(Press-News.org) RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- In the United States, low-income immigrant and minority children often live in environments that have highly polluted air. A study led by researchers at the University of California, Riverside, demonstrates this among the Latinx and Purépecha immigrant children and caregivers living along Inland Southern California’s Salton Sea, a highly saline drying lakebed surrounded by agricultural fields. The Purépecha community is an Indigenous group from the Mexican state of Michoacán.
“Children of Latinx and Indigenous Mexican immigrant families living near the Salton Sea are especially vulnerable to the sea’s environmental impact on chronic health conditions,” said Ann Marie Cheney, an associate professor of social medicine, population, and public health in the School of Medicine. “Our study uniquely focuses on caregivers’ understanding of the Salton Sea’s impact on the health of children diagnosed with asthma or chronic respiratory health problems.”
According to Cheney, caregivers offer a unique perspective of Salton Sea impacts on children’s health conditions as they pay attention to the environment and climatic changes, anticipating how they will affect child health.
“While they intimately understand children’s vulnerabilities to environmental and climatic conditions, they often do not have a platform to advocate for their children,” she said. “Through research, we can elevate their voices, what they understand in terms of the effects of the environment on health, and advocate for change to public health policy.”
Cheney and her team engaged with 36 people who participated in either focus groups or one-on-one interviews. Participants lived in the northern part of the Salton Sea and were Latinx and Indigenous Mexican caregivers of children with asthma and respiratory problems. The study, which used principles of community-based participatory research, was from fall 2019 to spring 2021.
Participants characterized the Salton Sea’s environment as toxic. They said it included sulfuric smells, dust storms, chemicals, and fires, which contribute to children’s chronic health conditions, including respiratory illnesses such as asthma, bronchitis, and pneumonia.
In the interviews, participants
shared that during the hot summer months, the Salton Sea emits sulfuric smells, affecting children’s health
noted that dust storms are pronounced during the hot summer months and increase respiratory symptoms and allergies, such as irritated and watery eyes, in children
expressed concern about children’s exposure to agricultural chemicals from the nearby agricultural fields
worried about local agricultural practices in which growers dump chemicals into the Salton Sea
talked about the burning of garbage on nearby tribal lands and its effects on air quality
explained how daily exposure to the Salton Sea environment contributed also to allergies and nosebleeds
noted that when they remove their children from the Salton Sea’s environment, their symptoms improve.
“Our study has important public health implications for vulnerable child populations,” Cheney said. “The Salton Sea and its effects on the children and families living along its border offer a preview into what is to come in the next several decades because of climate change. Without intervention, children, such as those in our study, will be especially vulnerable to respiratory health consequences of climate change and the effects of poor air quality on health.”
The research paper, titled “Latinx and Indigenous Mexican Caregivers’ Perspectives of the Salton Sea Environment on Children’s Asthma, Respiratory Health, and Co-Presenting Health Conditions,” appears in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
Cheney was joined in the study by Gabriela Ortiz, Ashley Trinidad, Sophia Rodriguez, Ashley Moran, and Jaír Chavez of UCR; Andrea Gonzalez of UCLA; and María Pozar of Conchita Servicios de la Comunidad in Mecca, California.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities of the National Institutes of Health. The content of this article does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
The University of California, Riverside is a doctoral research university, a living laboratory for groundbreaking exploration of issues critical to Inland Southern California, the state and communities around the world. Reflecting California's diverse culture, UCR's enrollment is more than 26,000 students. The campus opened a medical school in 2013 and has reached the heart of the Coachella Valley by way of the UCR Palm Desert Center. The campus has an annual impact of more than $2.7 billion on the U.S. economy. To learn more, visit www.ucr.edu.
END
Salton Sea environment detrimental to respiratory health of local children
UC Riverside-led study focuses on caregivers’ take on how the sea affects their children’s health
2023-06-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fellowship offers reporters valuable insight as America ages
2023-06-01
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) has received renewed grant support to welcome a new class of reporters for the Journalists in Aging Fellows Program. The 2023 funders to date include Silver Century Foundation, The John A. Hartford Foundation, Archstone Foundation, and NIHCM Foundation.
Since its founding in 2010, this program has been responsible for more than 800 news stories produced by 217 alumni. It has two goals: to educate journalists about issues in aging, better allowing them to spread a new awareness to general-audience, ethnic, and other minority populations; ...
Critical decision-3A clears way toward standard model test
2023-06-01
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – The U.S. Department of Energy has given the greenlight for the MOLLER experiment to begin procurement of key components with its granting of Critical Decision-3A (CD-3A): Approve Long Lead Procurements. The determination allows the MOLLER project at DOE’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility to begin spending $9.14 million for long-lead procurements of critical items for which designs are complete.
