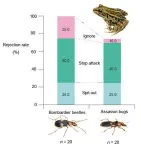
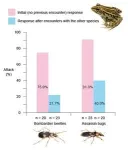
(Press-News.org)
One of the challenges in treating burn victims is the frequency of dressing changes, which can be extremely painful.
To bring relief to this and other problems, University of Waterloo researchers have created a new type of wound dressing material using advanced polymers. This new dressing could enhance the healing process for burn patients and have potential applications for drug delivery in cancer treatment as well as in the cosmetic industry.
"To treat burn victims, we can customize the shape using a 3D printer, secondly, the material has fine-tuned surface adhesion, which is a key feature", said Dr. Boxin Zhao, a professor in Waterloo's Department of Chemical Engineering, whose team has made significant strides in developing intelligent hydrogel materials for use as a reusable wound dressing. "The material can easily adhere to the skin and be taken off. It's a very delicate balance within the material to make the adhesion work."
In developing the dressing, the researchers conducted a 3D scan of the patient's face and body parts to customize it to an individual's needs. This enables the dressing to make good contact with surfaces like noses and fingers, making it ideal for creating personalized wound dressings for burn patients.
The material also has applications for cancer treatment. In traditional chemotherapy treatment, a patient may need to be in a clinic for hours, which can be tiring and uncomfortable. This dressing can provide a constant drug release outside the clinic setting, alleviating some of the challenges associated with traditional methods.
The material used to create these smart dressings includes a biopolymer derived from seaweed, a thermally responsive polymer, and cellulose nanocrystals. The dressing's thermal responsiveness allows it to warm on the skin and gently lower to room temperature. Additionally, when chilled in the fridge, the dressing expands but shrinks to a smaller size at body temperature, making it easier and less painful to remove. Also, the dressing is designed to provide time-release medication, allowing for longer-lasting pain relief.
"We also envision applications in the beauty and cosmetic industry," said Zhao, Waterloo's Endowed Chair in Nanotechnology. "Cosmetologists can utilize 3D scanning technology to analyze their clients' facial features and customize hydrogel masks infused with specific facial and skin regimen products. Additionally, this innovative approach can benefit plastic surgeons."
This research is proof of concept for Zhao's Surface Science and Bio- nanomaterials Laboratory Group. The next step for Zhao's research group is to continue improving the material's properties to make it healthier and commercially viable.
A study highlighting the team's progress was recently published in the Journal of Colloids and Interface Science.
END
Chatbots are increasingly becoming a part of health care around the world, but do they encourage bias? That’s what University of Colorado School of Medicine researchers are asking as they dig into patients’ experiences with the artificial intelligence (AI) programs that simulate conversation.
“Sometimes overlooked is what a chatbot looks like – its avatar,” the researchers write in a new paper published in Annals of Internal Medicine. “Current chatbot ...
An international research team from Tanzania and Japan created a smartphone app and conducted a pilot study of how the app might be used to improve midwives’ knowledge and skills in Tanzania. Their study focused on the app’s potential effects on the learning outcomes of midwives and birth preparedness of pregnant women in Tanzania.
The team’s work is published in the journal PLOS ONE on March 31, 2023.
“The smartphone app for midwives showed significant improvements in their learning outcomes, leading to better birth preparations for pregnant women in Tanzania. This study highlights the potential of leveraging technology ...
An international team of astronomers has detected complex organic molecules in the most distant galaxy to date using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope.
The discovery of the molecules, which are familiar on Earth in smoke, soot and smog, demonstrates the power of Webb to help understand the complex chemistry that goes hand-in-hand with the birth of new stars even in the earliest periods of the universe’s history. At least for galaxies, the new findings cast doubt on the old adage that where there’s smoke, there’s ...
Children who are breastfed for longer appear to be more likely to gain slightly better results in their school GSCEs at age 16 compared with non-breastfed children, suggests a study published online in the journal Archives of Disease in Childhood.
The evidence of improved educational outcomes is still apparent even when various factors are taken into account such as people’s socio-economic status and their parents’ intelligence.
Previous studies have suggested that children breastfed for longer have improved educational outcomes later in life. However these are relatively scarce, and ...
A method of care involving skin-to-skin contact between a mother and her prematurely born or low birth weight baby appears to impact the child’s chances of survival significantly, suggests a study published online in the journal BMJ Global Health.
Starting the intervention within 24 hours of birth and carrying it out for at least eight hours a day both appear to make the approach even more effective in reducing mortality and infection, researchers found.
The method of care known as ‘Kangaroo mother care’ (KMC) involves an infant being carried, usually by the mother, in a sling with skin-to-skin contact ...
Defibrillators are being used in just one in ten cardiac arrests where the lifesaving devices are available, according to new research presented at the British Cardiovascular Society Conference in Manchester.
The research drew upon data from the East of England Ambulance Service and The Circuit, the national defibrillator network developed by the British Heart Foundation (BHF). The Circuit maps the location of defibrillators across the whole of the UK, so that emergency services can direct bystanders to the nearest defibrillator in the event of ...
Patients with heart disease could benefit from less extensive interventions thanks to cutting-edge technology that creates 3D computer models of blood flow through the heart's arteries, according to research presented at the British Cardiovascular Society in Manchester.
When the research team trialled the VIRTUHeartTM technology with doctors treating heart attack patients, they found that using it would have changed the treatment of more than 20 per cent of patients. In many cases, it would have led to fewer patients undergoing an invasive procedure such ...
The International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) today released the ISSCR Standards for Human Stem Cell Use in Research, an international collaboration aimed at enhancing rigor in preclinical research and ultimately strengthening the pipeline of therapies for patients.
“This nearly two-year initiative is groundbreaking for the global stem cell research community,” said Haifan Lin, ISSCR president. “The international standards will make a big difference in the quality of science that is performed and published worldwide.”
The ISSCR is the preeminent international stem cell research society with a reputation ...
Have you ever wanted to convey a feeling but just couldn’t find the right words? Millions of people struggle with a personality trait known as alexithymia, which means “no words for feelings.” Individuals with alexithymia have difficulty identifying and describing their emotions. This trait can harm their social and intimate relationships. They are likely to miss social cues and thus fail to recognize or understand the feelings of others. Past research has suggested that a history of child maltreatment could play a role in developing adult alexithymia.
A new meta-analysis published this month in Psychological Bulletin, led by Stanford ...
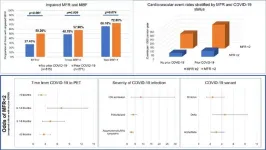
Patients infected with beta and delta COVID-19 variants, and those who required hospital stays for COVID-19 infection, were more likely to experience heart issues associated with long COVID, according to a recent Houston Methodist study published in the European Heart Journal – Cardiovascular Imaging. Patients recovering from the omicron variant were least likely to have microvascular involvement.
“This new data expands our understanding of myocardial flow reserve as an important prognostic marker in general and specifically in COVID-19,” said Mouaz Al-Mallah, M.D., corresponding author of the study and director of cardiovascular ...