(Press-News.org)
As the Co-Editors-in-Chief of Zoonoses, Dr. Lynn Soong (University of Texas Medical Branch, TX, USA) and Dr. Xiaoping Dong (Chinese Center for Disease Control & Prevention, Beijing, China) extend a warm welcome to Dr. Fernando Rosado Spilki, new Executive Editor-in-Chief (Vector Biology/Epidemiology) of Zoonoses.
Dr. Spilki is currently a Professor in the Institute of Health Sciences at Feevale University, Novo Hamburgo, Brazil. He received B.S. in Veterinary Medicine (2001), M.S. in Veterinary Sciences/Animal Virology (2004) both from the Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, and his Ph.D. in Genetics & Molecular Biology (2006) from the Universidade Estadual de Campinas. His research is focused on emerging and zoonotic viruses relevant to diseases in humans, domestic and wild animals, as well as viral contaminants of water and food. Dr Spilki has published more than 211 peer-reviewed articles in high-impact journals, served as the first-author for five books and a co-author for another 18 book chapters, and is an active reviewer of several international journals (see below links for more information).
Web of Science: https://www.webofscience.com/wos/author/record/E-3736-2010
Google Scholar: https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=a5HL89QAAAAJ&hl
Scopus Author Identifier: 6603486140
ORCID ID: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5804-7045
Commenting on his appointment, Dr. Spilki noted that:
Zoonoses can and should be a relevant communication channel for researchers working on the frontier of emergence and re-emergence of new pathogens. The integrated actions of research groups in the search for pathogens with potential impact on public health from the natural environment to their primary circulation in human populations, including surveillance, diagnosis, mitigation and therapeutic measures, are topics of interest to societies and have in Zoonoses an appropriate communication channel.
We look forward to working with Dr. Spilki and Zoonoses editorial board members to further advance the journal’s goal and publication scope, and more importantly, to promote international research related to medical sciences, veterinary sciences, and public health. We also extend our sincere appreciation to all our authors, reviewers, readers, and editors for their continued support for Zoonoses.
# # # # # #
Zoonoses is fully open access journal for research scientists, physicians, veterinarians, and public health professionals working on diverse disciplinaries of zoonotic diseases. Zoonoses is now open for submissions; articles can be submitted online at https://mc04.manuscriptcentral.com/zoonoses
There are currently no author submission or article processing fees.
Please visit https://zoonoses-journal.org/ to learn more about the journal.
Editorial Board: https://zoonoses-journal.org/index.php/editorial-board/
# # # # # #
Zoonoses is available on ScienceOpen (https://www.scienceopen.com/search#collection/839df240-327f-47dd-b636-9b728dff9700).
# # # # # #
Follow Zoonoses
Twitter @ZoonosesJ
Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/Zoonoses-Journal-100462755574114
LinkedIn (https://www.linkedin.com/company/zoonoses/)
END
Fungi stores a third of carbon from fossil fuel emissions and could be essential to reaching net zero, new study reveals
Mycorrhizal fungi are responsible for holding up to 36 per cent of yearly global fossil fuel emissions below ground - more than China emits each year
The fungi make up a vast underground network all over the planet underneath grasslands and forests, as well as roads, gardens, and houses on every continent on Earth
It is not only crucial to storing carbon and keeping the planet cooler, but are also essential to global biodiversity
Researchers ...
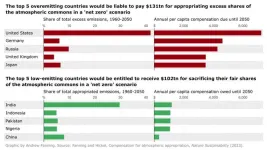
Industrialised nations responsible for excessive levels of carbon dioxide emissions could be liable to pay a total of $170 trillion in compensation or reparations by 2050 to ensure climate change targets are met, say researchers.
This money, which amounts to nearly $6 trillion per year or about 7% of annual global Gross Domestic Product (GDP), would be distributed as compensation to low-emitting countries that must decarbonise their economies far more rapidly than would otherwise be required.
Financial redress for the losses and damages that climate-vulnerable countries face due to the excessive CO2 emissions of others is seen as an increasingly important ...
Kim Kaplan
301-588-5314
Kim.Kaplan@usda.gov
BRIDGEcereal: Self-Teaching Web App Improves Speed, Accuracy of Classifying DNA Variations Among Cereal Varieties
PULLMAN, WA, June 5, 2023—Agricultural Research Service and Washington State University scientists have developed an innovative web app called BRIDGEcereal [https://bridgecereal.scinet.usda.gov/] that can quickly and accurately analyze the vast amount of genomic data now available for cereal crops and organize the material into intuitive charts that identify patterns locating genes of interest.
With the rapid advancements in ...
About The Study: This survey study found that 28% of youth-serving U.S. mental health facilities offered LGBTQ-specific mental health services in 2020. Although some states had relatively high levels of LGBTQ service availability as a percentage of facilities, many of these states had few facilities available to children per capita. Public mental health facilities were less likely to offer LGBTQ-specific mental health services, a concern given that the cost of care is a barrier to services. The findings suggest a need to expand availability of LGBTQ services ...
New research has revealed being active could lower the risk of type 2 diabetes, even in people with a high genetic risk of developing the medical condition.
The University of Sydney-led study found higher levels of total physical activity, especially moderate- to vigorous-intensity physical activity, had a strong association with a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
The findings were published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
The researchers say the study demonstrates higher levels of physical activity should be promoted as a major strategy for type 2 diabetes ...
Researchers who lead the world’s first comprehensive sequencing program for newborn infants have published the next chapter in the ongoing study of the BabySeq Project, with new findings on infants and families who have been followed for 3-5 years. In a study published today in the American Journal of Human Genetics, researchers from Mass General Brigham and Boston Children’s Hospital reported that over 10 percent of the first 159 infants to undergo screening through DNA sequencing were discovered ...
DURHAM, N.C. – Tirzepatide, a drug approved for diabetes and on the fast track for approval as a weight loss therapy, works through a unique ability to activate two different mechanisms the body uses to control insulin secretion and energy balance, Duke Health researchers report.
The finding, reported June 5 in the journal Nature Metabolism, is the first study to use cells from human donors to demonstrate how tirzepatide stimulates insulin secretion, an important action utilized by this drug to lower blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes.
“Understanding the potential of drugs ...
CHICAGO – Patients with early relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma had significantly improved overall survival when treated with the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) when compared to the current standard-of-care chemoimmunotherapy, according to results of the Phase III ZUMA-7 trial reported by researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Data from the study were presented today by Jason Westin, M.D., director of clinical research in the Department of Lymphoma and Myeloma, at the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting and published concurrently in ...
Women have long searched for remedies for the bothersome hot flashes that often come with menopause.
In a novel investigation, researchers at UC San Francisco tested the benefits of continuously wearing a nitroglycerin patch – an established treatment for chest pain from coronary artery disease – for menopausal women experiencing at least seven hot flashes a day. Unlike most treatments for hot flashes that target brain mechanisms, nitroglycerin works on blood vessels throughout the body.
The results were mixed. While ...
The assembly of the volant bird body plan from the ancestral bulky dinosaurian condition is an enduring topic of evolutionary biology. The body plan of volant birds demonstrates a pronounced decrease in body size and proportionate elongation of the forelimbs. Given the scaling relationship between limb and body size, changes to the former were likely clouded by changes to the entire body size.
Since changes to individual limb elements provides the direct basis for natural selection, they are essential to comprehending branch- and lineage-specific evolutionary patterns across the transition from terrestrial to ...