(Press-News.org)
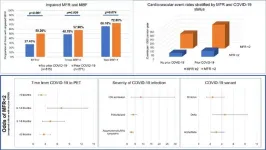
Patients infected with beta and delta COVID-19 variants, and those who required hospital stays for COVID-19 infection, were more likely to experience heart issues associated with long COVID, according to a recent Houston Methodist study published in the European Heart Journal – Cardiovascular Imaging. Patients recovering from the omicron variant were least likely to have microvascular involvement.
“This new data expands our understanding of myocardial flow reserve as an important prognostic marker in general and specifically in COVID-19,” said Mouaz Al-Mallah, M.D., corresponding author of the study and director of cardiovascular PET at Houston Methodist DeBakey Heart and Vascular Center.
“This is good news for individuals who had omicron and are concerned about long COVID. Patients with lingering symptoms such as chest pain or shortness of breath following a severe infection may want to have a PET scan with blood flow assessment to check for microvascular dysfunction,” said Al-Mallah, who is also the current president of the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology. The study also found that microvascular dysfunction started to be seen less often after nine months to one year following infection suggesting that this type of abnormality may be reversible.
The American Society for Nuclear Cardiology’s PET scan guidelines now recommend including blood flow assessment routinely.
Last year, Al-Mallah and team published an initial study in JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging examining the coronary microvasculature health of 393 patients, including 101 with prior COVID-19 infection who had lingering symptoms. This was the first published study linking reduced blood flow reserve in the heart and COVID-19.
With over 600 million confirmed cases and nearly seven million deaths, the COVID-19 pandemic has left a lasting mark on the world. While the World Health Organization (WHO) ended the global health emergency declaration in May, long COVID remains largely a mystery.
According to Al-Mallah, more studies are needed to further assess the microvascular health of patients with prior COVID-19 and identify how these findings could influence patient care in the context of long-haul COVID-19.
Additional collaborators on this study include Ahmed Ibrahim Ahmed, Mahmoud Al Rifai, Fares Alahdab, Jean Michel Saad, Yushui Han, Moath Said Alfawara, Malek Nayfeh, Maan Malahfji, Faisal Nabi, John J Mahmarian, John P. Cook, and William A Zoghbi.
This work was supported, in part, by grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01 HL133254; R01 HL148338; and R01 HL157790).
For more information about Houston Methodist, visit houstonmethodist.org. Follow us on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and our On Health and Leading Medicine blogs.
###
For more information: Coronary microvascular health in symptomatic patients with prior COVID-19 infection: an updated analysis. European Heart Journal (online May 31, 2023) Ahmed Ibrahim Ahmed, Mahmoud Al Rifai, Fares Alahdab, Jean Michel Saad, Yushui Han, Moath Said Alfawara, Malek Nayfeh, Maan Malahfji, Faisal Nabi, John J Mahmarian, John P. Cook, William A Zoghbi and Mouaz H Al-Mallah. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjci/jead118
END
Contact: Clare Leahy clare.leahy@hdruk.ac.uk 07748016062
Event registration for press: https://bit.ly/45rIQBr
Health Data Research UK (HDR UK) is launching its Health Data Science Black Internship Programme for the third year running at its Opening Ceremony on Wednesday 21 June from 12-5pm at the Curzon Building in Birmingham City University.
The programme, run in partnership with the UK Health Data Research Alliance and 10,000 Black Interns is helping to tackle the underrepresentation of Black people within science, technology, engineering, and mathematics ...
DARIEN, IL – Sleep researcher Dayna A. Johnson is the recipient of the 2023 Diversity, Equity and Inclusion Leadership Award from the Associated Professional Sleep Societies, a joint initiative of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the Sleep Research Society.
The award recognizes individuals who have made significant contributions to sleep medicine or sleep and circadian science through their work to increase the diversity, equity, and inclusion of sleep medicine providers, or to develop educational programs, research, or clinical work aimed at reducing disparities. The award presentation occurred Monday, June 5, during the plenary session of the ...
Patents from the Naval Postgraduate School (NPS) are a measure of novel inventions, but each also tells a story of a relevant idea with warfighting impact. NPS Department of Physics Associate Professor Ray Gamache and his former graduate student, NPS alumnus U.S. Marine Corps Maj. Chris Phifer, developed and recently patented a new polymer-based, self-sealing fuel line capable of withstanding a .50 caliber bullet without losing so much as a single drop.
“We’re not just a physics department, we’re the applied physics department,” Gamache said. “While ...
1. A supervised hospital walking program may reduce nursing facility admissions for older adults
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M22-3679
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
A randomized trial of older veterans found that hospitalized persons enrolled in a supervised walking program known as STRIDE (AssiSTed EaRly MobIlity for HospitalizeD VEterans) were less likely to be discharged to a skilled nursing facility. However, the authors noted that participation in the program was low and there was no change associated with length of hospital stay or inpatient falls. The study is ...
Tirzepatide is a recently approved treatment for type-2 diabetes. Treatment with tirzepatide decreases body weight while improving glucose metabolism in patients with obesity and type-2 diabetes. Although the drug is designed to activate receptors for glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), the contribution of activating the GIP receptor in the overall efficacy of tirzepatide is not fully understood. A team of researchers demonstrated for the first time that tirzepatide stimulates insulin secretion in the human pancreas via the GIP receptor. These results contrast with findings in ...
Tinnitus, the ringing, buzzing or hissing sound of silence, varies from slightly annoying in some to utterly debilitating in others. Up to 15% of adults in the United States have tinnitus, where nearly 40% of sufferers have the condition chronically and actively seek relief.
A recent study from researchers at the University of Michigan’s Kresge Hearing Research Institute suggests relief may be possible.
Susan Shore, Ph.D., Professor Emerita in Michigan Medicine’s Department of Otolaryngology and U-M’s Departments of Physiology and Biomedical Engineering, led research on how the brain processes bi-sensory ...
“The current study analyzed the correlation between BORIS mutations and the expression of the protein in breast cancer cases.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 5, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on May 26, 2023, entitled, “Association of mutation and expression of the brother of the regulator of imprinted sites (BORIS) gene with breast cancer progression.”
The brother of the regulator of imprinted sites (BORIS), 11 zinc-finger transcription factors, ...
The research, published in the journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia, is further evidence that the menopause transition is a particularly important time for women and their doctors to pay attention to heart health, in turn protecting their brain health.
“It is shocking to know that two-thirds of Americans with Alzheimer’s disease are women,” said Meiyuzhen (Chimey) Qi, first author and Ph.D. candidate in epidemiology at Pitt Public Health. “The most common modifiable risk factor for dementia is cardiovascular disease, and, interestingly, a woman’s ...
About The Study: Among patients diagnosed with cancer in California and Georgia between 2013 and 2019, only 6.8% underwent germline genetic testing. Compared with non-Hispanic white patients, rates of testing were lower among Asian, Black, and Hispanic patients.
Authors: Allison W. Kurian, M.D., M.Sc., of Stanford University in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.9526)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
Glut1 deficiency syndrome is a rare and disabling neurological disease still relatively unknown to the medical community. A mutation in the SLC2A1 gene in affected patients causes the glucose transporter GLUT1 to malfunction. Since this transporter is responsible for the glucose entering glial cells, the brain is deprived of some of the sugar it needs to function correctly, leading to seizures, bouts of abnormal movement, and developmental delays.
These symptoms can be improved by managing the metabolic disorder that causes the disease via a high-fat ...