(Press-News.org) Each person's gut microbiome contains a specific community of microorganisms that normally remains stable for years. However, it can be thrown off balance by factors such as dietary changes, infections or medications. Antibiotics in particular have a strong influence on the microbiome. In response, microorganisms employ various resistance mechanisms, with individual bacterial populations evolving through selection of antibiotic-resistant variants. Yet, the extent and mechanisms of these processes and their impact on the ecology of the microbial community are poorly understood.
In a comprehensive metagenomic study, DZIF scientists Prof. Bärbel Stecher and Prof. Alice McHardy, together with an international research team, investigated the evolution of intestinal bacteria exposed to repeated disruptions by antibiotics. For this purpose, they used a gnotobiotic mouse model, i.e., mice kept germ-free and stably colonised with a known consortium of bacteria. This model allows evolutionary studies of individual members of the community in the natural host under well-defined and controllable conditions. The researchers then analysed the effects of different classes of antibiotics on the microbiome over a period of 80 days. Using metagenomic analyses, they followed the selection of putative antibiotic resistance-promoting mutations in the bacterial populations, and subsequently analysed the characteristics of evolved bacterial clones isolated from the communities.
"We were able to track how repeated antibiotic therapy leads to the selection of antibiotic-resistant commensal bacteria, which after a while increases the resilience of the microbial community to certain antibiotics such as the tetracyclines. In addition to adaptation of the microbiome through evolution of individual microorganisms, we also found evidence of resistance development of individual bacteria through slowing of cell growth. The microbiome adapts to the treatment, so to speak, and is better able to withstand it," says Bärbel Stecher, coordinator of the Gastrointestinal Infections research area at the German Center for Infection Research (DZIF) and professor of Medical Microbiology and Hygiene at the Max von Pettenkofer Institute at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München (LMU).
In addition, the research team observed an induction of prophages triggered by treatment with certain antibiotics. In this process, lysogenic bacteriophages—whose genomes are integrated into bacterial genomes—are activated, whereupon they proliferate and lyse the host cells upon release of new viral particles. "This is an example of how antibiotics can also indirectly affect bacterial survival," says Dr Philipp Münch, first author of the study.
Overall, the study shows an immense diversity in the response of the microbiome to antibiotic treatments. This includes, for example, ecological effects such as the inhibition of a microorganism by the elimination of an important "partner" bacterium in the metabolic network of the gut ecosystem.
"Due to this high complexity of direct and indirect responses, it is difficult to predict which species will be affected by treatment with an antibiotic, even in gnotobiotic animal models with a defined community of microorganisms," summarises Prof. Alice McHardy, Deputy Coordinator Bioinformatics and Machine Learning at DZIF and head of the Department of Computational Biology for Infection Research at the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research, a member institution of the DZIF.
END
How the gut microbiome responds to antibiotics
2023-06-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New study finds that women and underrepresented groups experience higher rates of sexual harassment, cyber incivility and negative workplace climate in academic medicine
2023-06-06
(Atlanta – June 6, 2023) – A new study led by Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University researcher Reshma Jagsi, MD, DPhil, has found that women, racial and ethnic minorities and individuals identifying as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer are disproportionately affected by workplace mistreatment in academic medicine, and this mistreatment negatively impacts their mental health.
The study, which was published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association, looked specifically at three aspects of workplace mistreatment in academic medicine – sexual harassment, cyber incivility and negative workplace climate – and whether they differ by ...
Researchers target proteins, pathways behind congenital heart disease
2023-06-06
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Researchers at the UNC School of Medicine, UNC McAllister Heart Institute, and the UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center characterized the expression of thousands of cardiac proteins during eight critical stages of embryonic heart development.
This research, published in Development Cell, will provide scientists with much-needed information to identify biological causes for congenital heart disease, or CHD.
“We now have a foundational data set that shows how protein dynamics change in normal heart development,” said first ...
New push will digitize records of African plants held in herbaria and museums across the US
2023-06-06
LAWRENCE — Over the past few decades, herbaria and museums worldwide have created digital data records documenting millions of specimens in their holdings. The benefits of digitizing the contents of natural history museums and research institutions flow to the public and researchers worldwide.
