(Press-News.org) How do you study the effects of exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), when it is in everything?! To study the effect of a chemical, toxicologists typically expose animals to various doses of the chemical over a period of time so that they could then study the dose versus effect relationship. Such toxicology studies often employee several types of “blanks” for quality control. Blanks are experiments where the test animals are not given any dose of the chemical being studied (sort of like a placebo in human drug testing). Also, researchers often examine the amount of the substance under study in the blanks to also include it in the evaluation of the dose versus effect relationship. For example, if the study is in water, they may get water from a pristine site to use in the test and not add any chemical dose to it, but they would still analyze the water in order to detect any trace amounts of the study substance. Researchers would also analyze feed for the same reason.
One research group sought to examine how the presence of PFAS in test animal feed, test materials, and the animal subjects themselves may thwart the toxicology studies of the effect of PFAS and could lead to inaccurate results.
Matt Simick and co-authors sampled minnows raised in aquaculture facilities (used for toxicity testing), as well as different types of fish food: flakes, freeze-dried brine shrimp, freeze-dried blood worms and frozen brine shrimp, for PFAS. Both fish and fish feed were found to be contain PFAS at varying levels. The study documents the differences between food type, brand, and aquaculture practices, but ultimately recommends that any all feed and organisms should be tested for PFAS contamination prior to conducting basic or translational experiments.
END
PFAS, PFAS everywhere: how pristine are laboratory materials?
2023-06-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Groundbreaking study reveals new insights into human gut-brain connection
2023-06-13
Tulsa, Okla. – A pioneering study conducted by researchers at the Laureate Institute for Brain Research (LIBR) in Tulsa, Okla., has made significant strides in understanding the elusive gut-brain connection, a complex relationship that has long puzzled scientists due to the difficulty of accessing the body's interior. The study, “Parieto-occipital ERP indicators of gut mechanosensation in humans,” appears in the peer-reviewed scientific journal Nature Communications.
The research team successfully had ...
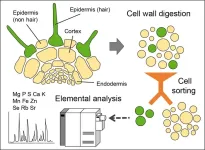
New approach opens avenue to investigate element distribution and transport pathways in plants
2023-06-13
Plant roots play a critical role in taking up, selecting, enriching and retaining a range of different mineral elements thereby supplying distant plant tissues with nutrients while sequestering excessive amounts of metals. To execute such element-specific functions, a range of ion transporters present at roots mediate the uptake, efflux and intracellular compartmentalization of different mineral elements. Most ion transporters show characteristic tissue and cell type-specific localization patterns, which can be altered in response to internal signalling or external cues. To fully ...
The best drug combos to prevent COVID recurrence
2023-06-13
A groundbreaking machine-learning study has unmasked the best drug combinations to prevent COVID-19 from coming back after an initial infection. It turns out these combos are not the same for every patient.
Using real-world data from a hospital in China, the UC Riverside-led study found that individual characteristics, including age, weight, and additional illness determine which drug combinations most effectively reduce recurrence rates. This finding has been published in the journal Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence.
That the data came from China is significant for two reasons. First, when patients are treated for COVID-19 in the U.S, it is ...
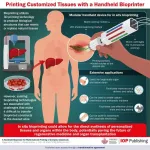
Bioprinting personalized tissues and organs within the body: A breakthrough in regenerative medicine
2023-06-13
In situ bioprinting, which involves 3D printing biocompatible structures and tissues directly within the body, has seen steady progress over the past few years. In a recent study, a team of researchers developed a handheld bioprinter that addresses key limitations of previous designs, i.e., the ability to print multiple materials and control the physicochemical properties of printed tissues. This device will pave the way for a wide variety of applications in regenerative medicine, drug development and testing, and custom orthotics and prosthetics.
The emergence of regenerative medicine has resulted ...
Why women with multiple sclerosis get better when pregnant
2023-06-13
Women suffering from the autoimmune disease multiple sclerosis temporarily get much better when pregnant. Researchers have now identified the beneficial changes naturally occurring in the immune system during pregnancy. The findings, published in Journal of Neuroinflammation, can show the way to new treatments.
Pregnancy is a very special condition from an immunological point of view. The immune system serves to defend us against foreign substances. However, although half of the genetic material of the foetus ...
Adhering to global health recommendations reduces cancer risk
2023-06-13
People who adhere to global Cancer Prevention Recommendations are putting themselves at lower risk of developing the disease, new research confirms.
Experts at Newcastle University have reviewed evidence of following the 2018 World Cancer Research Fund (WCRF) and American Institute for Cancer Research (AICR) lifestyle-based recommendations.
The findings, published today in Cancer, revealed that adhering to a healthier lifestyle, including maintaining a healthy body weight and eating little red meat and processed meats such as bacon, helps ...
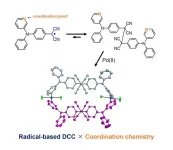
Creation of a new molecule through innovative combination of two reactions
2023-06-13
A research group led by Professor Hideki Fujiwara and Associate Professor Daisuke Sakamaki from the Graduate School of Science at Osaka Metropolitan University succeeded, for the first time, in synthesizing a new molecule using a novel combination of dynamic covalent chemistry, in which organic radicals couple and dissociate reversibly, and coordination chemistry, which binds radicals to metal ligands. The study shows that the two types of reactions work without inhibiting each other.
“This research was based on a very simple idea of combining two types of reactions,” stated Professor Sakamaki. “However, it was not clear ...
Elevated Lipoprotein(a) is the latest variant of ‘bad cholesterol’ found to increase the risk of recurrent coronary heart disease
2023-06-13
Increased levels of Lipoprotein(a), a variant of ‘bad cholesterol’, in the bloodstream are a risk factor for recurrent coronary heart disease (CHD) in people aged 60 or over, according to the results of a new study which tracked the issue over the course of 16 years.
The results, published today in Current Medical Research & Opinion, suggest that current cholesterol-lowering medications may not be effective at reducing the risk of recurrent CHD – such as a heart attack – due to elevated Lp(a).
“This finding adds to growing evidence of a relationship between increased Lp(a) and the risk of recurrent CHD,” says lead author Associate Professor ...
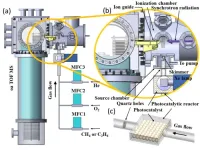
USTC achieves breakthrough in in-situ detection of gas-phase active intermediates in photocatalysis
2023-06-13
Prof. PAN Yang and Associate Researcher LIU Chengyuan, researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), have achieved significant progress in detecting intermediates in methane photocatalytic reactions. Their technique, Synchronous Radiation Photoionization Mass Spectrometry (SR-PIMS), allows for in-situ detection of active intermediates. The findings were published in the prestigious chemistry journal Angewandte Chemie International ...
USTC provides comprehensive review of quantum teleportation in Nature Review Physics
2023-06-13
A team led by Academician Prof. GUO Guangcan from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) provides a comprehensive overview of the progress achieved in the field of quantum teleportation. The team, which includes Prof. HU Xiaomin, Prof. GUO Yu, Prof. LIU Biheng, and Prof. LI Chuanfeng from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC),CAS, was invited to publish a review paper on quantum teleportation in Nature Review Physics. The paper was officially released online on May 24.
As one of the most important protocols in the field ...