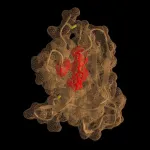
Scientists expand understanding of limb evolution in earliest birds
2023-06-05
(Press-News.org)
The assembly of the volant bird body plan from the ancestral bulky dinosaurian condition is an enduring topic of evolutionary biology. The body plan of volant birds demonstrates a pronounced decrease in body size and proportionate elongation of the forelimbs. Given the scaling relationship between limb and body size, changes to the former were likely clouded by changes to the entire body size.
Since changes to individual limb elements provides the direct basis for natural selection, they are essential to comprehending branch- and lineage-specific evolutionary patterns across the transition from terrestrial to volant theropods. Nevertheless, few studies have explicitly explored the evolutionary path of the characteristic avialan limb configuration in its earliest history.
Now, however, paleontologists from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have reported a detailed scientific study of limb size evolution across the theropod-bird transition.
The study was published in Nature Ecology & Evolution on June 5.
By quantifying morphological disparity and the evolutionary rate, the researchers discovered a shift to low disparity and a decelerated evolutionary rate near the origin of birds. This contrasts with the traditional wisdom that an evolutionary innovation such as powered flight would trigger and accelerate the evolutionary rate. This comparative, statistical analysis indicates that the decelerated evolutionary rate may be largely ascribed to the low disparity and low rate of forelimb evolution.
"We believe that forelimb evolution has been constrained to the basic 'blueprint' needed for powered flight, and thus the morphospace that can be realized by early diverging avialans was limited," said Dr. WANG Min, the lead and corresponding author of this study. The acquisition of derived flight-relevant musculoskeletal features by crownward taxa may have broken the limb proportion constraint and thus ultimately contributed to the enormous forelimb disparity seen in extant birds.
According to Dr. ZHOU Zhonghe, co-author of the study, "Our analyses reveal that avialan-like limb proportions were established earlier in forelimbs than in hindlimbs in theropod history, supporting the 'pectoral early-pelvic late' hypothesis."
The recovered patterns of disparity and rate of appendicular limb evolution demonstrate how the early avialan bauplan was shaped deeply by natural selection driven by powered flight.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-06-05
How do today’s indigenous communities of South America trace back to the history of human migration and contact in the continent? An international team has worked to reconstruct the legacy of Chile’s largest indigenous community, the Mapuche, in a quest to strengthen their representation in the history of the continent. It appears the Mapuche long lived in relative isolation but do bear some influences from other populations of the Central Andes and the far south of Chile.
South America was the last continent ...
2023-06-05
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – June 5, 2023 – Researchers at Sanford Burnham Prebys, collaborating with scientists from Eli Lilly and Company, have revealed the structure and function of a drug called LY3361237, which can reduce the harmful activity of the immune system to help treat autoimmune diseases. Their work laid the foundation for a new treatment that’s currently in a Phase 2 clinical trial for lupus, an autoimmune disease affecting multiple organs in the body. The study is published in Structure, a Cell Press journal.
The ...
2023-06-05
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Johns Hopkins scientists have developed a method involving artificial intelligence to visualize and track changes in the strength of synapses — the connection points through which nerve cells in the brain communicate — in live animals. The technique, described in Nature Methods, should lead, the scientists say, to a better understanding of how such connections in human brains change with learning, aging, injury and disease.
“If you want to learn more about how an orchestra plays, you have to watch individual players over time, and this ...
2023-06-05
Two new discoveries from the Dudley lab at UVA Cancer Center highlight the different roles of blood vessels in solid tumors – and the findings could help prevent breast cancer from spreading and enhance the effectiveness of one of the most important new cancer treatments in many years.
In one new scientific paper, researcher Andrew C. Dudley, PhD, and his team report that the effectiveness of immunotherapy drugs called immune check blockade is enhanced when blood vessels are targeted in a specific way. (Immunotherapy enhances the power of the immune system to fight cancer and other diseases.) In another paper, published ...
2023-06-05
Awash in a rowed sea of its brethren, a corn leaf relegated to the lowest rung of its stem spends much of a June afternoon doused in shade cast by the higher-ups.
Then a gust begins pushing, pulling and twisting the waxy wings in concert, cracking a window to the fireball roiling 93 million miles away. It’s a prime, precious opportunity for photosynthesis to transform the sunlight into food. Unfortunately, the photosynthetic equivalent of a surge protector — one evolved to help plants mitigate damage driven by sudden spikes of high-intensity light — is slow to reset after so much time in the shade. The gust dissipates, the moment ...
2023-06-05
Moving towards a more inclusive approach to medicine
Release of pangenome representing wide diversity of individuals ushers in new understanding of human biology and disease
The first human genome, which has served as the reference until now, was released approximately 20 years ago. It was a landmark accomplishment that had a huge impact on biomedical research and changed the way scientists study human biology. But it was based on just a few individuals and did not capture the full genetic diversity of the human population.
An important step forward for both biology and biomedical research
“Since ...
2023-06-05
SAN ANTONIO — June 5, 2023 —Southwest Research Institute is expanding its flow meter research in collaboration with NYSEARCH, a nonprofit research and development organization for the gas industry, to address the impact of introducing hydrogen and natural gas blends into the residential and commercial energy mix. In the second phase of the program, SwRI will expand its research in measuring the energy content of blended gas to determine the accuracy of current flow meter technology for monitoring usage in homes.
Natural gas is widely used to power appliances and heat ...
2023-06-05
Researchers from Queen Mary University of London analysed 2.6 million posts on popular social media network Nextdoor and accurately predicted individuals’ income by solely examining the posts they’ve published. Striking differences in the content shared by people who live in wealthier versus poorer neighbourhoods has led researchers to believe that our general online posting activity, beyond Nextdoor, can reveal our socioeconomic status, making user profiling possible.
Knowing users’ income could allow social media platforms to recommend income-based content, and advertisers and online shops can target people based on their ...
2023-06-05
ABSTRACTS: 3121, 4504, LBA4619
CHICAGO ― Three clinical trials led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center demonstrated positive results from the targeted therapy erdafitinib for patients with multiple tumor types harboring FGFR alterations. The data are being presented at the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting.
Erdafitinib is an oral medication that blocks the activity of FGFR signaling proteins, which are important for a variety of normal cellular processes. However, FGFR genetic alterations can drive the development of many ...
2023-06-05
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a major psychiatric condition that afflicts about 1% of people. Symptoms of BD include sudden onset of depressive mood with loss of interest which alternates with a manic state of hyperactivity. The suffering of the patients and societal cost of this disorder requires the use of continued therapeutic management. Current medications—although vital for patients with BD—are not perfect solutions, given their potential side-effects and treatment resistance. This necessitates ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists expand understanding of limb evolution in earliest birds