(Press-News.org) Cyber-physical systems, such as vehicles, trains, airplanes, smart homes, or production facilities, combine electronic and mechanical elements with software. Development of these systems is highly complex due to the large number of dependencies among the components. “When a car’s wire harness is modified, the diameter of the cable duct also has to be changed,” says Professor Ralf Reussner, Spokesman of the CRC at KIT. This must be agreed upon by electrical engineers, software engineers and mechanical engineers. Agreement is also required when modifying the software. In industry, this is done at regular meetings of the experts from the disciplines involved. These processes are very tedious, slow, and error-prone, Reussner says. “It would be ideal to update a car as quickly and easily as a smart phone and to just buy and download new functions.”
New Methods for Accelerated Industrial Development
The CRC is designed to study software engineering methods to structure and organize development work relating to CPS. The resulting new CPS design methods are expected to accelerated, agile development cycles for cyber-physical systems. For this purpose, about 20 new positions for excellent researchers will be created at KIT.
CRCs are long-term research structures of universities, in which researchers collaborate in a multi-disciplinary program. CRCs are funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG). The funding period ranges from four to twelve years. The CRC “Konsistenz in der sichtenbasierten Entwicklung Cyber-Physikalischer Systeme” (consistence in the view-based development of cyber-physical systems) is the sixth CRC at KIT. Among the partners are TU München, TU Dresden, and the University of Mannheim.
More Information:
https://gepris.dfg.de/gepris/projekt/389000774?context=projekt&task=showDetail&id=389000774&
https://www.waves.kit.edu/
END
Updating cars as fast as a smart phone
New Collaborative Research Center for Software Methods at KIT – DFG funds excellent KIT research with around EUR 11 million
2023-06-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Excessive alcohol consumption may accelerate Alzheimer’s disease progression
2023-06-12
LA JOLLA, CA—Alcohol use disorder (AUD) quickens the pace of Alzheimer’s disease progression when paired with genetic susceptibility. Scripps Research and University of Bologna scientists reported in the journal eNeuro on June 12, 2023, that repeated alcohol intoxication is associated with changes to gene expression indicative of disease progression in the brains of mice that are genetically predisposed to Alzheimer’s. When repeatedly exposed to intoxicating amounts of alcohol, ...
A step toward safe and reliable autopilots for flying
2023-06-12
In the film “Top Gun: Maverick,” Maverick, played by Tom Cruise, is charged with training young pilots to complete a seemingly impossible mission — to fly their jets deep into a rocky canyon, staying so low to the ground they cannot be detected by radar, then rapidly climb out of the canyon at an extreme angle, avoiding the rock walls. Spoiler alert: With Maverick’s help, these human pilots accomplish their mission.
A machine, on the other hand, would struggle to complete the same pulse-pounding task. To an autonomous aircraft, for instance, the most straightforward path toward the target is in conflict with what the machine needs ...
Mass General Hospital researchers uncover why light-to-moderate drinking is tied to better heart health
2023-06-12
BOSTON – A new study led by investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, offers an explanation for why light-to-moderate alcohol consumption may be associated with lower risk of heart disease. For the first time, researchers found that alcohol, in light to moderate quantities, was associated with long-term reductions in stress signaling in the brain. This impact on the brain’s stress systems appeared to significantly account for the reductions in cardiovascular events seen in light to moderate drinkers participating in the ...
NIH grant backs study focused on Alzheimer’s in women
2023-06-12
HOUSTON – (June 12, 2023) – Two-thirds of the people suffering from Alzheimer’s disease are women, yet most research has ignored differences between the sexes.
To help fill this gap, Rice University postdoctoral fellow Hannah Ballard will look at how Alzheimer’s risk, estrogen levels and menopausal status interact with memory-related brain function and behavioral outcomes in women age 35-80.
Supported by a three-year grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Ballard’s research could help identify the physiological factors ...
Self-esteem of kids with short stature tied to social supports, not height
2023-06-12
Philadelphia, June 12, 2023—Challenging the assumption that short stature negatively impacts children and adolescents’ self-esteem, a new study by researchers at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) has found that in otherwise healthy short youth, quality of life and self-esteem are associated with coping skills and how supported they feel and not the degree of their short stature. The findings were published in The Journal of Pediatrics.
“There is a notion among some parents and caregivers that short stature will negatively impact their children in terms of self-esteem and social adjustment, so they seek out growth hormone ...
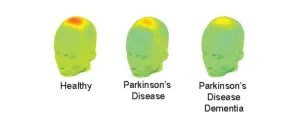
Brain waves may predict cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease
2023-06-12
A few minutes of data recorded from a single electrode placed on top of the head may be sufficient to predict thinking problems, including dementia, in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD). The finding from a new University of Iowa study might help improve diagnosis of cognitive disability in PD and develop new biomarkers and targeted therapies for cognitive symptoms of the disease.
“Cognitive decline, including dementia, is a significant and underappreciated symptom of Parkinson’s disease. ...
The Face Game: A citizen science project to learn how Artificial Intelligence will choose to appear to humans
2023-06-12
Online, profile pictures of human faces are everywhere, and they play a crucial role in shaping the first impression we make on others. Right now, AI gives people the digital tools to transform their online appearance in any way they desire, often making themselves look younger or more attractive. But this is just the beginning: AI is not only helping us play this face game amongst ourselves, but it is also learning the game from us and quietly deciding which face it will showcase as itself when interacting with us.
To better understand these mechanisms, researchers from the Max Planck ...
Ethics & Human Research, May-June 2023
2023-06-12
Making an Advance Research Directive: An Interview Study with Adults Aged 55 and Older with Interests in Dementia Research
Nola M. Ries, Briony Johnston
Many people with dementia are interested in taking part in research, including when they no longer have capacity to provide informed consent. Advance research directives (ARD) enable people to document their wishes about research participation prior to becoming decisionally incapacitated. However, there are few available ARD resources. This Australian interview study elicited the views of people aged 55 years and older about the content of an ...
Visionary report unveils ambitious roadmap to harness the power of AI in scientific discovery
2023-06-12
Innovations in artificial intelligence (AI) are rapidly shaping our world, from virtual assistants and chatbots to self-driving cars and automated manufacturing. Seizing on the potential of AI to transform science, the nation’s leading experts in science and technology have released a blueprint for the United States to accelerate progress by expanding its capabilities in AI and big data analysis.
“AI for Science, Energy, and Security” lays out a comprehensive vision ...
Masai giraffes more endangered than previously thought
2023-06-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Giraffes in eastern Africa may be even more endangered than previously thought. A new study led by researchers at Penn State reveals that populations of Masai giraffes separated geographically by the Great Rift Valley have not interbred — or exchanged genetic material — in more than a thousand years, and in some cases hundreds of thousands of years. The researchers recommend that the two populations be considered separately for conservation purposes, with separate but coordinated conservation efforts to manage each population.
Populations of giraffes have declined rapidly in the last thirty years, with ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
[Press-News.org] Updating cars as fast as a smart phoneNew Collaborative Research Center for Software Methods at KIT – DFG funds excellent KIT research with around EUR 11 million