that even short periods of especially warm or cold conditions should easily kill ticks, but the Washington State University-led analysis reveals this is only the case for larval ticks in the environment. Instead, ...
Integrating robotics into wildlife conservation: enhancing predator deterrents through innovative movement strategies
2023-06-01
The coexistence of wildlife and agricultural practices has long posed challenges for wildlife conservation, especially when conflicts arise. Livestock predation is a prime example of such conflicts, requiring effective management strategies that minimize human-wildlife conflict while preserving valuable agricultural resources. A new study published in PeerJ Life & Environment, titled "Integrating Robotics into Wildlife Conservation: Testing Improvements to Predator Deterrents through Movement," explores the integration of robotics and agricultural ...
BU researchers identify several new genetic risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease unique to Ashkenazi Jews
2023-06-01
EMBARGOED by Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association, until June 1, 2023, 7 a.m., ET.
Contact: Gina DiGravio, 617-358-7838, ginad@bu.edu
(Boston)—Alzheimer disease (AD), the most common neurodegenerative disorder in the world, affects individuals of all races and ethnicities; however, most genetic research for AD has been performed on individuals of European ancestry (EA) with a limited number of large-scale genetic studies in other populations.
For many centuries, Ashkenazi Jews lived in communities in Eastern Europe and were genetically isolated from their non-Jewish neighbors. As a result, ...
DNA damage repaired by antioxidant enzymes
2023-06-01
In crisis, the nucleus calls antioxidant enzymes to the rescue. The nucleus being metabolically active is a profound paradigm shift with implications for cancer research.
Summary points
The human nucleus is metabolically active, according to the findings of a new study in Molecular Systems Biology by researchers at the CRG in Barcelona and CeMM/Medical University of Vienna,
In a state of crisis, such as widespread DNA damage, the nucleus protects itself by appropriates mitochondrial machinery to carry out urgent repairs that threaten the genome’s integrity
The ...
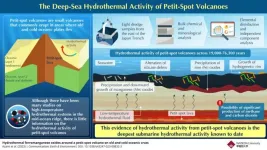
Petit-spot volcanoes involve the deepest known submarine hydrothermal activity, possibly release CO2 and methane
2023-06-01
Underwater volcanism on the Earth's crust are active contributors of many different elements to the oceanic environment. Hence, they play an important role in biogeochemical and chemosynthetic cycles of the ocean. Although there have been many studies on high-temperature hydrothermal systems in the mid-ocean ridge—a series of underwater volcanoes that trace the edges of the different oceanic plates—there is little information on low-temperature hydrothermal systems in other volcanoes, such as "petit-spot" volcanoes.
Petit-spot volcanoes are small volcanoes ...
Producing large, clean 2D materials made easy: just KISS
2023-06-01
Ever since the discovery of the two-dimensional form of graphite (called graphene) almost twenty years ago, interest in 2D materials with their special physical properties has skyrocketed. Famously, graphene was produced by exfoliating bulk graphite using sticky tape. Although it was good enough for a Nobel Prize, this method has its drawbacks. An international team of surface scientists has now developed a simple method to produce large and very clean 2D samples from a range of materials using three different substrates. Their method, kinetic in situ single-layer synthesis (KISS) ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
[Press-News.org] SISAQOL-IMI: Setting standards for the use of patient-reported outcome data in cancer trialsPublication of the first consensus paper by the SISAQOL-IMI Consortium