(Press-News.org) The skies aircraft fly through are bumpier today than four decades ago, scientists have found, after producing a new analysis showing that turbulence has increased as the climate changed.
New research from the University of Reading shows that clear-air turbulence, which is invisible and hazardous to aircraft, has increased in various regions around the world.
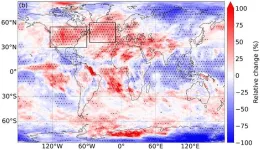
At a typical point over the North Atlantic – one of the world’s busiest flight routes – the total annual duration of severe turbulence increased by 55% from 17.7 hours in 1979 to 27.4 hours in 2020, the research found. Moderate turbulence increased by 37% from 70.0 to 96.1 hours, and light turbulence increased by 17% from 466.5 to 546.8 hours.
The team behind the study, which is published today (Thursday, 8 June) in Geophysical Research Letters, say the increases are consistent with the effects of climate change. Warmer air from CO2 emissions is increasing windshear in the jet streams, strengthening clear-air turbulence in the North Atlantic and globally.
PhD researcher Mark Prosser said: "Turbulence makes flights bumpy and can occasionally be dangerous. Airlines will need to start thinking about how they will manage the increased turbulence, as it costs the industry $150–500m annually in the USA alone. Every additional minute spent travelling through turbulence increases wear-and-tear on the aircraft, as well as the risk of injuries to passengers and flight attendants.”
While the USA and North Atlantic have experienced the largest increases, the new study found that other busy flight routes over Europe, the Middle East, and the South Atlantic also saw significant increases in turbulence.
Professor Paul Williams, an atmospheric scientist at the University of Reading who co-authored the study, said: “Following a decade of research showing that climate change will increase clear-air turbulence in the future, we now have evidence suggesting that the increase has already begun. We should be investing in improved turbulence forecasting and detection systems, to prevent the rougher air from translating into bumpier flights in the coming decades.”
END
Aviation turbulence strengthened as the world warmed — study
2023-06-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Giving parents better school quality data encourages them to consider less affluent, less white schools -- To a Point
2023-06-08
Washington, June 8, 2023—For years, parents looking for data to compare the academic quality of schools for their children had one primary measure to turn to: average student scores on standardized tests. However, these scores are often related to factors that have nothing to do with instructional quality—such as family income or racial and ethnic background—and push parents toward schools that are Whiter and more affluent, exacerbating school segregation in the U.S. As a result, many education ...
UMass Amherst epidemiologist updates and validates ‘gold standard’ of prenatal physical activity tools
2023-06-08
A University of Massachusetts Amherst public health researcher has updated and validated the widely used Pregnancy Physical Activity Questionnaire (PPAQ) to improve the measurement performance of this self-report physical activity method.
Lisa Chasan-Taber, professor and chair of biostatistics and epidemiology, and her research group used novel and innovative tools – an advanced accelerometer and wearable camera – to assess PPAQ performance. The researchers developed the PPAQ in 2004 as the first validated pregnancy physical activity questionnaire. Listed on the UMass Amherst timeline ...
Researchers tune thermal conductivity of materials ‘on the fly’ for more energy-efficient devices
2023-06-08
A team led by University of Minnesota Twin Cities scientists and engineers discovered a new method for tuning the thermal conductivity of materials to control heat flow ”on the fly.” Their tuning range is the highest ever recorded among one-step processes in the field, and will open a door to developing more energy-efficient and durable electronic devices.
The researchers’ paper is published in Nature Communications, a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the natural sciences.
Just as electrical ...
Topological phase protection reams to sub-symmetry
2023-06-08
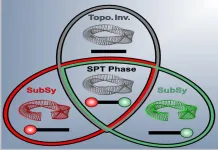
An international team led by researchers at Nankai University in China and at University of Zagreb in Croatia, along with team at the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS) in Canada, led by Roberto Morandotti has made an important breakthrough in the study of topological phases. Their findings were recently published in Nature Physics – a journal published by Nature Publishing Group.
In the last decade, topological photonics has attracted increasing attention due to the unique prospects to achieve light manipulation with high performance in terms of robustness and stability. Discoveries in topological photonics ...
Identifying the cause of heart muscle disease in children is key to effective treatment
2023-06-08
Statement Highlights:
A new American Heart Association scientific statement focuses on treatment strategies for pediatric cardiomyopathy (diseases of the heart muscle’s structure and function that may lead to heart failure and death) and is a companion to a 2019 scientific statement focused on diagnosis of the condition.
There are several types of cardiomyopathies in children, and treatment should include personalized therapies based on the root cause, symptoms and progression of the condition in each child, according to the new scientific statement.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET, Thursday, June 8, 2023
DALLAS, June 8, 2023 — Treating ...
Why earthquakes happen more frequently in Britain than Ireland
2023-06-08
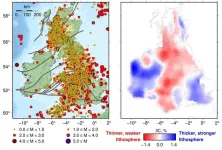
Researchers from the University of Cambridge and the Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies have discovered that variations in the thickness of tectonic plates relate directly to the distribution of earthquakes in Britain, Ireland and around the world.
The study also solves an enduring mystery as to why small earthquakes happen frequently in Britain but are almost completely absent from neighbouring Ireland.
The researchers produced a computer-generated image of Earth’s interior using a technique called seismic tomography, which works in a similar way to a medical CT scan. The data they collected revealed variations in the thickness of the ...
Greenhouse gas emissions at ‘an all-time high’ - and it is causing an unprecedented rate of global warming, say scientists
2023-06-08
University of Leeds Press Release
Under embargo until 09.00 am (British Summer Time) on Thursday, June 8
**With details of a linked press conference at the UNFCC meeting in Bonn - see under notes to journalists**
Greenhouse gas emissions at ‘an all-time high’ - and it is causing an unprecedented rate of global warming, say scientists
Human-induced ...
Birmingham spinout to develop 20-minute test following surge in sexually transmitted infections
2023-06-08
University of Birmingham spinout Linear Diagnostics has received funding to finesse a point-of-care test for rapid diagnosis of gonorrhoea and Chlamydia in men who have sex with men (MSM), and women who have sex with women (WSW).
The funding from the National Institute of Health and Social Care Research (NIHR) will cover essential work to optimise and validate Linear’s platform technology (LDx-CTNG), so it can diagnose infection from rectal and pharyngeal (throat) swabs.
Gonorrhoea and Chlamydia are both major public health concerns. While Chlamydia remains the most commonly detected sexually ...
Study finds socially tolerant monkeys have better impulse control
2023-06-08
Researchers have tested one of the ideas put forward to explain how humanity evolved to become smarter, on non-human primates.
The study, led by a team at the University of Portsmouth, found a significant connection between social organisation and cognitive skills in monkeys.
They assessed three species of macaques with different social tolerance levels, from authoritarian to more relaxed societies, in a series of cognitive touchscreen touchscreen tasks to work out how impulsive and reactive ...
Shirley Ryan AbilityLab receives $8.7 Million NIH grant for first-of-its-kind bionic arm osseointegration study
2023-06-08
Today, an estimated 41,000 people in the United States live with the loss of an upper limb, including hundreds of service men and women. Although significant progress has been made in the durability, control and function of upper-limb prosthetic devices, they lack complete integration into the body and, importantly, do not enable their users to feel.
Now, with the award of an $8.7 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Shirley Ryan AbilityLab — the top-ranked physical medicine and rehabilitation hospital — and its research partners have an opportunity ...