(Press-News.org) A new study from researchers in the Khurana lab at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, in close collaboration with researchers from the Ritz lab at UCLA and the Rubin lab at Harvard University, identified pesticides that could be relevant to the development of Parkinson’s disease. The study was led by Richard Krolewski, MD, PhD, a neurologist in the Brigham’s Division of Movement Disorders and Ann Romney Center for Neurologic Diseases, and Kimberly Paul, PhD, from UCLA, along with collaboration with Edinson Lucumi Moreno within the Khurana lab at the Brigham.
Both genetic and environmental factors may influence the likelihood of developing Parkinson’s disease. Using agricultural records, the researchers investigated 288 pesticides, finding that long-term exposure to 53 of these pesticides was associated with Parkinson’s disease. The team then used a screening system in dopamine neurons derived from Parkinson’s patients to study 39 of those pesticides and identified 10 that were directly toxic to dopamine neurons. The study also found exposure to multiple pesticides used in combination, such as in cotton farming, is more toxic to dopamine neurons than any single pesticide.
“The combination of bench science and epidemiology is quite novel here,” said Krolewski. “The bench science is able to address questions that are difficult to answer with epidemiology while the epidemiology helps direct the bench science – the sum is greater than the parts.”
The Department of Defense supported this project and has now supported the group to utilize diverse stem-cell models derived from Parkinson’s patients to investigate how pesticides and the gut microbiome disrupt key neuronal processes affecting both movement and cognition.
“The findings advance a major goal of the BWH Movement Division to tailor therapies to specific triggers of Parkinson’s in each patient,” said Khurana.
in Nature Communications.
END
Bench-to-field study identifies pesticides that could influence Parkinson's disease
2023-06-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Results of SWOG S1929 trial show patients with small-cell lung cancer with SLFN11 expression can benefit from PARP inhibitor added to immune checkpoint blockade
2023-06-02
Among patients with extensive stage small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) that is positive for expression of the Schlafen-11 gene (SLFN11), those who received maintenance atezolizumab immunotherapy plus the PARP inhibitor talazoparib had significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS) times than those who received atezolizumab alone (median PFS 4.2 months versus 2.8 months).
These results from the phase II S1929 trial conducted by the SWOG Cancer Research Network, a clinical trials group funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), will be reported ...
UCSF Health Cancer experts featured at premier cancer meeting
2023-06-02
Oncology specialists from around the globe will gather for the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting to discuss the latest cancer therapies, technologies, research and education.
The theme this year is Partnering With Patients: The Cornerstone of Cancer Care and Research. More than 30,000 people are expected to attend the meeting taking place in Chicago and online June 2-6, 2023.
“As the world’s leading clinical cancer meeting, ASCO is an important event for oncology professionals to share information on the latest ...
Multiple sclerosis more prevalent in Black Americans than previously thought
2023-06-02
Multiple sclerosis has traditionally been considered a condition that predominantly affects white people of European ancestry. However, a new analysis conducted by a North American team led by University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers suggests that the debilitating neurological condition is more prevalent in Black Americans than once thought. It is also far more prevalent in Northern regions of the country including New England, the Dakotas, and the Pacific Northwest.
Findings from the new study were recently published in the journal JAMA Neurology.
“We found a much higher prevalence of multiple sclerosis in Black Americans than previously ...
Sensory adapted dental rooms significantly reduce autistic children’s physiological and behavioral stress during teeth cleanings
2023-06-02
New results from a study led by USC researchers at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles show that a sensory adapted dental clinic environment creates less distressing oral care experiences for autistic children. The open-access article is available today in JAMA Network Open.
“We’ve shown that the combination of curated visual, auditory and tactile adaptations — all of which are easily implemented, relatively inexpensive and don’t require training to safely use — led to statistically significant decreases in autistic children’s behavioral ...
Couples’ social networks took long-lasting hit during COVID
2023-06-02
Key takeaways:
A UCLA study shows that a the outset of the COVID-19 pandemic, social interactions, both virtual and in person, declined significantly for married couples.
The decline was found to be greater and more long-lasting for Black and Latino couples and lower-income couples than for white couples and wealthier couples.
The researchers suggest exploring new ways of protecting public health during crises that also help more vulnerable populations sustain meaningful relationships.
Following the lockdowns and restrictions on public gatherings in the early days of COVID-19, the social networks of white, ...
AI software can provide ‘roadmap’ for biological discoveries
2023-06-02
Predicting a protein’s location within a cell can help researchers unlock a plethora of biological information that’s critical for developing future scientific discoveries related to drug development and treating diseases like epilepsy. That’s because proteins are the body’s “workhorses,” largely responsible for most cellular functions.
Recently, Dong Xu, Curators Distinguished Professor in the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at the University of Missouri, and colleagues updated their protein localization prediction model, MULocDeep, ...
Study helps explain what drives psoriasis severity and offers clues as to how disease may spread to other body parts
2023-06-02
Beneath and beyond the reddish, flaky lesions that form in the skin of those with psoriasis, mild and severe forms of the disease can be told apart by the activity of key cells and signaling pathways, a new study shows.
Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the study mapped hidden features of inflammation and how they compared in cases of increasing severity of psoriatic disease. The team’s findings may help explain how small areas of skin inflammation can have wide-ranging effects in other parts of the body. Up to one-fifth of those with the skin disease, the researchers note, ...
New study finds strengthening protection of existing parks is crucial for biodiversity conservation
2023-06-02
-With pictures-
In a new study, bioscientists argue that strengthening the protection given to areas already protected under law or by local communities is as critical for safeguarding biodiversity as creating new protected areas.
The research team, which included scientists from Durham University, National University of Singapore (NUS) and Princeton University, found that about 70 per cent of the roughly 5000 species analysed either have no apparent representation in protected areas, occur in protected areas that have been downgraded, downsized or degazetted, ...
Scientists reveal new details of cellular process which prevents spread of cancer
2023-06-02
Researchers have for the first time characterised a unique molecular mechanism of the early stages of programmed cell death or apoptosis, a process which plays a crucial role in prevention of cancer.
The study, which is published today (Friday 2nd June 2023) in Science Advances, was led by Dr Luke Clifton at the STFC ISIS Neutron and Muon Source (ISIS) in Oxfordshire, alongside co-lead Professor Gerhard Gröbner at the University of Umeå and partners at the European Spallation Source in Sweden. It is ...
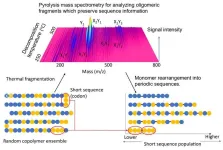
Development of an AI-based mass spectrometric technique capable of determining the monomeric sequence of a polymer
2023-06-02
1. The National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) has developed an AI-based mass spectrometric technique capable of determining the monomeric sequence of a polymer. This technique may be useful in gaining a deeper understanding of basic polymeric structures, facilitating the development of new materials and helping solve plastic recycling problems.
2. A polymer is a very large molecule composed of a chain of many (ranging from hundreds to hundreds of thousands) small molecules called monomers that are bonded together. Many common polymers (e.g., plastics and resins) are copolymers, consisting of several different types of monomers. During the copolymerization process, the monomers ...