(Press-News.org)
“The current study analyzed the correlation between BORIS mutations and the expression of the protein in breast cancer cases.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 5, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on May 26, 2023, entitled, “Association of mutation and expression of the brother of the regulator of imprinted sites (BORIS) gene with breast cancer progression.”
The brother of the regulator of imprinted sites (BORIS), 11 zinc-finger transcription factors, is a member of the cancer-testis antigen (CTA) family. It is mapped to chromosome number 20q13.2 and this region is genetically linked to the early onset of breast cancer.
In the current study, researchers Mohammad Salman Akhtar, Naseem Akhter, Arshi Talat, Raed A. Alharbi, Abdulmajeed A.A. Sindi, Faisal Klufah, Hanan E. Alyahyawi, Abdulmohsen Alruwetei, Abrar Ahmad, Mazin A. Zamzami, SVS Deo, Syed Akhtar Husain, Osama A. Badi, and Mohammad Jahir Khan from Al-Baha University, Jamia Millia Islamia, ITS Dental College, Qassim University, King Abdulaziz University, All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), Henry Ford Health System, and Jawahar Lal Nehru University analyzed the correlation between BORIS mutations and the expression of the protein in breast cancer cases.
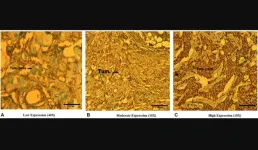
“The present study is to find out the mutations of BORIS genes in hot spot exons by PCR-SSCP and by automated DNA sequencing in breast cancer tissue samples along with adjacent normal samples.”
A population-based study including a total of 155 breast cancer tissue samples and an equal number of normal adjacent tissues from Indian female breast cancer patients was carried out. Mutations of the BORIS gene were detected by polymerase chain reaction-single standard confirmation polymorphisms (PCR-SSCP) and automated DNA sequencing and by immunohistochemistry for BORIS protein expression were performed. The observed findings were correlated with several clinicopathological parameters to find out the clinical relevance of associations.
“The BORIS mutations and high protein expression occur frequently in carcinoma of the breast suggesting their association with the onset and progression of breast carcinoma. Further, the BORIS has the potential to be used as a biomarker.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28442
Correspondence to: Mohammad Salman Akhtar
Emails: mdsalmanakhtar@yahoo.com, milyas@bu.edu.sa
Keywords: BORIS, breast cancer, mutation, transcription factor, PCR-SSCP
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
LabTube
Soundcloud
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact: media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
The research, published in the journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia, is further evidence that the menopause transition is a particularly important time for women and their doctors to pay attention to heart health, in turn protecting their brain health.
“It is shocking to know that two-thirds of Americans with Alzheimer’s disease are women,” said Meiyuzhen (Chimey) Qi, first author and Ph.D. candidate in epidemiology at Pitt Public Health. “The most common modifiable risk factor for dementia is cardiovascular disease, and, interestingly, a woman’s ...
About The Study: Among patients diagnosed with cancer in California and Georgia between 2013 and 2019, only 6.8% underwent germline genetic testing. Compared with non-Hispanic white patients, rates of testing were lower among Asian, Black, and Hispanic patients.
Authors: Allison W. Kurian, M.D., M.Sc., of Stanford University in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.9526)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
Glut1 deficiency syndrome is a rare and disabling neurological disease still relatively unknown to the medical community. A mutation in the SLC2A1 gene in affected patients causes the glucose transporter GLUT1 to malfunction. Since this transporter is responsible for the glucose entering glial cells, the brain is deprived of some of the sugar it needs to function correctly, leading to seizures, bouts of abnormal movement, and developmental delays.
These symptoms can be improved by managing the metabolic disorder that causes the disease via a high-fat ...
The use of mobile technologies to collect and analyze individuals’ location information has produced massive amounts of consumer location data, giving rise to an elaborate multi-billion-dollar system in which consumers can share personal data in exchange for economic benefits. But privacy risks prevail.
In a new study, researchers used machine learning to create and test a framework that quantifies personalized privacy risks; performs personalized data obfuscation; and accommodates a variety of risks, utilities, and acceptable levels of risk-utility tradeoff. The framework ...
Among the most fundamental questions in astronomy is: How did the first stars and galaxies form? NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is already providing new insights into this question. One of the largest programs in Webb’s first year of science is the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey, or JADES, which will devote about 32 days of telescope time to uncover and characterize faint, distant galaxies. While the data is still coming in, JADES already has discovered hundreds of galaxies that existed when the universe was less than 600 million years old. The team also has identified galaxies sparkling with a multitude of young, hot ...
A delicate tracery of dust and bright star clusters threads across this image from the James Webb Space Telescope. The bright tendrils of gas and stars belong to the barred spiral galaxy NGC 5068, whose bright central bar is visible in the upper left of this image – a composite from two of Webb’s instruments. NASA Administrator Bill Nelson revealed the image Friday during an event with students at the Copernicus Science Centre in Warsaw, Poland.
NGC 5068 lies around 20 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Virgo. This image of the central, bright star-forming regions ...
A new ‘digital decision support tool’ enabling the transition towards more diversified and sustainable agricultural systems has been developed by an international team of researchers from Germany, France, and Czech Republic.
The research led by Dr Ioanna Mouratiadou from the Leibniz Centre for Agricultural Landscape Research, and published in Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, presents the ‘Digital Agricultural Knowledge and Information System (DAKIS)’ as a data integration ...
Baltimore, MD—New work led by Carnegie’s Phillip Cleves uses cutting-edge CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing tools to reveal a gene that’s critical to stony corals’ ability to build their reef architectures. It is published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Stony corals are marine invertebrates that build large skeletons, which form the basis of reef ecosystems. These biodiversity hotspots are home to about a quarter of known marine species.
“Coral reefs have ...
Human influences have the potential to reduce the effectivity of communication in bees adding further stress to struggling colonies, according to new analysis.
Scientists at the University of Bristol studying honeybees, bumblebees and stingless bees found that variation in communication strategies are explained by differences in the habitats that bees inhabit and differences in the social lifestyle such colony size and nesting habits.
The findings, published today in PNAS, reveal that anthropogenic change, such as habitat conversion, climate change and the use of agrochemicals, are altering the world bees occupy, and it is becoming increasingly clearer that this affects communication ...
· Regulating cell mechanics stimulates hair growth in mice
· Next step will be testing if delivering microRNA via nanoparticles grows hair
· Potential for human hair growth
CHICAGO --- Just as people’s joints can get stiff as they age and make it harder for them to move around, hair follicle stem cells also get stiff, making it harder for them to grow hair, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study.
But if the hair follicle’s stem cells are softened, ...