After imagining what it would look like for 17 years, Krishna Kumar felt chills the first time he saw fully engineered drawings of the MOLLER experiment.
“Seeing the designs on paper gave me pins and needles,” said Kumar, professor of ...
Sandia scientists achieve breakthrough in tackling PFAS contamination
2023-06-01
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — A team at Sandia National Laboratories is developing materials to tackle what has become one of the biggest problems in the world: human exposure to a group of chemicals known as PFAS through contaminated water and other products. Sandia is now investing more money to take their research to the next level.
“It’s in the news constantly. It seems every day we hear of another product that is contaminated. We saw sparkling water with PFAS, toilet paper with PFAS, so it’s ...
Better search for the cause of hereditary diseases
2023-06-01
So far, it has not been possible to explain the causes of around half of all rare hereditary diseases. A Munich research team has developed an algorithm that predicts the effects of genetic mutations on RNA formation six times more precisely than previous models. As a result, the genetic causes of rare hereditary diseases and cancer can be identified more precisely.
Variations of genetic sequence occur relatively frequently – on average, one in a thousand nucleotide of a person’s genome is affected. In rare cases, these changes can lead to defective RNAs and hence non-functional proteins. This can lead to dysfunction in individual organs. If a rare disease is suspected, computer-assisted ...
Cross-cultural analysis reveals evolution and persistence of body-based measurement systems
2023-06-01
Body-based units of measure have cognitive and behavioral advantages over standardized measurement systems, according to a new cross-cultural analysis of the use of body-based measurement in more than 180 cultures worldwide, particularly in the design of ergonomic technologies. The findings reveal new insights into body-based measurement as a cultural phenomenon and may help explain the long-term persistence of their use for centuries after the emergence of standardized measurement systems were invented. The ability to measure things plays a central role in how humans understand and interact with the surrounding world and are important drivers in cultural complexity ...
Autonomous realignment and self-healing in multilayer soft electronic devices
2023-06-01
By combining two dynamic polymers, researchers present a new method for achieving autonomous realignment and self-healing in multilayered soft electronic devices and robots, according to a new study. Like human skin, self-healing polymers allow soft electronic and robotic devices to recover autonomously from various forms of damage. Such devices are often multilayered and embedded with conductive or dielectric materials to achieve functional properties while also maintaining the soft mechanical properties of the self-healing ...
Low-temperature method for 3D printing nanoscale optical-grade glass
2023-06-01
A hybrid organic-inorganic polymer resin enables the three-dimensional (3D) printing of nanoscale optical-grade glass at temperatures roughly half of what other approaches require, researchers report. According to the authors, the approach may help redefine the paradigm for the free-form manufacturing of silica glass and enable its use across a wide variety of new technological applications. Silica glasses possess a unique combination of properties, making them one of the most important materials for ...
Study tracks social, genetic evolution in Asian colobine primates
2023-06-01
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Asian colobines, also known as leaf-eating monkeys, have been on the planet for about 10 million years. Their ancestors crossed land bridges, dispersed across continents, survived the expansion and contraction of ice sheets and learned to live in tropical, temperate and colder climes.
A new study reported in the journal Science finds parallels between Asian colobines’ social, environmental and genetic evolution, revealing for the first time that colobines living in colder regions experienced genetic changes and alterations to their ancient social structure that likely enhanced their ability ...
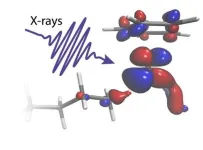
X-rays visualize how one of nature’s strongest bonds breaks
2023-06-01
Embargoed until 1-Jun-2023 14:00 ET (1-Jun-2023 18:00 GMT/UTC)
The use of short flashes of X-ray light brings scientists one big step closer toward developing better catalysts to transform the greenhouse gas methane into a less harmful chemical. The result, published in the journal Science, reveals for the first time how carbon-hydrogen bonds of alkanes break and how the catalyst works in this reaction.
Methane, one of the most potent greenhouse gases, is being released into the atmosphere at an increasing rate by livestock farming as well as the continuing unfreezing of permafrost. Transforming methane and longer-chain alkanes into less harmful and in fact useful chemicals ...
New study shows how adaptations to living in a cold climate promoted social evolution
2023-06-01
For the first time ever, scientists have uncovered evidence that a species’ long-term adaptation to living in an extremely cold climate has led to the evolution of social behaviours including extended care by mothers, increased infant survival and the ability to live in large complex multilevel societies.
The new study, published today in the journal Science, was led by researchers from Northwest University in China and a team including the University of Bristol (UK) and the University of Western Australia, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Salton Sea environment detrimental to respiratory health of local childrenUC Riverside-led study focuses on caregivers’ take on how the sea affects their children’s health