Now, through a group of related grants from the National Science Foundation, researchers are systemically digitizing more than a million specimens of plants from across tropical Africa held at 20 institutions throughout the United States. The tropical African plant specimens — documenting some of ...
Turning up the heat
2023-06-06
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists found that a small tweak created big performance improvements in a type of solid-state battery, a technology considered vital to broader electric vehicle adoption.
These batteries use a solid electrolyte instead of a potentially flammable liquid. When the battery charges or operates, ions move between electrodes through the electrolyte between them. A new method for pressing the solid electrolyte practically eliminates tiny air pockets that block ion flow, so the battery charges twice as fast.
ORNL lead researcher Marm Dixit said the approach involved heating the press after spreading ...
CityU invents wireless olfactory feedback system to let users smell in the VR world
2023-06-06
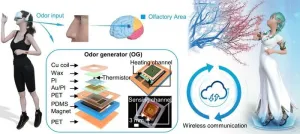
A research team co-led by researchers from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently invented a novel, wireless, skin-interfaced olfactory feedback system that can release various odours with miniaturised odour generators (OGs). The new technology integrates odours into virtual reality (VR)/augmented reality (AR) to provide a more immersive experience, with broad applications ranging from 4D movie watching and medical treatment to online teaching.
“Recent human machine interfaces highlight the importance of human sensation feedback, including vision, audio and haptics, associated with wide applications in entertainment, medical treatment and VR/AR. Olfaction also plays a significant ...
Proposed design could double the efficiency of lightweight solar cells for space-based applications
2023-06-06
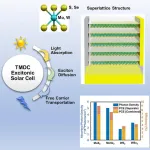
When it comes to supplying energy for space exploration and settlements, commonly available solar cells made of silicon or gallium arsenide are still too heavy to be feasibly transported by rocket. To address this challenge, a wide variety of lightweight alternatives are being explored, including solar cells made of a thin layer of molybdenum selenide, which fall into the broader category of 2D transition metal dichalcogenide (2D TMDC) solar cells. Publishing June 6 in the inaugural issue of the journal Device, researchers propose a device design that can take the efficiencies of 2D TMDC ...
Workplace harassment, cyber incivility, and climate in academic medicine
2023-06-06
About The Study: In this survey of clinician-researchers who received career development grants from the National Institutes of Health, there were concerning rates of sexual harassment, cyber incivility, and negative perceptions of climate, disproportionately affecting minoritized groups and affecting mental health. Ongoing efforts to transform culture are necessary.
Authors: Reshma Jagsi, M.D., D.Phil., of Emory University in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
Gene therapy produces long-term contraception in female domestic cats
2023-06-06
BOSTON—Currently there are no contraceptives capable of producing permanent sterilization in companion animals. Spaying, the surgical removal of the ovaries and uterus, is the most widely used strategy to control unwanted reproduction in female cats.
For the first time, researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), and their collaborators have demonstrated that a single dose of anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) gene therapy can induce long-term contraception in the domestic cat, potentially providing a safe and effective alternative to surgical spaying. The research ...
Outcomes of different quality of life assessment modalities after breast cancer therapy
2023-06-06
About The Study: In this network meta-analysis of 10 observational studies including 3,083 patients with breast cancer who received surgical treatment, expert panel–based and computer-based aesthetic outcome evaluation consistently scored lower than patient-perceived outcomes. Standardization and supplementation of expert panel and software aesthetic outcome tools with racially, ethnically, and culturally inclusive patient-reported outcome measures is needed to improve clinical evaluation of the journey of patients with breast cancer and to prioritize components ...
Effect of peer health coaching on clinical outcomes among veterans with cardiovascular disease risks
2023-06-06
About The Study: This randomized clinical trial found that, although the peer health coaching program did not significantly decrease systolic blood pressure, participants who received the intervention reported better mental health-related quality of life compared with the control group. The results suggest that a peer-support model that is integrated into primary care can create opportunities for well-being improvements beyond blood pressure control.
Authors: Karin M. Nelson, M.D., M.S.H.S., of the Veterans Affairs Puget Sound Health Care System in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access ...